Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of endoscopic low-pressure liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy in the esophagus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of endoscopic low-pressure liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy in the esophagus
Bruce D Greenwald et al. Dis Esophagus. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
Endoscopic cryotherapy is a new technique for ablation of esophageal dysplasia and neoplasia. Preliminary studies have shown it to be safe and effective for this indication. The objective of this study is to characterize safety, tolerability, and efficacy of low-pressure liquid nitrogen endoscopic spray cryotherapy ablation in a large cohort across multiple study sites. Parallel prospective treatment studies at four tertiary care academic medical centers in the U.S. assessed spray cryotherapy in patients with Barrett's esophagus with or without dysplasia, early stage esophageal cancer, and severe squamous dysplasia who underwent cryotherapy ablation of the esophagus. All patients were contacted between 1 and 10 days after treatment to assess for side effects and complications of treatment. The main outcome measurement was the incidence of serious adverse events and side effects from treatment. Complete response for high-grade dysplasia (HGD) (CR-HGD), all dysplasia (CR-D), intestinal metaplasia (CR-IM) and cancer (CR-C) were assessed in patients completing therapy during the study period. A total of 77 patients were treated for Barrett's high-grade dysplasia (58.4%), intramucosal carcinoma (16.9%), invasive carcinoma (13%), Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia (9.1%), and severe squamous dysplasia (2.6%). Twenty-two patients (28.6%) reported no side effects throughout treatment. In 323 procedures, the most common complaint was chest pain (17.6%) followed by dysphagia (13.3%), odynophagia (12.1%), and sore throat (9.6%). The mean duration of any symptoms was 3.6 days. No side effects were reported in 48% of the procedures (155/323). Symptoms did not correlate with age, gender, diagnosis, or to treatment early versus late in the patient's or site's experience. Logit analysis showed that symptoms were greater in those with a Barrett's segment of 6 cm or longer. Gastric perforation occurred in one patient with Marfan's syndrome. Esophageal stricture developed in three, all successfully treated with dilation. In 17 HGD patients, cryotherapy produced CR-HGD, CR-D, and CR-IM of 94%, 88%, and 53%, respectively. Complete regression of cancer and HGD was seen in all seven patients with intramucosal carcinoma or stage I esophageal cancer. Endoscopic spray cryotherapy ablation using low-pressure liquid nitrogen in the esophagus is safe, well-tolerated, and efficacious.
Figures
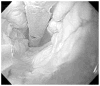
Fig. 1
Endoscopic appearance during endoscopic cryotherapy in the esophagus. The decompression tube is seen in the lumen of the esophagus.
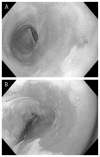
Fig. 2
Endoscopic appearance of the esophagus (a) before and (b) immediately after endoscopic cryotherapy ablation. The mucosa appears hyperemic but remains intact.
Similar articles
- Cryotherapy in the management of premalignant and malignant conditions of the esophagus.
Lal P, Thota PN. Lal P, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov 21;24(43):4862-4869. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4862. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30487696 Free PMC article. Review. - Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy in Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia: long-term results.
Gosain S, Mercer K, Twaddell WS, Uradomo L, Greenwald BD. Gosain S, et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013 Aug;78(2):260-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013. PMID: 23622979 - Safety and efficacy of endoscopic spray cryotherapy for Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia.
Shaheen NJ, Greenwald BD, Peery AF, Dumot JA, Nishioka NS, Wolfsen HC, Burdick JS, Abrams JA, Wang KK, Mallat D, Johnston MH, Zfass AM, Smith JO, Barthel JS, Lightdale CJ. Shaheen NJ, et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010 Apr;71(4):680-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.01.018. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010. PMID: 20363409 Free PMC article. - Endoscopic treatment of Barrett's esophagus: From metaplasia to intramucosal carcinoma.
Chennat J, Waxman I. Chennat J, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 14;16(30):3780-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3780. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20698040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Neoadjuvant cryotherapy improves dysphagia and may impact remission rates in advanced esophageal cancer.
Shah T, Kushnir V, Mutha P, Majhail M, Patel B, Schutzer M, Mogahanaki D, Smallfield G, Patel M, Zfass A. Shah T, et al. Endosc Int Open. 2019 Nov;7(11):E1522-E1527. doi: 10.1055/a-0957-2798. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Endosc Int Open. 2019. PMID: 31681831 Free PMC article. - Endoscopic therapies for Barrett's esophagus.
Ventre S, Shahid H. Ventre S, et al. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Oct 25;6:62. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2020.02.04. eCollection 2021. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34805584 Free PMC article. Review. - Cryotherapy in the management of premalignant and malignant conditions of the esophagus.
Lal P, Thota PN. Lal P, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov 21;24(43):4862-4869. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4862. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30487696 Free PMC article. Review. - Endoscopic Optical Coherence Tomography for Clinical Gastroenterology.
Tsai TH, Fujimoto JG, Mashimo H. Tsai TH, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2014 May 5;4(2):57-93. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics4020057. Diagnostics (Basel). 2014. PMID: 26852678 Free PMC article. Review. - Advances in the management of Barrett's esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Singh A, Chak A. Singh A, et al. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2015 Nov;3(4):303-15. doi: 10.1093/gastro/gov048. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 26486568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Johnston MH, Eastone JA, Horwhat JD, Cartledge J, Mathews J, Foggy JR. Cryoablation of Barrett’s Esophagus: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:842–8. - PubMed
- Overholt BF, Lightdale CJ, Wang KK, et al. Photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium for ablation of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: international, partially blinded, randomized phase III trial. Gastrointest Endosc. (Published erratum appears in Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Feb; 63(2): 359.) Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:488–98. - PubMed
- Overholt BF, Wang KK, Burdick JS, et al. Five-year efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy with Photofrin in Barrett’s high-grade dysplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:460–8. - PubMed
- Dulai GS, Jensen DM, Cortina G, Fontana L, Ippoliti A. Randomized trial of argon plasma coagulation vs. multipolar electrocoagulation for ablation of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:232–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources