Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells
Uppoor G Bhat et al. PLoS One. 2009.
Abstract
Forkhead box M1 (FoxM1) oncogenic transcription factor represents an attractive therapeutic target in the fight against cancer, because it is overexpressed in a majority of human tumors. Recently, using a cell-based assay system we identified thiazole antibiotic Siomycin A as an inhibitor of FoxM1 transcriptional activity. Here, we report that structurally similar thiazole antibiotic, thiostrepton also inhibits the transcriptional activity of FoxM1. Furthermore, we found that these thiopeptides did not inhibit the transcriptional activity of other members of the Forkhead family or some non-related transcription factors. Further experiments revealed that thiazole antibiotics also inhibit FoxM1 expression, but not the expression of other members of the Forkhead box family. In addition, we found that the thiazole antibiotics efficiently inhibited the growth and induced potent apoptosis in human cancer cell lines of different origin. Thiopeptide-induced apoptosis correlated with the suppression of FoxM1 expression, while overexpression of FoxM1 partially protected cancer cells from the thiazole antibiotic-mediated cell death. These data suggest that Siomycin A and thiostrepton may specifically target FoxM1 to induce apoptosis in cancer cells and FoxM1 inhibitors/thiazole antibiotics could be potentially developed as novel anticancer drugs against human neoplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
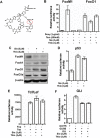
Figure 1. Thiazole antibiotics inhibit FoxM1-dependent transcription and FoxM1 expression.
(A) The chemical structure of the thiazole antibiotic, thiostrepton that differs from Siomycin A by only two residues (Thiostrepton-R1-R2: Isoleucine-alanine; Siomycin- R1-R2: valine-dehydroalanine). (B) Luciferase assays after treatment of the C3-Luc2.3-FoxO1 cell line with the combination of either 1 µg/mL doxycycline (Doxy) or 300 nM tamoxifen (Tam) and 3 µM of Siomycin A (Sio) or thiostrepton (Tio), respectively revealed that thiostrepton is also a negative regulator of FoxM1 transcriptional activity and thiazole antibiotics inhibit FoxM1 transcriptional activity among the Forkhead family members. (C) Thiazole antibiotics downregulated FoxM1 protein levels, but not FoxA1, FoxO1 and FoxO3a levels as detected by immunoblotting. (D) The HCT116-p53RE-Luc cell line, which stably expressing firefly luciferase under the control of multiple p53 response elements treated with the indicated concentration of Siomycin A or thiostrepton. After overnight treatment the luciferase activity was measured. (E) SW480 colon cancer cell line was transiently transfected with the Tcf/Lef-dependent TOPFlash and the control FOPFlash constructs. Twenty-four hrs following transfection the cells were treated with 3 µM of Siomycin A or thiostrepton. The next day the luciferase activity was measured. (F) A549 lung cancer cells were transiently transfected with the GLI-dependent GLIBS-Luc, the control miniTK reporter constructs and the GLI expression plasmid. Cells were treated with the indicated concentration of the thiopeptides 24 hrs after transfection and the luciferase activity was measured the following day. Bars in B, D–F are representative mean values of triplicate experiments+/−SD.
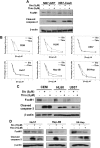
Figure 2. Evaluation of the effects of the thiopeptides on a panel of human cancer cell lines.
(A) Treatment of caspase-8 deficient and reconstituted NB7 neuroblastoma cell lines with the thiazole antibiotics revealed that thiopeptide-induced apoptosis mainly involves the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. (B) Leukemia cancer cell lines CEM [IC50/µM: Sio-0.73 (0.08); Thio-1.47 (0.1)], HL60 [IC50/µM: Sio-0.68 (0.06); Thio-1.78 (0.4)], and U937 [IC50/µM: Sio-0.53 (0.1); Thio-0.73 (0.3)], and liver cancer cell lines Hep-3B [IC50/µM: Sio-3.6 (1.3); Thio-2.3 (0.8)], Huh7 [IC50/µM: Sio-2.3 (0.5); Thio-1.8 (0.2)], and SK-Hep [IC50/µM: Sio-3.7 (0.4); Thio-6.0 (1.4)], showed sensitivity in low micromolar range to the thiazole antibiotics as determined by growth inhibition assays. (C–D) Siomycin A and thiostrepton inhibit FoxM1 expression and induce potent apoptosis in leukemia and liver cancer cells.
Figure 3. Overexpression of FoxM1 partially protects cancer cell lines from thiazole antibiotic-induced apoptosis.
(A) Immunoblot analysis after treatment with Siomycin A revealed close correlation between downregulation of FoxM1 and induction of apoptosis. (B) Following treatment with thiostrepton, thiopeptide-induced apoptosis and inhibition of FoxM1 protein expression are more prominent in the presence of cyclohexamide (Chx) as depicted by immunoblotting for FoxM1 and cleaved caspase-3. (C) The expression of endogenous FoxM1 decreased in a time-dependent fashion in the presence of thiostrepton and Chx, while the levels of exogenous FoxM1 were not affected. Overexpression of FoxM1 protected against cell death induced by thiostrepton as detected by immunoblotting for cleaved caspase-3. (D) FoxM1 overexpressing cells were resistant to the treatment with increasing amount of Siomycin A as analyzed by immunoblotting for cleaved caspase-3. (E) Immunoblot analysis revealed that overexpression of FoxM1 also protected against Siomycin A-induced apoptosis in the presence of Chx.
Similar articles
- FoxM1 inhibitors as potential anticancer drugs.
Gartel AL. Gartel AL. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008 Jun;12(6):663-5. doi: 10.1517/14728222.12.6.663. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008. PMID: 18479213 - A new target for proteasome inhibitors: FoxM1.
Gartel AL. Gartel AL. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Feb;19(2):235-42. doi: 10.1517/13543780903563364. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20074015 Free PMC article. Review. - FoxM1 is a general target for proteasome inhibitors.
Bhat UG, Halasi M, Gartel AL. Bhat UG, et al. PLoS One. 2009 Aug 12;4(8):e6593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006593. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19672316 Free PMC article. - A novel mode of FoxM1 regulation: positive auto-regulatory loop.
Halasi M, Gartel AL. Halasi M, et al. Cell Cycle. 2009 Jun 15;8(12):1966-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.12.8708. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19411834 - Suppression of the Oncogenic Transcription Factor FOXM1 by Proteasome Inhibitors.
Gartel AL. Gartel AL. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:596528. doi: 10.1155/2014/596528. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014. PMID: 25093142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Thiostrepton is an inducer of oxidative and proteotoxic stress that impairs viability of human melanoma cells but not primary melanocytes.
Qiao S, Lamore SD, Cabello CM, Lesson JL, Muñoz-Rodriguez JL, Wondrak GT. Qiao S, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 May 1;83(9):1229-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.027. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22321511 Free PMC article. - Molecular mechanism of Forkhead box M1 inhibition by thiostrepton in breast cancer cells.
Kongsema M, Wongkhieo S, Khongkow M, Lam EW, Boonnoy P, Vongsangnak W, Wong-Ekkabut J. Kongsema M, et al. Oncol Rep. 2019 Sep;42(3):953-962. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7225. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31322278 Free PMC article. - Structure-based virtual screening identified novel FOXM1 inhibitors as the lead compounds for ovarian cancer.
Zhou ZY, Han XY, Sun LQ, Li SY, Xue ST, Li ZR. Zhou ZY, et al. Front Chem. 2022 Nov 24;10:1058256. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1058256. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36505747 Free PMC article. - Structural basis and dynamics of multidrug recognition in a minimal bacterial multidrug resistance system.
Habazettl J, Allan M, Jensen PR, Sass HJ, Thompson CJ, Grzesiek S. Habazettl J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 23;111(51):E5498-507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1412070111. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25489067 Free PMC article. - Forkhead box L1 is frequently downregulated in gallbladder cancer and inhibits cell growth through apoptosis induction by mitochondrial dysfunction.
Qin Y, Gong W, Zhang M, Wang J, Tang Z, Quan Z. Qin Y, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e102084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102084. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010679 Free PMC article.
References
- Laoukili J, Stahl M, Medema RH. FoxM1: At the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775:92–102. - PubMed
- Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:847–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous