Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy of the assembly and disassembly of SNAREs: The proteins involved in membrane fusion in cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy of the assembly and disassembly of SNAREs: The proteins involved in membrane fusion in cells
Jeremy D Cook et al. Chem Phys Lett. 2008.
Abstract
In this study, we report for the first time that both t-SNAREs and v-SNARE and their complexes in buffered suspension, exhibit defined peaks at CD signals of 208 and 222 nm wavelengths, consistent with a higher degree of helical secondary structure. Surprisingly, when incorporated in lipid membrane, both SNAREs and their complexes exhibit reduced folding. In presence of NSF-ATP, the SNARE complex disassembles, as reflected from the CD signals demonstrating elimination of α-helices within the structure.
Figures
Fig. 1
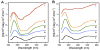
Circular dichroism data reflecting structural changes to SNAREs, both in suspension and in association with membrane. Structural changes, following the assembly and disassembly of the t-/v-SNARE complex is further shown. (A) CD spectra of purified full-length SNARE proteins in suspension and (B) in membrane-associated; their assembly and (NSF–ATP)-induced disassembly is demonstrated. (i) v-SNARE; (ii) t-SNAREs; (iii) t-/v-SNARE complex; (iv) t-/v-SNARE + NSF and (v) t-/v-SNARE + NSF + 2.5 mM ATP, is shown. CD spectra were recorded at 25 °C in 5 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), at a protein concentration of 10 μM. In each experiment, 30 scans were averaged per sample for enhanced signal to noise, and data were acquired on duplicate independent samples to ensure reproducibility.
Fig. 2
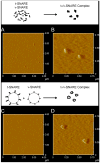
AFM micrographs of t-/v-SNARE complex formed in buffered suspension (A, B) and when membrane-associated t-SNAREs and v-SNARE interact (C, D). (A) and (C) are low resolution images; (B) and (D) are high resolution images of the t-/v-SNARE complexes formed.
Similar articles
- Assembly and disassembly of SNAREs in membrane fusion.
Jena BP. Jena BP. Methods Cell Biol. 2008;90:157-82. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)00808-X. Methods Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 19195550 - A vacuolar v-t-SNARE complex, the predominant form in vivo and on isolated vacuoles, is disassembled and activated for docking and fusion.
Ungermann C, Nichols BJ, Pelham HR, Wickner W. Ungermann C, et al. J Cell Biol. 1998 Jan 12;140(1):61-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.1.61. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9425154 Free PMC article. - Homotypic vacuolar fusion mediated by t- and v-SNAREs.
Nichols BJ, Ungermann C, Pelham HR, Wickner WT, Haas A. Nichols BJ, et al. Nature. 1997 May 8;387(6629):199-202. doi: 10.1038/387199a0. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9144293 - Membrane fusion: role of SNAREs and calcium.
Jena BP. Jena BP. Protein Pept Lett. 2009;16(7):712-7. doi: 10.2174/092986609788681869. Protein Pept Lett. 2009. PMID: 19601899 Review. - Role of SNAREs in membrane fusion.
Jena BP. Jena BP. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;713:13-32. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0763-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21432012 Review.
Cited by
- Membrane lipids influence protein complex assembly-disassembly.
Shin L, Cho WJ, Cook JD, Stemmler TL, Jena BP. Shin L, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Apr 28;132(16):5596-7. doi: 10.1021/ja101574d. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20373736 Free PMC article. - 'Porosome' discovered nearly 20 years ago provides molecular insights into the kiss-and-run mechanism of cell secretion.
Jena BP. Jena BP. J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jul;19(7):1427-40. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12598. Epub 2015 May 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26033351 Free PMC article. Review. - Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits membrane-associated SNARE complex disassembly.
Shin L, Wang S, Lee JS, Flack A, Mao G, Jena BP. Shin L, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Aug;16(8):1701-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01433.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21883893 Free PMC article. - 3D organization and function of the cell: Golgi budding and vesicle biogenesis to docking at the porosome complex.
Wang S, Lee JS, Bishop N, Jeremic A, Cho WJ, Chen X, Mao G, Taatjes DJ, Jena BP. Wang S, et al. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;137(6):703-18. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-0948-x. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22527693 - Porosome in Cystic Fibrosis.
Jena BP. Jena BP. Discoveries (Craiova). 2014 Jul-Sep;2(3):e24. doi: 10.15190/d.2014.16. Discoveries (Craiova). 2014. PMID: 26413568 Free PMC article.
References
- Malhotra V, Orci L, Glick BK, Block MR, Rothman JE. Cell. 1988;54:221. - PubMed
- Bennett K, Calakos N, Scheller RH. Science. 1992;257:255. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources