Urinary biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery - PubMed (original) (raw)
Urinary biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery
Won K Han et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 May.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Serum creatinine (Scr) does not allow for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI). The diagnostic utility of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) was evaluated for the early detection of postoperative AKI in a prospective study of 90 adults undergoing cardiac surgery. Designs, setting, participants, & measurements: Urinary KIM-1, NAG, and NGAL were measured at 5 time points for the first 24 h after operation and normalized to the urinary creatinine concentration after cardiac surgery. Receiver-operating characteristic curves were generated and the areas under the curve (AUCs) compared for performance of biomarkers in detection of postoperative AKI.
Results: Thirty-six patients developed AKI, defined as an increase in Scr of > or =0.3 mg/dl within 72 h after surgery. The AUCs for KIM-1 to predict AKI immediately and 3 h after operation were 0.68 and 0.65; 0.61 and 0.63 for NAG; and 0.59 and 0.65 for NGAL, respectively. Combining the three biomarkers enhanced the sensitivity of early detection of postoperative AKI compared with individual biomarkers: the AUCs for the three biomarkers combined were 0.75 and 0.78. The performance of combining biomarkers was even better among 16 early postoperative AKI patients with AUCs of 0.80 and 0.84, respectively.
Conclusions: The results of this study support that a combination of urinary biomarkers may allow for early detection of postoperative AKI after cardiac surgery before a rise in Scr.
Figures
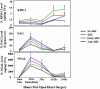
Figure 1.
Pattern of urinary biomarker expression. Graphs show mean normalized urinary kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) concentrations at multiple time points after cardiac surgeries. Error bars are SEM. AKI, acute kidney injury; early AKI, development of acute kidney injury within first 24 h after operation; late AKI, development of acute kidney injury between 24 and 72 h after operation; Ucr, urine creatinine concentration.
Similar articles
- Implication of combined urinary biomarkers in early diagnosis of acute kidney injury following percutaneous coronary intervention.
Luo Q, Zhou F, Dong H, Wu L, Chai L, Lan K, Wu M. Luo Q, et al. Clin Nephrol. 2013 Feb;79(2):85-92. doi: 10.5414/CN106852. Clin Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23110770 - Urinary L-FABP and its combination with urinary NGAL in early diagnosis of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in adult patients.
Liu S, Che M, Xue S, Xie B, Zhu M, Lu R, Zhang W, Qian J, Yan Y. Liu S, et al. Biomarkers. 2013 Feb;18(1):95-101. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2012.740687. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Biomarkers. 2013. PMID: 23167703 - Urinary, Plasma, and Serum Biomarkers' Utility for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Cardiac Surgery in Adults: A Meta-analysis.
Ho J, Tangri N, Komenda P, Kaushal A, Sood M, Brar R, Gill K, Walker S, MacDonald K, Hiebert BM, Arora RC, Rigatto C. Ho J, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Dec;66(6):993-1005. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.018. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26253993 Review. - Urinary and serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury: an in-depth review of the literature.
Vanmassenhove J, Vanholder R, Nagler E, Van Biesen W. Vanmassenhove J, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Feb;28(2):254-73. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs380. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23115326 Review.
Cited by
- Erythropoietin improves long-term outcomes in patients with acute kidney injury after coronary artery bypass grafting.
Oh SW, Chin HJ, Chae DW, Na KY. Oh SW, et al. J Korean Med Sci. 2012 May;27(5):506-11. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.5.506. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Korean Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22563215 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Proteomic identification of early biomarkers of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in children.
Devarajan P, Krawczeski CD, Nguyen MT, Kathman T, Wang Z, Parikh CR. Devarajan P, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010 Oct;56(4):632-42. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.04.014. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010. PMID: 20599305 Free PMC article. - Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) - a biomarker of renal dysfunction in patients with liver cirrhosis: Do we have enough proof?
Firu SG, Streba CT, Firu D, Tache DE, Rogoveanu I. Firu SG, et al. J Med Life. 2015;8 Spec Issue(Spec Issue):15-20. J Med Life. 2015. PMID: 26361506 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical significance of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein as a predictor of ESRD and CVD in patients with CKD.
Matsui K, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Imai N, Sugaya T, Yasuda T, Tatsunami S, Toyama T, Shimizu M, Furuichi K, Wada T, Shibagaki Y, Kimura K. Matsui K, et al. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016 Apr;20(2):195-203. doi: 10.1007/s10157-015-1144-9. Epub 2015 Jul 19. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26189083
References
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV: Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 334: 1448–1460, 1996 - PubMed
- Chertow GM, Lee J, Kuperman GJ, Burdick E, Horsky J, Seger DL, Lee R, Mekala A, Song J, Komaroff AL, Bates DW: Guided medication dosing for inpatients with renal insufficiency. JAMA 286: 2839–2844, 2001 - PubMed
- Liangos O, Wald R, O'Bell JW, Price L, Pereira BJ, Jaber BL: Epidemiology and outcomes of acute renal failure in hospitalized patients: A national survey. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 43–51, 2006 - PubMed
- de Mendonca A, Vincent JL, Suter PM, Moreno R, Dearden NM, Antonelli M, Takala J, Sprung C, Cantraine F: Acute renal failure in the ICU: Risk factors and outcome evaluated by the SOFA score. Intensive Care Med 26: 915–921, 2000 - PubMed
- Zanardo G, Michielon P, Paccagnella A, Rosi P, Calo M, Salandin V, Da Ros A, Michieletto F, Simini G: Acute renal failure in the patient undergoing cardiac operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 107: 1489–1495, 1994 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous