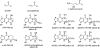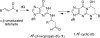Chemistry and biology of DNA containing 1,N(2)-deoxyguanosine adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Chemistry and biology of DNA containing 1,N(2)-deoxyguanosine adducts of the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-hydroxynonenal
Irina G Minko et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 May.
Abstract
The alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes (enals) acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and trans-4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) are products of endogenous lipid peroxidation, arising as a consequence of oxidative stress. The addition of enals to dG involves Michael addition of the N(2)-amine to give N(2)-(3-oxopropyl)-dG adducts, followed by reversible cyclization of N1 with the aldehyde, yielding 1,N(2)-dG exocyclic products. The 1,N(2)-dG exocyclic adducts from acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-HNE exist in human and rodent DNA. The enal-induced 1,N(2)-dG lesions are repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway in both Escherichia coli and mammalian cells. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing structurally defined 1,N(2)-dG adducts of acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-HNE were synthesized via a postsynthetic modification strategy. Site-specific mutagenesis of enal adducts has been carried out in E. coli and various mammalian cells. In all cases, the predominant mutations observed are G-->T transversions, but these adducts are not strongly miscoding. When placed into duplex DNA opposite dC, the 1,N(2)-dG exocyclic lesions undergo ring opening to the corresponding N(2)-(3-oxopropyl)-dG derivatives. Significantly, this places a reactive aldehyde in the minor groove of DNA, and the adducted base possesses a modestly perturbed Watson-Crick face. Replication bypass studies in vitro indicate that DNA synthesis past the ring-opened lesions can be catalyzed by pol eta, pol iota, and pol kappa. It also can be accomplished by a combination of Rev1 and pol zeta acting sequentially. However, efficient nucleotide insertion opposite the 1,N(2)-dG ring-closed adducts can be carried out only by pol iota and Rev1, two DNA polymerases that do not rely on the Watson-Crick pairing to recognize the template base. The N(2)-(3-oxopropyl)-dG adducts can undergo further chemistry, forming interstrand DNA cross-links in the 5'-CpG-3' sequence, intrastrand DNA cross-links, or DNA-protein conjugates. NMR and mass spectrometric analyses indicate that the DNA interstand cross-links contain a mixture of carbinolamine and Schiff base, with the carbinolamine forms of the linkages predominating in duplex DNA. The reduced derivatives of the enal-mediated N(2)-dG:N(2)-dG interstrand cross-links can be processed in mammalian cells by a mechanism not requiring homologous recombination. Mutations are rarely generated during processing of these cross-links. In contrast, the reduced acrolein-mediated N(2)-dG peptide conjugates can be more mutagenic than the corresponding monoadduct. DNA polymerases of the DinB family, pol IV in E. coli and pol kappa in human, are implicated in error-free bypass of model acrolein-mediated N(2)-dG secondary adducts, the interstrand cross-links, and the peptide conjugates.
Figures
Figure 1
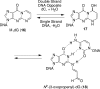
Structures of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and 4-HNE and their cyclic 1,_N_2-dG adducts.
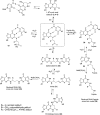
Scheme 1. 1,_N_2-dG Cyclic Adducts Arising from Michael Addition of Enals to dG
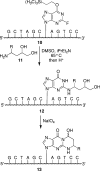
Scheme 2. Site-Specific Synthesis of Oligodeoxynucleotides Containing 1,_N_2-dG Adducts of Acrolein, Crotonaldehyde, and 4-HNE by the Postsynthetic Modification Strategy
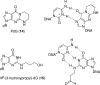
Figure 2
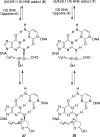
Model substrates for the γ-HO-PdG adduct in DNA. Top left: PdG (14), a model for the ring-closed form of γ-HO-PdG (2). Top right: PdG forms a Hoogsteen pair with dC in duplex DNA. Bottom left: Reduced γ-HO-PdG adduct (15), a model for the ring-opened _N_2-(3-oxopropyl)-dG (1). Bottom right: _N_2-(3-oxopropyl)-dG (1) forms a Watson−Crick pair with dC in duplex DNA.
Scheme 3. Ring-Opening Chemistry of the M1dG Adduct Opposite dC in Duplex DNA
Scheme 4. Ring-Opening and Cross-Linking Chemistry of 1,_N_2-Enal-Derived dG Adducts Opposite dC in Duplex DNA
Scheme 5. (6_S_,8_R_,11_S_)- and (6_R_,8_S_,11_R_)-4-HNE-dG Adducts (6 and 7) Form Cyclic Hemiacetals after Initial Ring Opening Opposite dC in Duplex DNA
Figure 3
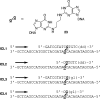
Oligodeoxynucleotides containing the reduced acrolein-mediated _N_2-dG:_N_2-dG interstrand cross-link (23).
Similar articles
- Rearrangement of the (6S,8R,11S) and (6R,8S,11R) exocyclic 1,N2-deoxyguanosine adducts of trans-4-hydroxynonenal to N2-deoxyguanosine cyclic hemiacetal adducts when placed complementary to cytosine in duplex DNA.
Huang H, Wang H, Qi N, Kozekova A, Rizzo CJ, Stone MP. Huang H, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Aug 20;130(33):10898-906. doi: 10.1021/ja801824b. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18661996 Free PMC article. - Stereospecific formation of interstrand carbinolamine DNA cross-links by crotonaldehyde- and acetaldehyde-derived alpha-CH3-gamma-OH-1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine adducts in the 5'-CpG-3' sequence.
Cho YJ, Wang H, Kozekov ID, Kurtz AJ, Jacob J, Voehler M, Smith J, Harris TM, Lloyd RS, Rizzo CJ, Stone MP. Cho YJ, et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006 Feb;19(2):195-208. doi: 10.1021/tx050239z. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16485895 Free PMC article. - Spectroscopic characterization of interstrand carbinolamine cross-links formed in the 5'-CpG-3' sequence by the acrolein-derived gamma-OH-1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine DNA adduct.
Cho YJ, Kim HY, Huang H, Slutsky A, Minko IG, Wang H, Nechev LV, Kozekov ID, Kozekova A, Tamura P, Jacob J, Voehler M, Harris TM, Lloyd RS, Rizzo CJ, Stone MP. Cho YJ, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Dec 21;127(50):17686-96. doi: 10.1021/ja053897e. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 16351098 Free PMC article. - DNA cross-link induced by trans-4-hydroxynonenal.
Huang H, Kozekov ID, Kozekova A, Wang H, Lloyd RS, Rizzo CJ, Stone MP. Huang H, et al. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010 Jul;51(6):625-34. doi: 10.1002/em.20599. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010. PMID: 20577992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The sphingolipid degradation product trans-2-hexadecenal forms adducts with DNA.
Upadhyaya P, Kumar A, Byun HS, Bittman R, Saba JD, Hecht SS. Upadhyaya P, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jul 20;424(1):18-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22727907 Free PMC article. - Phytochemical antioxidants modulate mammalian cellular epigenome: implications in health and disease.
Malireddy S, Kotha SR, Secor JD, Gurney TO, Abbott JL, Maulik G, Maddipati KR, Parinandi NL. Malireddy S, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Jul 15;17(2):327-39. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4600. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22404530 Free PMC article. Review. - Formation of deoxyguanosine cross-links from calf thymus DNA treated with acrolein and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal.
Kozekov ID, Turesky RJ, Alas GR, Harris CM, Harris TM, Rizzo CJ. Kozekov ID, et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010 Nov 15;23(11):1701-13. doi: 10.1021/tx100179g. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20964440 Free PMC article. - Minor groove orientation of the KWKK peptide tethered via the N-terminal amine to the acrolein-derived 1,N2-gamma-hydroxypropanodeoxyguanosine lesion with a trimethylene linkage.
Huang H, Kozekov ID, Kozekova A, Rizzo CJ, McCullough AK, Lloyd RS, Stone MP. Huang H, et al. Biochemistry. 2010 Jul 27;49(29):6155-64. doi: 10.1021/bi100364f. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20604523 Free PMC article. - Analysis of acrolein-derived 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts in human leukocyte DNA from smokers and nonsmokers.
Zhang S, Balbo S, Wang M, Hecht SS. Zhang S, et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Jan 14;24(1):119-24. doi: 10.1021/tx100321y. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21090699 Free PMC article.
References
- Burcham P. C. (1998) Genotoxic lipid peroxidation products: Their DNA damaging properties and role in formation of endogenous DNA adducts. Mutagenesis 13, 287–305. - PubMed
- Chung F. L.; Zhang L.; Ocando J. E.; Nath R. G. (1999) Role of 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts as endogenous DNA lesions in rodents and humans. IARC Sci. Publ. 150, 45–54. - PubMed
- Chung F. L.; Nath R. G.; Nagao M.; Nishikawa A.; Zhou G. D.; Randerath K. (1999) Endogenous formation and significance of 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts. Mutat. Res. 424, 71–81. - PubMed
- Nair U.; Bartsch H.; Nair J. (2007) Lipid peroxidation-induced DNA damage in cancer-prone inflammatory diseases: A review of published adduct types and levels in humans. Free Radical Biol. Med. 43, 1109–1120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 ES-05355/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000267-42/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES005355/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES005355-18/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RR-05805/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES-00267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous