Control of the activity of WW-HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases by NDFIP proteins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Control of the activity of WW-HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases by NDFIP proteins
Thomas Mund et al. EMBO Rep. 2009 May.
Abstract
HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases of the NEDD4 family control many cellular processes, but their regulation is poorly understood. They contain multiple WW domains that recognize PY elements. Here, we show that the small PY-containing membrane proteins, NDFIP1 and NDFIP2 (NEDD4 family-interacting proteins), activate the catalytic activity of ITCH and of several other HECT ligases by binding to them. This releases them from an autoinhibitory intramolecular interaction, which seems to be characteristic of these enzymes. Activation of ITCH requires multiple PY-WW interactions, but little else. Binding of NDFIP proteins is highly dynamic, potentially allowing activated ligases to access other PY-containing substrates. In agreement with this, NDFIP proteins promote ubiquitination in vivo both of Jun proteins, which have a PY motif, and of endophilin, which does not.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
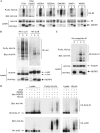
NDFIP2 induces ubiquitination of HECT domain ligases and potential substrates. (A) HEK293T cells expressed His-tagged ubiquitin (His-Ub), HA-tagged E3 ligases as indicated and an empty vector control (lane 1), Myc–NDFIP2 (lane 2) or Myc–NDFIP2 with triple PY motif mutations (lane 3). (B) Cells expressed His-tagged ubiquitin, HA-tagged c-Jun or JunB and either an empty vector (1), Myc-tagged NDFIP2 (2) or the PY mutant NDFIP2 (3). (C) As in (B) but with HA–endophilin A1 instead of Jun proteins. Lane 0 is a control in which His–ubiquitin is omitted. (D) As in (B,C), with indicated proteins expressed. All samples are from the same experiment, but the panels to the right are from a separate gel. HA, hemagglutinin; HECT, homologous to E6-AP carboxy terminus; HEK, human embryonic kidney; NDFIP, NEDD4 family-interacting protein.
Figure 2
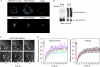
Recruitment of NEDD4 by NDFIP2. (A) COS-7 cells expressing both GFP-tagged NEDD4 and either Myc-NDFIP2 or the PY mutant form of this were imaged. (B) Cells expressing HA-ITCHΔC2 with or without NDFIP2 were lysed and centrifuged, and the supernatant (S100) and pellet (P100) were blotted. (C) Examples of FRAP experiments; time 0 is immediately after bleaching. (D) Quantitation of FRAP experiments. Each curve represents one bright dot in the bleached region. FRAP, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; HA, hemagglutinin; NDFIP, NEDD4 family-interacting protein.
Figure 3
NDFIPs are substrates that increase autoubiquitination of E3 ligases in vitro. (A) Coomassie-stained gels and immunoblots (IB) of assays containing the indicated proteins and the cytoplasmic domains of NDFIP1 (1cyt) or NDFIP2 (2cyt) or the same with all three PY motifs mutated (PY*). Asterisks indicate the smaller ubiquitinated forms of the NDFIPs; X is a constitutively active fragment of NEDD4. (B) Assay with methylated ubiquitin. (C) Assays with NDFIP2 fragments. This experiment used His–ubiquitin, which reduces modification and allows a clear separation of the modified forms of NDFIP and ITCH. (D) Assays with Y to F changes in individual PY motifs of NDFIP2. Note that polyubiquitinated proteins sometimes transfer poorly to the blot. (E) Modification of NDFIP1 by various ITCH WW mutants. The schematic diagram summarizes the results. NDFIP, NEDD4 family-interacting protein; Ub, ubiquitin; WT, wild type.
Figure 4
Sequences required for autoinhibition of NEDD4 and ITCH. (A) Ubiquitination assays using His-ubiquitin were Coomassie stained. PR indicates the proline-rich region in ITCH. (B) Cartoon indicating proposed model; NDFIP, NEDD4 family-interacting protein.
Figure 5
NDFIP2 promotes the modification of endophilin by ITCH in vitro. Ubiquitination assays containing the indicated proteins were analysed by immunoblotting. GST, glutathione S-transferase; NDFIP, NEDD4 family-interacting protein; Ub, ubiquitin.
Similar articles
- Itch WW Domains Inhibit Its E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity by Blocking E2-E3 Ligase Trans-thiolation.
Riling C, Kamadurai H, Kumar S, O'Leary CE, Wu KP, Manion EE, Ying M, Schulman BA, Oliver PM. Riling C, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 25;290(39):23875-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.649269. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26245901 Free PMC article. - Comparative analysis of the catalytic regulation of NEDD4-1 and WWP2 ubiquitin ligases.
Jiang H, Thomas SN, Chen Z, Chiang CY, Cole PA. Jiang H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 15;294(46):17421-17436. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009211. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31578285 Free PMC article. - NDFIP allows NEDD4/NEDD4L-induced AQP2 ubiquitination and degradation.
Trimpert C, Wesche D, de Groot T, Pimentel Rodriguez MM, Wong V, van den Berg DTM, Cheval L, Ariza CA, Doucet A, Stagljar I, Deen PMT. Trimpert C, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0183774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183774. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931009 Free PMC article. - Ubiquitination and endocytosis of plasma membrane proteins: role of Nedd4/Rsp5p family of ubiquitin-protein ligases.
Rotin D, Staub O, Haguenauer-Tsapis R. Rotin D, et al. J Membr Biol. 2000 Jul 1;176(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s00232001079. J Membr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10882424 Review. - Physiological Functions of the Ubiquitin Ligases Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2.
Rotin D, Prag G. Rotin D, et al. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024 Jan 1;39(1):18-29. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00023.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Physiology (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 37962894 Review.
Cited by
- Ubiquitin Ser65 phosphorylation affects ubiquitin structure, chain assembly and hydrolysis.
Wauer T, Swatek KN, Wagstaff JL, Gladkova C, Pruneda JN, Michel MA, Gersch M, Johnson CM, Freund SM, Komander D. Wauer T, et al. EMBO J. 2015 Feb 3;34(3):307-25. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489847. Epub 2014 Dec 19. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25527291 Free PMC article. - Itch WW Domains Inhibit Its E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity by Blocking E2-E3 Ligase Trans-thiolation.
Riling C, Kamadurai H, Kumar S, O'Leary CE, Wu KP, Manion EE, Ying M, Schulman BA, Oliver PM. Riling C, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 25;290(39):23875-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.649269. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26245901 Free PMC article. - Transmembrane adaptor protein WBP1L regulates CXCR4 signalling and murine haematopoiesis.
Borna S, Drobek A, Kralova J, Glatzova D, Splichalova I, Fabisik M, Pokorna J, Skopcova T, Angelisova P, Kanderova V, Starkova J, Stanek P, Matveichuk OV, Pavliuchenko N, Kwiatkowska K, Protty MB, Tomlinson MG, Alberich-Jorda M, Korinek V, Brdicka T. Borna S, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(2):1980-1992. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14895. Epub 2019 Dec 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31845480 Free PMC article. - Uncovering new insights into the role of the ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 on the regulation of innate immune signaling and resistance to infection.
Souza-Costa LP, Andrade-Chaves JT, Andrade JM, Costa VV, Franco LH. Souza-Costa LP, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 May 9;14:1185741. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1185741. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37228615 Free PMC article. Review. - Engineered Exosomes as Vehicles for Biologically Active Proteins.
Sterzenbach U, Putz U, Low LH, Silke J, Tan SS, Howitt J. Sterzenbach U, et al. Mol Ther. 2017 Jun 7;25(6):1269-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.030. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28412169 Free PMC article.
References
- Angers A, Ramjaun AR, McPherson PS (2004) The HECT domain ligase itch ubiquitinates endophilin and localizes to the trans-Golgi network and endosomal system. J Biol Chem 279: 11471–11479 - PubMed
- Anindya R, Aygun O, Svejstrup JQ (2007) Damage-induced ubiquitylation of human RNA polymerase II by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, but not Cockayne syndrome proteins or BRCA1. Mol Cell 28: 386–397 - PubMed
- Bai Y, Yang C, Hu K, Elly C, Liu YC (2004) Itch E3 ligase-mediated regulation of TGF-β signaling by modulating smad2 phosphorylation. Mol Cell 15: 825–831 - PubMed
- Cristillo AD, Nie L, Macri MJ, Bierer BE (2003) Cloning and characterization of N4WBP5A, an inducible, cyclosporine-sensitive, Nedd4-binding protein in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 278: 34587–34597 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous