Using neuroplasticity-based auditory training to improve verbal memory in schizophrenia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Using neuroplasticity-based auditory training to improve verbal memory in schizophrenia
Melissa Fisher et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Objective: Impaired verbal memory in schizophrenia is a key rate-limiting factor for functional outcome, does not respond to currently available medications, and shows only modest improvement after conventional behavioral remediation. The authors investigated an innovative approach to the remediation of verbal memory in schizophrenia, based on principles derived from the basic neuroscience of learning-induced neuroplasticity. The authors report interim findings in this ongoing study.
Method: Fifty-five clinically stable schizophrenia subjects were randomly assigned to either 50 hours of computerized auditory training or a control condition using computer games. Those receiving auditory training engaged in daily computerized exercises that placed implicit, increasing demands on auditory perception through progressively more difficult auditory-verbal working memory and verbal learning tasks.
Results: Relative to the control group, subjects who received active training showed significant gains in global cognition, verbal working memory, and verbal learning and memory. They also showed reliable and significant improvement in auditory psychophysical performance; this improvement was significantly correlated with gains in verbal working memory and global cognition.
Conclusions: Intensive training in early auditory processes and auditory-verbal learning results in substantial gains in verbal cognitive processes relevant to psychosocial functioning in schizophrenia. These gains may be due to a training method that addresses the early perceptual impairments in the illness, that exploits intact mechanisms of repetitive practice in schizophrenia, and that uses an intensive, adaptive training approach.
Figures
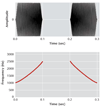
FIGURE 1
Stimuli in Exercise 1 of Auditory Training Given to Patients With Schizophrenia to Improve Verbal Memorya a The learner must perform a time-order judgment task and identify each of two successive frequency modulation sweeps as either “up” (sweep on left) or “down” (sweep on right). Sweep duration and interstimulus interval are modified parametrically as the learner’s performance improves.
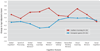
FIGURE 2
Change in Cognitive Performance in Patients With Schizophrenia After 50 Hours of Computerized Auditory Training or 50 Hours of Computer Games aSignificant difference between groups (p<0.01, repeated-measures ANOVA). bSignificant difference between groups (p<0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA). cNonsignificant difference between groups (p=0.10, repeated-measures ANOVA).
Comment in
- Improving verbal memory performance in schizophrenia.
Van den Noort M, Bosch P, Mondt K, Lim S. Van den Noort M, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2009 Dec;166(12):1412; author reply 1412. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09081092. Am J Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19952087 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Neuroplasticity-based auditory training via laptop computer improves cognition in young individuals with recent onset schizophrenia.
Fisher M, Loewy R, Carter C, Lee A, Ragland JD, Niendam T, Schlosser D, Pham L, Miskovich T, Vinogradov S. Fisher M, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2015 Jan;41(1):250-8. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbt232. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Schizophr Bull. 2015. PMID: 24444862 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Combining computerized social cognitive training with neuroplasticity-based auditory training in schizophrenia.
Sacks S, Fisher M, Garrett C, Alexander P, Holland C, Rose D, Hooker C, Vinogradov S. Sacks S, et al. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses. 2013 Summer;7(2):78-86A. doi: 10.3371/CSRP.SAFI.012513. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses. 2013. PMID: 23367504 Free PMC article. - Neuroplasticity-based cognitive training in schizophrenia: an interim report on the effects 6 months later.
Fisher M, Holland C, Subramaniam K, Vinogradov S. Fisher M, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2010 Jul;36(4):869-79. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn170. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Schizophr Bull. 2010. PMID: 19269924 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - When top-down meets bottom-up: auditory training enhances verbal memory in schizophrenia.
Adcock RA, Dale C, Fisher M, Aldebot S, Genevsky A, Simpson GV, Nagarajan S, Vinogradov S. Adcock RA, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2009 Nov;35(6):1132-41. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbp068. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Schizophr Bull. 2009. PMID: 19745022 Free PMC article. Review. - Cognitive and psychomotor effects of risperidone in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Houthoofd SA, Morrens M, Sabbe BG. Houthoofd SA, et al. Clin Ther. 2008 Sep;30(9):1565-89. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.09.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18840365 Review.
Cited by
- Auditory emotion recognition impairments in schizophrenia: relationship to acoustic features and cognition.
Gold R, Butler P, Revheim N, Leitman DI, Hansen JA, Gur RC, Kantrowitz JT, Laukka P, Juslin PN, Silipo GS, Javitt DC. Gold R, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2012 Apr;169(4):424-32. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11081230. Am J Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22362394 Free PMC article. - Use of cognitive event-related potentials in the management of psychiatric disorders: Towards an individual follow-up and multi-component clinical approach.
Campanella S. Campanella S. World J Psychiatry. 2021 May 19;11(5):153-168. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i5.153. eCollection 2021 May 19. World J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34046312 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic correlate of cognitive training response in schizophrenia.
Panizzutti R, Hamilton SP, Vinogradov S. Panizzutti R, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2013 Jan;64(1):264-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.07.048. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22992330 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Role of visual integration in gaze perception and emotional intelligence in schizophrenia.
Tso IF, Carp J, Taylor SF, Deldin PJ. Tso IF, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2014 May;40(3):617-25. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbt058. Epub 2013 May 10. Schizophr Bull. 2014. PMID: 23666503 Free PMC article. - The FDA-NIMH-MATRICS guidelines for clinical trial design of cognitive-enhancing drugs: what do we know 5 years later?
Buchanan RW, Keefe RS, Umbricht D, Green MF, Laughren T, Marder SR. Buchanan RW, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2011 Nov;37(6):1209-17. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbq038. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Schizophr Bull. 2011. PMID: 20410237 Free PMC article.
References
- Keefe RS, Bilder RM, Davis SM, Harvey PD, Palmer BW, Gold JM, Meltzer HY, Green MF, Capuano G, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Davis CE, Hsiao JK, Lieberman JA. Neurocognitive effects of antipsychotic medications in patients with chronic schizophrenia in the CATIE trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:633–647. - PubMed
- Keefe RS, Malhotra AK, Meltzer HY, Kane JM, Buchanan RW, Murthy A, Sovel M, Li C, Goldman R. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: significant placebo/practice effects in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:1217–1228. - PubMed
- Buchanan RW, Conley RR, Dickinson D, Ball MP, Feldman S, Gold JM, McMahon RP. Galantamine for the treatment of cognitive impairments in people with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165:82–89. - PubMed
- Chouinard S, Stip E, Poulin J, Melun JP, Godbout R, Guillem F, Cohen H. Rivastigmine treatment as an add-on to antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia and cognitive deficits. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23:575–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R42 MH-073358/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-068725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068725-05/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R42 MH073358/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical