The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain
Skirmantas Kriaucionis et al. Science. 2009.
Abstract
Despite the importance of epigenetic regulation in neurological disorders, little is known about neuronal chromatin. Cerebellar Purkinje neurons have large and euchromatic nuclei, whereas granule cell nuclei are small and have a more typical heterochromatin distribution. While comparing the abundance of 5-methylcytosine in Purkinje and granule cell nuclei, we detected the presence of an unusual DNA nucleotide. Using thin-layer chromatography, high-pressure liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry, we identified the nucleotide as 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxycytidine (hmdC). hmdC constitutes 0.6% of total nucleotides in Purkinje cells, 0.2% in granule cells, and is not present in cancer cell lines. hmdC is a constituent of nuclear DNA that is highly abundant in the brain, suggesting a role in epigenetic control of neuronal function.
Figures
Fig. 1
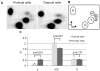
Quantification of mC and “x” abundance in Purkinje and granule neurons. A, 2D TLC separation of nucleoside monophosphates from genomic DNA in Purkinje and granule cells. B, reference map to the TLC spots (A is dAMP, etc) (14), with added “x” position. C, percentage shows the abundance of a nucleotide neighboring G. Error bars show SEM (n=11), p values were derived from Matt-Whitney statistics. Neither abundance of dTMP or dAMP were different between the samples (p=0.743 and p=0.793 respectively).
Fig. 2
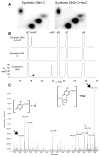
2D TLC, HPLC and MS identification of hmC. A, 2D TLC analysis of synthetic DNA templates indicates that hmC comigrates with the “x” spot (Fig 1). B, HPLC chromatograms (A, 254 nm) of the nucleosides derived from synthetic and cerebellum DNA. The peaks were identified using MS. The black arrow points to the peak, which elutes at the same time as hmdC. C, MS of the fraction corresponding to the HPLC peak indicated above. Closed black arrows indicate the masses of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethyl-2′-deoxylcytidine sodium ions (structures are shown on the insets). Open arrows indicate the ions generated by 2′-deoxycytidine, which elutes in a large nearby peak and spills over into the analyzed fraction.
Comment in
- 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, a modified mammalian DNA base with a potential regulatory role.
Pfeifer GP, Szabo PE. Pfeifer GP, et al. Epigenomics. 2009 Oct;1(1):21-2. doi: 10.2217/epi.09.18. Epigenomics. 2009. PMID: 22122633 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Quantitative assessment of Tet-induced oxidation products of 5-methylcytosine in cellular and tissue DNA.
Liu S, Wang J, Su Y, Guerrero C, Zeng Y, Mitra D, Brooks PJ, Fisher DE, Song H, Wang Y. Liu S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(13):6421-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt360. Epub 2013 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23658232 Free PMC article. - Determination of genomic 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxycytidine in human DNA by capillary electrophoresis with laser induced fluorescence.
Krais AM, Park YJ, Plass C, Schmeiser HH. Krais AM, et al. Epigenetics. 2011 May;6(5):560-5. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.5.15678. Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 21593596 - Alteration in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic regulation leads to Purkinje cell vulnerability in ATM deficiency.
Jiang D, Zhang Y, Hart RP, Chen J, Herrup K, Li J. Jiang D, et al. Brain. 2015 Dec;138(Pt 12):3520-36. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv284. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26510954 Free PMC article. - The cells and molecules that make a cerebellum.
Goldowitz D, Hamre K. Goldowitz D, et al. Trends Neurosci. 1998 Sep;21(9):375-82. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(98)01313-7. Trends Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9735945 Review. - [Progress of research on 5-hydroxymethylcytosine].
Zhang YX, Gao KR, Yu SY. Zhang YX, et al. Yi Chuan. 2012 May;34(5):509-18. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2012.00509. Yi Chuan. 2012. PMID: 22659422 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Epigenetic Mechanisms of Serotonin Signaling.
Holloway T, González-Maeso J. Holloway T, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):1099-109. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00033. Epub 2015 Mar 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25734378 Free PMC article. Review. - Stereochemistry of benzylic carbon substitution coupled with ring modification of 2-nitrobenzyl groups as key determinants for fast-cleaving reversible terminators.
Stupi BP, Li H, Wang J, Wu W, Morris SE, Litosh VA, Muniz J, Hersh MN, Metzker ML. Stupi BP, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Feb 13;51(7):1724-7. doi: 10.1002/anie.201106516. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012. PMID: 22231919 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Developmental epigenetics of the murine secondary palate.
Seelan RS, Mukhopadhyay P, Pisano MM, Greene RM. Seelan RS, et al. ILAR J. 2012;53(3-4):240-52. doi: 10.1093/ilar.53.3-4.240. ILAR J. 2012. PMID: 23744964 Free PMC article. Review. - Measurements of DNA methylation at seven loci in various tissues of CD1 mice.
Daugela L, Nüsgen N, Walier M, Oldenburg J, Schwaab R, El-Maarri O. Daugela L, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044585. Epub 2012 Sep 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970256 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic changes in the developing brain: Effects on behavior.
Keverne EB, Pfaff DW, Tabansky I. Keverne EB, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 2;112(22):6789-95. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501482112. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26034282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases