The orthography-specific functions of the left fusiform gyrus: evidence of modality and category specificity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
The orthography-specific functions of the left fusiform gyrus: evidence of modality and category specificity
Kyrana Tsapkini et al. Cortex. 2010 Feb.
Abstract
We report on an investigation of the cognitive functions of an individual with a resection of the left fusiform gyrus. This individual and a group of control participants underwent testing to examine the question of whether or not there are neural substrates within the left fusiform gyrus that are dedicated to orthographic processing. We evaluated the modality specificity (written vs spoken language) and the category specificity (written language vs other visual categories) of this individual's impairments. The results clearly reveal deficits affecting lexical processes in both reading and spelling. Specifically, we find disruption of normal, rapid access to meaning from print in reading and of accurate retrieval of the spellings of words from their meaning in writing. These deficits stand in striking contrast with intact processing of spoken language and categories of visual stimuli such as line drawings of objects and faces. The modality and category specificity of the deficits provide clear evidence of neural substrates within the left-mid-fusiform gyrus that are specialized and necessary for normal orthographic processing.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Srl. All rights reserved.
Figures
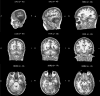
Figure 1
Sagittal, coronal and horizontal views of DPT’s lesion
Similar articles
- Neural systems for reading aloud: a multiparametric approach.
Graves WW, Desai R, Humphries C, Seidenberg MS, Binder JR. Graves WW, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2010 Aug;20(8):1799-815. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp245. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 19920057 Free PMC article. - Beyond the visual word form area: the orthography-semantics interface in spelling and reading.
Purcell JJ, Shea J, Rapp B. Purcell JJ, et al. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2014;31(5-6):482-510. doi: 10.1080/02643294.2014.909399. Epub 2014 May 16. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2014. PMID: 24833190 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Neural correlates of orthographic and phonological consistency effects in children.
Bolger DJ, Hornickel J, Cone NE, Burman DD, Booth JR. Bolger DJ, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2008 Dec;29(12):1416-29. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20476. Hum Brain Mapp. 2008. PMID: 17957704 Free PMC article. - The literate brain: the relationship between spelling and reading.
Rapp B, Lipka K. Rapp B, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011 May;23(5):1180-97. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2010.21507. Epub 2010 Apr 30. J Cogn Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20433242 Free PMC article. - Learning to read an alphabet of human faces produces left-lateralized training effects in the fusiform gyrus.
Moore MW, Durisko C, Perfetti CA, Fiez JA. Moore MW, et al. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014 Apr;26(4):896-913. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00506. Epub 2013 Oct 29. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24168219 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Cortical thinning in chemotherapy-treated older long-term breast cancer survivors.
Daniel E, Deng F, Patel SK, Sedrak MS, Kim H, Razavi M, Sun CL, Root JC, Ahles TA, Dale W, Chen BT. Daniel E, et al. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023 Feb;17(1):66-76. doi: 10.1007/s11682-022-00743-5. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. PMID: 36369620 Free PMC article. - Language processing from the perspective of electrical stimulation mapping.
Rofes A, Mandonnet E, de Aguiar V, Rapp B, Tsapkini K, Miceli G. Rofes A, et al. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2019 May-Jun;36(3-4):117-139. doi: 10.1080/02643294.2018.1485636. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 29996708 Free PMC article. Review. - Inter-relationships among behavioral markers, genes, brain and treatment in dyslexia and dysgraphia.
Berninger V, Richards T. Berninger V, et al. Future Neurol. 2010 Jul 1;5(4):597-617. doi: 10.2217/fnl.10.22. Future Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20953351 Free PMC article. - Patterns of brain reorganization subsequent to left fusiform damage: fMRI evidence from visual processing of words and pseudowords, faces and objects.
Tsapkini K, Vindiola M, Rapp B. Tsapkini K, et al. Neuroimage. 2011 Apr 1;55(3):1357-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.024. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21168516 Free PMC article. - Dissociable neural systems underwrite logical reasoning in the context of induced emotions with positive and negative valence.
Smith KW, Vartanian O, Goel V. Smith KW, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 Sep 23;8:736. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00736. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25294997 Free PMC article.
References
- Army Individual Test Battery. Manual of directions and scoring. Washington, DC: War Department, Adjutant General’s Office; 1944.
- Baker CI, Hutchison TL, Kanwisher N. Does the fusiform face area contain subregions highly selective for nonfaces? Nature neuroscience. 2007a;10(1):3–4. - PubMed
- Bar M, Tootell RB, Schacter DL, Greve DN, Fischl B, Mendola JD, et al. Cortical mechanisms specific to explicit visual object recognition. Neuron. 2001;29(2):529–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources