Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the population of mainland China - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Jul;52(7):1315-21.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1375-y. Epub 2009 May 12.
D Z Zhou, D Zhang, Z Chen, T Zhao, Z Zhang, M Ning, X Hu, Y F Yang, Z F Zhang, L Yu, L He, H Xu
Affiliations
- PMID: 19448982
- PMCID: PMC2688614
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1375-y
Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the population of mainland China
Y Liu et al. Diabetologia. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Two recent genome-wide association studies have identified several novel type 2 diabetes susceptibility variants in intron 15 of the KCNQ1 gene. We aimed to evaluate the effects of the variants in KCNQ1 on type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits in the population of mainland China.
Methods: Three candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms were genotyped in 1,912 individuals with type 2 diabetes and 2,041 normal controls using the ligase detection reaction method.
Results: We confirmed the association of KCNQ1 with type 2 diabetes in the population of mainland China. Allele frequency ORs of the three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were: rs2237892 (OR 1.19, 95% CI 1.08-1.31, p = 3.0 x 10(-4)); rs2237895 (OR 1.20, 95% CI 1.09-1.32, p = 1.9 x 10(-4)); and rs2237897 (OR 1.24, 95% CI 1.13-1.36, p = 3.9 x 10(-5)). We also found a significant difference in the distribution of the global haplotypes between the type 2 diabetes group and the normal control group (p = 2.6 x 10(-5)). In addition, in the control group SNP rs2237892 was marginally associated with increasing fasting plasma glucose and SNPs rs2237892 and rs2237897 were associated with HbA(1c). Furthermore, for all three variants, homozygous carriers of the diabetes-associated allele had significantly decreased BMI and waist circumferences.
Conclusions/interpretation: Our investigation confirmed the effects of KCNQ1 variants on type 2 diabetes risk in the Chinese population.
Figures
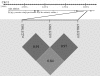
Fig. 1
Linkage disequilibrium structure of the SNPs in KCNQ1. Pairwise D′ values are colour coded: high D′ values are dark, low D′ values are light (values were generated by SHEsis software [22]). The numbers shown at the top represent the degrees of the location of the region on chromosome 11 (Chr11)
Similar articles
- Variations in KCNQ1 are associated with type 2 diabetes and beta cell function in a Chinese population.
Hu C, Wang C, Zhang R, Ma X, Wang J, Lu J, Qin W, Bao Y, Xiang K, Jia W. Hu C, et al. Diabetologia. 2009 Jul;52(7):1322-5. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1335-6. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19308350 - Relationship between the polymorphisms in KCNQ1 and type 2 diabetes in Chinese Kazakh population.
Cui LJ, Chang XY, Zhu LY, Feng G, Zhou T, Zhang CX, Chong KY, Sun K. Cui LJ, et al. Genet Mol Res. 2016 May 13;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027503. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27323013 - KCNQ1 haplotypes associate with type 2 diabetes in Malaysian Chinese Subjects.
Saif-Ali R, Ismail IS, Al-Hamodi Z, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Siang LC, Alabsi AM, Muniandy S. Saif-Ali R, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(9):5705-18. doi: 10.3390/ijms12095705. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22016621 Free PMC article. - Associations of KCNQ1 Polymorphisms with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis.
Yu XX, Liao MQ, Zeng YF, Gao XP, Liu YH, Sun W, Zhu S, Zeng FF, Ye YB. Yu XX, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jul 3;2020:7145139. doi: 10.1155/2020/7145139. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32695830 Free PMC article. Review. - Association of KCNQ1rs2237892C⟶T Gene with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis.
Han WJ, Deng JY, Jin H, Yin LP, Yang JX, Sun JJ. Han WJ, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2021 Nov 22;2021:6606830. doi: 10.1155/2021/6606830. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34853793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Perspectives on genetic studies of type 2 diabetes from the genome-wide association studies era to precision medicine.
Imamura M, Maeda S. Imamura M, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Apr;15(4):410-422. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14149. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 38259175 Free PMC article. Review. - Relationship Between KCNQ1 Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Risk in Northwestern China.
Xu J, Zhang W, Song W, Cui J, Tian Y, Chen H, Huang P, Yang S, Wang L, He X, Wang L, Shi B, Cui W. Xu J, et al. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Dec 31;14:1731-1751. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S340813. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 35002291 Free PMC article. - Meta-analysis of the effect of KCNQ1 gene polymorphism on the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Liu J, Wang F, Wu Y, Huang X, Sheng L, Xu J, Zha B, Ding H, Chen Z, Sun T. Liu J, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2013 May;40(5):3557-67. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2429-7. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23271129 - Implication of genetic variants near SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, FTO, TCF2, KCNQ1, and WFS1 in type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population.
Han X, Luo Y, Ren Q, Zhang X, Wang F, Sun X, Zhou X, Ji L. Han X, et al. BMC Med Genet. 2010 May 28;11:81. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-81. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 20509872 Free PMC article. - Association of genetic variants with isolated fasting hyperglycaemia and isolated postprandial hyperglycaemia in a Han Chinese population.
Kong X, Hong J, Chen Y, Chen L, Zhao Z, Li Q, Ge J, Chen G, Guo X, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Zhou Z, Shan G, Yang W. Kong X, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 19;8(8):e71399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071399. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23990951 Free PMC article.
References
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diacare.27.5.1047', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.5.1047'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15111519', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15111519/'}\]}
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27:1047–1053 - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/ng1732', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1732'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16415884', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16415884/'}\]}
- Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I et al (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 38:320–323 - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diabetes.52.2.568', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.2.568'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12540637', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12540637/'}\]}
- Gloyn AL, Weedon MN, Owen KR et al (2003) Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell KATP channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) confirm that the KCNJ11 E23K variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52:568–572 - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/79839', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/79839'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10973253', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10973253/'}\]}
- Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M et al (2000) The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 26:76–80 - PubMed
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.1142364', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1142364'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC3772310', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3772310/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17463249', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17463249/'}\]}
- Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM et al (2007) Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316:1336–1341 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous