Discordance of MLL-rearranged (MLL-R) infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia in monozygotic twins with spontaneous clearance of preleukemic clone in unaffected twin - PubMed (original) (raw)
Discordance of MLL-rearranged (MLL-R) infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia in monozygotic twins with spontaneous clearance of preleukemic clone in unaffected twin
Meredith K Chuk et al. Blood. 2009.
Abstract
Concordance of MLL-rearranged acute leukemia in infant monozygotic twins is thought to be 100% with a very short latency period, suggesting that either the MLL fusion itself is sufficient to cause leukemia or that it promotes the rapid acquisition of additional oncogenic events that result in overt disease. We report the first case of discordance in an infant monozygotic twin pair. Twin A presented at age 9 months with MLL-ENL(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia and twin B remains healthy 3 years later. The presence and eventual clearance of a clonal population of MLL-ENL(+) cells was shown in the bone marrow and peripheral blood of twin B. Clearance of this clone was temporally associated with viral-induced cytopenias, suggesting an immune-mediated clearance of the clone before the development of leukemia. Thus, concordance of MLL-rearranged acute leukemia in infant monozygotic twins is not universal. The implications of this case for MLL-rearranged leukemogenesis are discussed.
Figures
Figure 1
Twin B's ANC, platelet count, and MLL-ENL RT-PCR status over time from twin A's diagnosis. ANC indicates absolute neutrophil count; PB, peripheral blood; and BM, bone marrow.
Figure 2
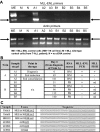
Laboratory results. (A) MLL-ENL RT-PCR for twins A and B with actin control. (B) Summary of MLL-ENL RT-PCR and MLL FISH results for twins A and B; BM indicates bone marrow; PB, peripheral blood; n/a, not applicable; nd, not done. (C) Sequencing results (wt MLL and ENL sequences included as reference).
Similar articles
- Revisiting the biology of infant t(4;11)/MLL-AF4+ B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Sanjuan-Pla A, Bueno C, Prieto C, Acha P, Stam RW, Marschalek R, Menéndez P. Sanjuan-Pla A, et al. Blood. 2015 Dec 17;126(25):2676-85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-667378. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26463423 Free PMC article. Review. - Differential expression of Ikaros isoforms in monozygotic twins with MLL-rearranged precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Russell T, Oliver JM, Wilson BS, Tarleton CA, Winter SS, Meng X. Russell T, et al. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008 Dec;30(12):941-4. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e318180bbf5. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19131787 - Complex MLL rearrangement in non-infiltrated bone marrow in an infant with stage II precursor B-lymphoblastic lymphoma.
Ahlmann M, Meyer C, Marschalek R, Burkhardt B, Koehler G, Klapper W, Juergens H, Rossig C. Ahlmann M, et al. Eur J Haematol. 2014 Oct;93(4):349-53. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12314. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Eur J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24635731 - Two pairs of monozygotic twins with concordant acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): case report.
Li X, Sun N, Huang X, Ju X. Li X, et al. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014 Jul;36(5):e299-303. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000098. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24807006 - MLL-SEPT5 fusion transcript in infant acute myeloid leukemia with t(11;22)(q23;q11).
Launay E, Henry C, Meyer C, Chappé C, Taque S, Boulland ML, Ben Abdelali R, Dugay F, Marschalek R, Bastard C, Fest T, Gandemer V, Belaud-Rotureau MA. Launay E, et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Mar;55(3):662-7. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.809528. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 23725386 Review.
Cited by
- CD22 EXON 12 deletion as a pathogenic mechanism of human B-precursor leukemia.
Uckun FM, Goodman P, Ma H, Dibirdik I, Qazi S. Uckun FM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 28;107(39):16852-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007896107. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20841423 Free PMC article. - Revisiting the biology of infant t(4;11)/MLL-AF4+ B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Sanjuan-Pla A, Bueno C, Prieto C, Acha P, Stam RW, Marschalek R, Menéndez P. Sanjuan-Pla A, et al. Blood. 2015 Dec 17;126(25):2676-85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-667378. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26463423 Free PMC article. Review. - Pbx3-mediated suppression of type I interferon response contributes to leukemia progression driven by MLL-AF9.
Tang L, Lu M, Du Y, Sun J. Tang L, et al. Cancer Gene Ther. 2025 Apr;32(4):475-485. doi: 10.1038/s41417-025-00888-7. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Cancer Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 40108441 - Genetic and Epigenetic Characterization of a Discordant _KMT2A/AFF1_-Rearranged Infant Monozygotic Twin Pair.
Russo A, Viberti C, Mareschi K, Casalone E, Guarrera S, Birolo G, Cazzaniga G, Corral L, Trentin L, Basso G, Fagioli F, Matullo G. Russo A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 9;22(18):9740. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189740. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575904 Free PMC article. - KMT2A-MAML2 rearrangement emerged and regressed during neuroblastoma therapy without leukemia after 12.8-year follow-up.
Felix CA, Slater DJ, Davenport JW, Yu X, Gregory BD, Li MM, Rappaport EF, Cheung NV. Felix CA, et al. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022 Jan;69(1):e29344. doi: 10.1002/pbc.29344. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34550633 Free PMC article.
References
- Greaves MF, Maia AT, Wiemels JL, Ford AM. Leukemia in twins: lessons in natural history. Blood. 2003;102:2321–2333. - PubMed
- Ford AM, Ridge SA, Cabrera ME, et al. In utero rearrangements in the trithorax-related oncogene in infant leukaemias. Nature. 1993;363:358–360. - PubMed
- Gill Super HJ, Rothberg PG, Kobayashi H, Freeman AI, Diaz MO, Rowley JD. Clonal, nonconstitutional rearrangements of the MLL gene in infant twins with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: in utero chromosome rearrangement of 11q23. Blood. 1994;83:641–644. - PubMed
- Jansen MW, Corral L, van der Velden VH, et al. Immunobiological diversity in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia is related to the occurrence and type of MLL gene rearrangement. Leukemia. 2007;21:633–641. - PubMed
- Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 2007;446:758–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical