Efficient isolation of highly purified tonsil B lymphocytes using RosetteSep with allogeneic human red blood cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Efficient isolation of highly purified tonsil B lymphocytes using RosetteSep with allogeneic human red blood cells
Jonathan Zuccolo et al. BMC Immunol. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Human tonsils are a rich source of B lymphocytes exhibiting a variety of phenotypes and activation states. Existing methods of purification are time consuming or costly. The aim of the present study was to optimize conditions to isolate large numbers of highly purified primary B lymphocytes from tonsils in a short and cost-effective single step, using a commercially available reagent designed for purifying cells from whole blood (RosetteSep). This technique relies on the presence of the large excess of red blood cells in whole blood for the formation of immunorosettes, whereas single cell suspensions from tonsils contain relatively few red blood cells.
Results: B cell enrichment from tonsils was achieved using RosetteSep with no modification to the whole blood procedure; however, the degree of purity depended on the extent of red blood cell contamination of the starting tonsil cell suspension. Addition of a 50-fold excess of allogeneic human red blood cells, but not sheep red blood cells, reproducibly resulted in high levels of purity. Depletion of mononuclear cells from the donor red blood cells eliminated potential contamination with allogeneic B cells.
Conclusion: RosetteSep reagent can be used in combination with allogeneic human red blood cells to reproducibly isolate tonsil B lymphocytes to high levels of purity with no change in phenotype or loss of cells. This method provides considerable time and cost savings compared to other methods.
Figures
Figure 1
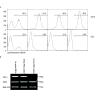
Depletion of lymphocytes from donor blood. To test for lymphocyte contamination of donor RBCs, cDNA was generated from whole blood (WB), purified RBCs and mononuclear cells (MC). CD20, CD3-γ and beta actin were amplified by PCR (n = 2).
Figure 2
Comparison of tonsil B lymphocytes isolated using RosetteSep with added human or sheep RBCs. A. Unpurified tonsil cells, and B lymphocytes isolated using RosetteSep without added RBCs (n = 5), or with sheep RBCs (n = 2), or with human RBCs (n = 9), were analyzed by flow cytometry using anti-CD19 and anti-CD3, as indicated. Percentages of CD19-positive and CD3-positive cells in a representative experiment are shown. B. Reverse transcription PCR was used to further examine the purity of the tonsil B lymphocyte preparations. A PCR product for CD3-γ was amplified from cells purified with either no added RBCs or sheep RBCs (upper panel), but no PCR product was detected in cells purified using added human RBCs (n = 2). CD20 and beta actin were amplified to show that there were equal amounts of cDNA used for amplification.
Figure 3
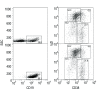
Comparison of tonsil B lymphocyte phenotypes before and after purification. Unpurified tonsil cells (upper panels) and purified B cells (lower panels) were stained with anti-CD19-TC, anti-IgD-PE and anti-CD38-FITC, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Unpurified tonsil lymphocytes were gated for CD19 expression before analyzing the IgD/CD38 profile (n = 5).
Similar articles
- Studies on the identification of B lymphocytes using protein A. Lymphocytes of human palatine tonsil.
Ito H. Ito H. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1979;6(2):97-103. doi: 10.1016/s0385-8146(79)80013-9. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1979. PMID: 399435 - Separation of human B lymphocytes by combined rosetting with mouse and sheep red cells.
Matej H, Kunicka J. Matej H, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 1980;28(1):45-51. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 1980. PMID: 6968193 - [Analysis and fractionation of human tonsillar lymphocytes].
Csuka I, Vincze I, Antoni F. Csuka I, et al. Tsitologiia. 1980 Nov;22(11):1351-6. Tsitologiia. 1980. PMID: 6969480 Russian. - [Comparative study of different types of rosette-forming cells in human peripheral blood and tonsils].
Umanskiĭ IuA, Sidorenko SP, Iudin VM, Fedorovskaia MI. Umanskiĭ IuA, et al. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1979 Jan;(1):94-6. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1979. PMID: 425752 Russian. - Induction of human antibody responses in vitro with emphasis on allogeneic helper factors.
Chiorazzi N, Fu SM, Kunkel HG. Chiorazzi N, et al. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:219-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00279.x. Immunol Rev. 1979. PMID: 89729 Review.
Cited by
- Aberrant O-GlcNAcylation characterizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Shi Y, Tomic J, Wen F, Shaha S, Bahlo A, Harrison R, Dennis JW, Williams R, Gross BJ, Walker S, Zuccolo J, Deans JP, Hart GW, Spaner DE. Shi Y, et al. Leukemia. 2010 Sep;24(9):1588-98. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.152. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Leukemia. 2010. PMID: 20668475 Free PMC article. - Expression of MS4A and TMEM176 Genes in Human B Lymphocytes.
Zuccolo J, Deng L, Unruh TL, Sanyal R, Bau JA, Storek J, Demetrick DJ, Luider JM, Auer-Grzesiak IA, Mansoor A, Deans JP. Zuccolo J, et al. Front Immunol. 2013 Jul 15;4:195. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00195. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23874341 Free PMC article. - An innovative cascade system for simultaneous separation of multiple cell types.
Pierzchalski A, Mittag A, Bocsi J, Tarnok A. Pierzchalski A, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Sep 6;8(9):e74745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074745. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040334 Free PMC article. - Liquid biopsy: a step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments.
Lone SN, Nisar S, Masoodi T, Singh M, Rizwan A, Hashem S, El-Rifai W, Bedognetti D, Batra SK, Haris M, Bhat AA, Macha MA. Lone SN, et al. Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 18;21(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01543-7. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35303879 Free PMC article. Review. - Technical challenges in the isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells.
van der Toom EE, Verdone JE, Gorin MA, Pienta KJ. van der Toom EE, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):62754-62766. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11191. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27517159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Walker H, Hall W, Hurst J. Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations. Boston: Butterworth publishers; 1990. - PubMed
- Nunez C, et al. B cells are generated throughout life in humans. J Immunol. 1996;156:866–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources