Association of common genetic variation in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway with human longevity - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00493.x. Epub 2009 May 31.
Donglei Hu, Scott Huntsman, Andrew Sung, Catherine Chu, Justin Chen, Alexander H Joyner, Nicholas J Schork, Wen-Chi Hsueh, Alexander P Reiner, Bruce M Psaty, Gil Atzmon, Nir Barzilai, Steven R Cummings, Warren S Browner, Pui-Yan Kwok, Elad Ziv; Study of Osteoporotic Fractures
Affiliations
- PMID: 19489743
- PMCID: PMC3652804
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00493.x
Association of common genetic variation in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway with human longevity
Ludmila Pawlikowska et al. Aging Cell. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
The insulin/IGF1 signaling pathways affect lifespan in several model organisms, including worms, flies and mice. To investigate whether common genetic variation in this pathway influences lifespan in humans, we genotyped 291 common variants in 30 genes encoding proteins in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway in a cohort of elderly Caucasian women selected from the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF). The cohort included 293 long-lived cases (lifespan > or = 92 years (y), mean +/- standard deviation (SD) = 95.3 +/- 2.2y) and 603 average-lifespan controls (lifespan < or = 79y, mean = 75.7 +/- 2.6y). Variants were selected for genotyping using a haplotype-tagging approach. We found a modest excess of variants nominally associated with longevity. Nominally significant variants were then replicated in two additional Caucasian cohorts including both males and females: the Cardiovascular Health Study and Ashkenazi Jewish Centenarians. An intronic single nucleotide polymorphism in AKT1, rs3803304, was significantly associated with lifespan in a meta-analysis across the three cohorts (OR = 0.78 95%CI = 0.68-0.89, adjusted P = 0.043); two intronic single nucleotide polymorphisms in FOXO3A demonstrated a significant lifespan association among women only (rs1935949, OR = 1.35, 95%CI = 1.15-1.57, adjusted P = 0.0093). These results demonstrate that common variants in several genes in the insulin/IGF1 pathway are associated with human lifespan.
Figures
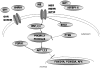
Figure 1. Graphic of insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway showing proteins encoded by scanned genes
Figure 2. Genomic context and linkage disequilibrium for (A) AKT1 and (B, C) FOXO3A
UCSC genome browser tracks show mRNA isoforms for both genes, CpG islands, ESPERR regulatory potential and conservation across 28 mammalian species (indicator line at 70%). Linkage disequilibrium plots below show r2 in HapMap Caucasians. All HapMap variants are tagged at r2>0.8. SNPs genotyped in SOF are marked by black triangles. Longevity-associated SNPs are marked by white triangles and red lines and other SNPs in LD with them are boxed.
Figure 2. Genomic context and linkage disequilibrium for (A) AKT1 and (B, C) FOXO3A
UCSC genome browser tracks show mRNA isoforms for both genes, CpG islands, ESPERR regulatory potential and conservation across 28 mammalian species (indicator line at 70%). Linkage disequilibrium plots below show r2 in HapMap Caucasians. All HapMap variants are tagged at r2>0.8. SNPs genotyped in SOF are marked by black triangles. Longevity-associated SNPs are marked by white triangles and red lines and other SNPs in LD with them are boxed.
Figure 2. Genomic context and linkage disequilibrium for (A) AKT1 and (B, C) FOXO3A
UCSC genome browser tracks show mRNA isoforms for both genes, CpG islands, ESPERR regulatory potential and conservation across 28 mammalian species (indicator line at 70%). Linkage disequilibrium plots below show r2 in HapMap Caucasians. All HapMap variants are tagged at r2>0.8. SNPs genotyped in SOF are marked by black triangles. Longevity-associated SNPs are marked by white triangles and red lines and other SNPs in LD with them are boxed.
Similar articles
- Genetic variation and human longevity.
Soerensen M. Soerensen M. Dan Med J. 2012 May;59(5):B4454. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22549493 - Genetic variation in insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways and longevity.
Ziv E, Hu D. Ziv E, et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2011 Apr;10(2):201-4. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2010.09.002. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Ageing Res Rev. 2011. PMID: 20868776 Review. - Association between genetic variations in the insulin/insulin-like growth factor (Igf-1) signaling pathway and longevity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Di Bona D, Accardi G, Virruso C, Candore G, Caruso C. Di Bona D, et al. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(5):674-81. doi: 10.2174/1570161111666131218152807. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24350933 Review. - Association analyses of insulin signaling pathway gene polymorphisms with healthy aging and longevity in Americans of Japanese ancestry.
Morris BJ, Donlon TA, He Q, Grove JS, Masaki KH, Elliott A, Willcox DC, Willcox BJ. Morris BJ, et al. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Mar;69(3):270-3. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt082. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 23770741 Free PMC article. - Impaired IGF1R signaling in cells expressing longevity-associated human IGF1R alleles.
Tazearslan C, Huang J, Barzilai N, Suh Y. Tazearslan C, et al. Aging Cell. 2011 Jun;10(3):551-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00697.x. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Aging Cell. 2011. PMID: 21388493 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Association between large detectable clonal mosaicism and type 2 diabetes with vascular complications.
Bonnefond A, Skrobek B, Lobbens S, Eury E, Thuillier D, Cauchi S, Lantieri O, Balkau B, Riboli E, Marre M, Charpentier G, Yengo L, Froguel P. Bonnefond A, et al. Nat Genet. 2013 Sep;45(9):1040-3. doi: 10.1038/ng.2700. Epub 2013 Jul 14. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23852171 - Nutraceutical interventions for promoting healthy aging in invertebrate models.
Dong Y, Guha S, Sun X, Cao M, Wang X, Zou S. Dong Y, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:718491. doi: 10.1155/2012/718491. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012. PMID: 22991584 Free PMC article. Review. - Review: a meta-analysis of GWAS and age-associated diseases.
Jeck WR, Siebold AP, Sharpless NE. Jeck WR, et al. Aging Cell. 2012 Oct;11(5):727-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00871.x. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Aging Cell. 2012. PMID: 22888763 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of the Transcription Factor Foxo3 in Hearing Maintenance: Informed Speculation on a New Player in the Cochlea.
White PM. White PM. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:1870675. doi: 10.1155/2016/1870675. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27818997 Free PMC article. Review. - Genes and Longevity of Lifespan.
Bin-Jumah MN, Nadeem MS, Gilani SJ, Al-Abbasi FA, Ullah I, Alzarea SI, Ghoneim MM, Alshehri S, Uddin A, Murtaza BN, Kazmi I. Bin-Jumah MN, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1499. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031499. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263–265. - PubMed
- Bartke A. Minireview: role of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor system in mammalian aging. Endocrinology. 2005;146:3718–3723. - PubMed
- Barzilai N, Atzmon G, Schechter C, Schaefer EJ, Cupples AL, Lipton R, Cheng S, Shuldiner AR. Unique lipoprotein phenotype and genotype associated with exceptional longevity. Jama. 2003;290:2030–2040. - PubMed
- Bluher M, Michael MD, Peroni OD, Ueki K, Carter N, Kahn BB, Kahn CR. Adipose tissue selective insulin receptor knockout protects against obesity and obesity-related glucose intolerance. Dev Cell. 2002;3:25–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035584/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG05394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC55222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007752/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC75150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5U19AG023122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R01 AG005394-22A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG023122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR35582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC85086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2 R01 AG027574-22A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG023122-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027576-22/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR35583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR35584/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC85079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous