Measurement of serum 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (or 7alphaC4), a surrogate test for bile acid malabsorption in health, ileal disease and irritable bowel syndrome using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry - PubMed (original) (raw)
Measurement of serum 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (or 7alphaC4), a surrogate test for bile acid malabsorption in health, ileal disease and irritable bowel syndrome using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
M Camilleri et al. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Bile acid malabsorption (BAM) is reported in up to 50% of patients with functional diarrhoea and irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea (IBS-D). Serum 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (7alphaHCO or 7alphaC4), an indirect measurement of hepatic bile acid synthesis, has been validated as a measurement of BAM relative to the (75)SeHCAT retention test. Our aim was to develop a serum 7alphaC4 assay, normal values, and compare results from healthy controls, patients with ileal Crohn's disease or resection, and patients with IBS-D or IBS with constipation (IBS-C). Stored serum samples were used from adult men and women in the following groups: 111 normal healthy controls, 15 IBS-D, 15 IBS-C, 24 with distal ileal Crohn's disease and 20 with distal ileal resection for Crohn's disease. We adapted a published high pressure liquid chromatography, tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) assay. The HPLC-MS/MS assay showed good linearity in concentration range 0-200 ng mL(-1), sensitivity (lowest limit of detection 0.04 ng mL(-1)), and high analytical recovery (average 99%, range 93-107%). The 5th to 95th percentile for 111 normal healthy controls was 6-60.7 ng mL(-1). There were significant overall group differences (anovaon ranks, P < 0.001), with significantly higher values for terminal ileal disease or resection. There were significant differences between health and IBS (anova, P = 0.043) with higher mean values in IBS-D relative to controls (rank sum test, P = 0.027). We have established a sensitive non-isotopic assay based on HPLC-MS/MS, determined normal 7alphaC4 values, and identified increased 7alphaC4 in IBS-D and in distal ileal resection and disease. This assay has potential as a non-invasive test for BAM in IBS.
Figures
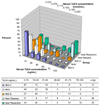
Figure 1
Histogram plots of all groups showing the percentage of each group with serum 7αC4 (ng/mL) in different concentrations. Note that values above 60ng/mL fall outside the normal range. Thus, >50% of patients with distal ileal disease or resection and 20% of patients with IBS-D had abnormal serum 7αC4.
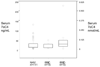
Figure 2
Comparison of serum 7αC4 (ng/mL) in IBS and healthy volunteers. Data show median and interquartile (box) range, 5th and 95th percentiles and outliers (individual symbols). There are overall significant group differences (ANOVA on ranks, p=0.043), with a borderline significant difference between the healthy volunteer and IBS-D group (Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test, p=0.027).
Similar articles
- SeHCAT [tauroselcholic (selenium-75) acid] for the investigation of bile acid malabsorption and measurement of bile acid pool loss: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.
Riemsma R, Al M, Corro Ramos I, Deshpande SN, Armstrong N, Lee YC, Ryder S, Noake C, Krol M, Oppe M, Kleijnen J, Severens H. Riemsma R, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2013 Dec;17(61):1-236. doi: 10.3310/hta17610. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 24351663 Free PMC article. Review. - Bile acid malabsorption: an under-investigated differential diagnosis in patients presenting with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome type symptoms.
Kurien M, Evans KE, Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Harris A, Sanders DS. Kurien M, et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul;46(7-8):818-22. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2011.574728. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21492055 - Methods for diagnosis of bile acid malabsorption in clinical practice.
Vijayvargiya P, Camilleri M, Shin A, Saenger A. Vijayvargiya P, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.04.029. Epub 2013 May 2. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23644387 Free PMC article. - Increased bile acid biosynthesis is associated with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea.
Wong BS, Camilleri M, Carlson P, McKinzie S, Busciglio I, Bondar O, Dyer RB, Lamsam J, Zinsmeister AR. Wong BS, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Sep;10(9):1009-15.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 18. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22610000 Free PMC article. - Systematic review: the prevalence of idiopathic bile acid malabsorption as diagnosed by SeHCAT scanning in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
Wedlake L, A'Hern R, Russell D, Thomas K, Walters JR, Andreyev HJ. Wedlake L, et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Oct;30(7):707-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04081.x. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19570102 Review.
Cited by
- Corn silk polysaccharides attenuate diabetic nephropathy through restoration of the gut microbial ecosystem and metabolic homeostasis.
Dong W, Zhao Y, Li X, Huo J, Wang W. Dong W, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 4;14:1232132. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1232132. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38111708 Free PMC article. - Elobixibat for the treatment of constipation.
Chedid V, Vijayvargiya P, Camilleri M. Chedid V, et al. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Oct;12(10):951-960. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1522248. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30204504 Free PMC article. - A Clostridia-rich microbiota enhances bile acid excretion in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.
Zhao L, Yang W, Chen Y, Huang F, Lu L, Lin C, Huang T, Ning Z, Zhai L, Zhong LL, Lam W, Yang Z, Zhang X, Cheng C, Han L, Qiu Q, Shang X, Huang R, Xiao H, Ren Z, Chen D, Sun S, El-Nezami H, Cai Z, Lu A, Fang X, Jia W, Bian Z. Zhao L, et al. J Clin Invest. 2020 Jan 2;130(1):438-450. doi: 10.1172/JCI130976. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 31815740 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - New insights into bile acid malabsorption.
Johnston I, Nolan J, Pattni SS, Walters JR. Johnston I, et al. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011 Oct;13(5):418-25. doi: 10.1007/s11894-011-0219-3. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21805078 Review. - Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
Gomez-Ospina N, Potter CJ, Xiao R, Manickam K, Kim MS, Kim KH, Shneider BL, Picarsic JL, Jacobson TA, Zhang J, He W, Liu P, Knisely AS, Finegold MJ, Muzny DM, Boerwinkle E, Lupski JR, Plon SE, Gibbs RA, Eng CM, Yang Y, Washington GC, Porteus MH, Berquist WE, Kambham N, Singh RJ, Xia F, Enns GM, Moore DD. Gomez-Ospina N, et al. Nat Commun. 2016 Feb 18;7:10713. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10713. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26888176 Free PMC article.
References
- Larsson MH, Simrén M, Thomas EA, Bornstein JC, Lindström E, Sjövall H. Elevated motility-related transmucosal potential difference in the upper small intestine in the irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007;19:812–820. - PubMed
- Fernández-Bañares F, Esteve M, Salas A, Alsina M, Farré C, González C, Buxeda M, Forné M, Rosinach M, Espinós JC, Maria Viver J. Systematic evaluation of the causes of chronic watery diarrhea with functional characteristics. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2520–2528. - PubMed
- Wildt S, Nørby Rasmussen S, Lysgård Madsen J, Rumessen JJ. Bile acid malabsorption in patients with chronic diarrhoea: clinical value of SeHCAT test. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:826–830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK067071-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067071/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054681-08/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK67071/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002638-10/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK02638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous