Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency - PubMed (original) (raw)
Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency
Robert L Judson et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2009 May.
Abstract
This report demonstrates that introduction of microRNAs (miRNAs) specific to embryonic stem cells enhances the production of mouse induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. The miRNAs miR-291-3p, miR-294 and miR-295 increase the efficiency of reprogramming by Oct4, Sox2 and Klf4, but not by these factors plus cMyc. cMyc binds the promoter of the miRNAs, suggesting that they are downstream effectors of cMyc during reprogramming. However, unlike cMyc, the miRNAs induce a homogeneous population of iPS cell colonies.
Figures
Figure 1
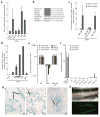
The ESCC miRNAs promote three-factor, but not four-factor induced pluripotency. (a) Fold increase of day 10 Oct-GFP+ colonies with retroviruses expressing Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4 (OSK) together with 16nM miRNA mimic relative to transfection reagent only (Mock). N=3. Raw data in Supplementary Table 1. (b) Sequence of miR-290 cluster, miR-302d, and miR-294 seed sequence mutant. Bold indicates seed sequence. Capitals indicate point mutations. Grey box highlights ESCC seed-sequence. (c) Fold increase in day 10 Oct4-GFP+ colonies with addition of mimic to OSK in the presence (light grey) or absence (dark grey) of cMyc retrovirus. Bars represent the number of GFP+ colonies after mimic transfection divided by the number of GFP+ colonies after mock transfection. N= 6, 26, 2, 5, & 3 left to right. Asterisk indicates p-value ≤ 0.0001. Raw data for bars 1&2 in Supplementary Table 2. (d) Percent day 10 Oct4-GFP colonies for OSK plus 1.6, 16 and 160nM transfected miR-294 mimic or 160nM miR-1 relative to OSKM. (e) Quantitative RT-PCR for endogenous pluripotency markers in control (V6.5) ES cells, MEFs, and miR-294-iPS lines. N=3, 3, & 5. RPL7 was used as input control. Data was normalized to ES expression. (f) Quantitative RT-PCR for exogenous Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4 in MEFs 6 days after viral infection, control (V6.5) ES cells, and MEFs (each N=3) and 5 individual miR-294-iPS lines. Horizontal black bars indicate Ct > 40. RPL7 was used as input control. Data was normalized to MEF expression 6 days after viral infection. (g) X-gal staining demonstrates miR-294-iPS chimeric contribution to ectoderm (neural tissue, N), endoderm (lung, L), and mesoderm (cartilage, C). (h) GFP expression in genital ridges of E12.5 chimera demonstrates Oct4-GFP miR-294-iPS contribution to germline. All error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 2
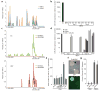
Characterization of the relationship between Myc and miR-294. (a) cMyc (blue) and nMyc (yellow) bind the miR-290 cluster promoter. ChIP-seq data reads were aligned to the mm9 assembly of the genome and peaks were generated with Findpeaks. Vertical hash marks denote the positions of the miR-290 cluster miRNAs. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR for total mature miR-294 expression in control (V6.5) ES cells, MEFs, and MEFs infected with viruses expressing Sox2 (S), Oct4 (O), Klf4 (K) or cMyc (M). RNA was collected on days 2 and 6. N=3. Horizontal black bars indicate Ct > 40. Sno202 was used as input control. Data was normalized to ES cells. (c) H3K4me3 (green) and H3K27me3 (red) surrounding the miR-290 cluster in MEFs. Chip-seq data were analyzed as described in a. (d) Quantitative RT-PCR for total mature miR-294 expression in control (V6.5) ES cells (E), MEFs (M), MEFs infected with either Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 (OSK); Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and cMyc (OSKM); or OSK+miR-294, and established iPS lines resulting from these conditions (iPS). RNA was collected on days 2, 6, and 10 of reprogramming. Three independent experiments are shown. Horizontal black bars indicate Ct > 40. Sno202 was used as input control. Data was normalized to ES cells. (e) Total cell number during reprogramming. Cells were counted on day 7 after infection with OSKM or OSK +/− miRNA mimic. Concentrations of miR-294 mimic: 1.6, 16 and 160nM. Concentration of miR-1 mimic: 160nM. (f) GFP negative colonies in presence of cMyc. Oct4-GFP+, ES-like colonies (black arrow) and GFP-negative, nonES-like colonies (white arrow). (g) Quantification of number of day 10 GFP-negative colonies after infection with OSKM or OSK +/− miR-294 mimic. All error bars indicate standard deviation of N=3.
Similar articles
- Emerging roles of microRNAs in the control of embryonic stem cells and the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells.
Mallanna SK, Rizzino A. Mallanna SK, et al. Dev Biol. 2010 Aug 1;344(1):16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.05.014. Epub 2010 May 15. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20478297 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells.
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS. Xu N, et al. Cell. 2009 May 15;137(4):647-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.038. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19409607 - Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?
Gunaratne PH. Gunaratne PH. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review. - Trib2 regulates the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells and enhances reprogramming efficiency.
Do EK, Park JK, Cheon HC, Kwon YW, Heo SC, Choi EJ, Seo JK, Jang IH, Lee SC, Kim JH. Do EK, et al. Exp Mol Med. 2017 Nov 24;49(11):e401. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.191. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 29170476 Free PMC article. - The timing of retroviral silencing correlates with the quality of induced pluripotent stem cell lines.
Okada M, Yoneda Y. Okada M, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1810(2):226-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20965232
Cited by
- Advances in understanding the regulation of pluripotency fate transition in embryonic stem cells.
Jia YK, Yu Y, Guan L. Jia YK, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 16;12:1494398. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1494398. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39479513 Free PMC article. Review. - The miR-290 and miR-302 clusters are essential for reprogramming of fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells.
Ye J, Boileau RM, Parchem RJ, Judson-Torres RL, Blelloch R. Ye J, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 3:2024.09.02.610895. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.02.610895. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39282363 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs as Novel Potential Approach for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment.
Tahmasebi F, Asl ER, Vahidinia Z, Barati S. Tahmasebi F, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May 7;44(1):44. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01478-1. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38713302 Free PMC article. Review. - MiR-290 Family Maintains Pluripotency and Self-Renewal by Regulating MAPK Signaling Pathway in Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells.
Liu Y, Li X, Ma X, Du Q, Wang J, Yu H. Liu Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 26;25(5):2681. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052681. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473927 Free PMC article. - Human retinal ganglion cell neurons generated by synchronous BMP inhibition and transcription factor mediated reprogramming.
Agarwal D, Dash N, Mazo KW, Chopra M, Avila MP, Patel A, Wong RM, Jia C, Do H, Cheng J, Chiang C, Jurlina SL, Roshan M, Perry MW, Rho JM, Broyer R, Lee CD, Weinreb RN, Gavrilovici C, Oesch NW, Welsbie DS, Wahlin KJ. Agarwal D, et al. NPJ Regen Med. 2023 Sep 29;8(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41536-023-00327-x. NPJ Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37773257 Free PMC article.
References
- Houbaviy HB, Murray MF, Sharp PA. Embryonic stem cell-specific MicroRNAs. Dev Cell. 2003;5:351–358. - PubMed
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 NS048118-01A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057221-01A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS048118-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS058042/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS058042-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS048118-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS048118-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32NS058042/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS048118/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057221/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057221-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS48118/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources