Nuclear pore complex biogenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Nuclear pore complex biogenesis
Javier Fernandez-Martinez et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are the sole mediators of transport between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. NPCs have a life cycle: they assemble, disassemble, turnover, and age. The molecular mechanisms governing these different vital steps are beginning to emerge, suggesting key roles for the core structural scaffold of the NPC and auxiliary factors in the assembly of this large macromolecular complex, and connections between NPC maintenance, NPC turnover, and aging of the cell.
Figures
Figure 1
Structure of the NPC. Major features of the interphase NPC and its surrounding NE are indicated; see main text for details (map based on [5•]).
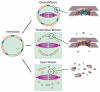
Figure 2
Schematic Illustrating the Different Types of Mitosis. During mitosis, the mitotic spindle (purple) forms while the NE (orange) and NPCs (blue) are retained to differing degrees, resulting in the nucleoplasm (green) being retained only in the closed form of mitosis. To the right are shown which major features of the NPC are still intact, and which are dispersed.
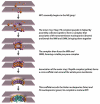
Figure 3
Proposed Path of Interphase NPC Assembly; see main text for details.
Similar articles
- The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex.
Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, Sali A, Rout MP. Alber F, et al. Nature. 2007 Nov 29;450(7170):695-701. doi: 10.1038/nature06405. Nature. 2007. PMID: 18046406 - Functional architecture of the nuclear pore complex.
Grossman E, Medalia O, Zwerger M. Grossman E, et al. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012;41:557-84. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102328. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22577827 Review. - Regulation and coordination of nuclear envelope and nuclear pore complex assembly.
Clever M, Mimura Y, Funakoshi T, Imamoto N. Clever M, et al. Nucleus. 2013 Mar-Apr;4(2):105-14. doi: 10.4161/nucl.23796. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Nucleus. 2013. PMID: 23412657 Free PMC article. - Nuclear pore complex composition: a new regulator of tissue-specific and developmental functions.
Raices M, D'Angelo MA. Raices M, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;13(11):687-99. doi: 10.1038/nrm3461. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23090414 Review. - Peering through the pore: nuclear pore complex structure, assembly, and function.
Suntharalingam M, Wente SR. Suntharalingam M, et al. Dev Cell. 2003 Jun;4(6):775-89. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00162-x. Dev Cell. 2003. PMID: 12791264 Review.
Cited by
- The yeast nuclear pore complex and transport through it.
Aitchison JD, Rout MP. Aitchison JD, et al. Genetics. 2012 Mar;190(3):855-83. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.127803. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22419078 Free PMC article. - Nucleoporin 62-like protein activates canonical Wnt signaling through facilitating the nuclear import of β-catenin in zebrafish.
Yang X, Gu Q, Lin L, Li S, Zhong S, Li Q, Cui Z. Yang X, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;35(7):1110-24. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01181-14. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25605329 Free PMC article. - The nucleoporin ELYS/Mel28 regulates nuclear envelope subdomain formation in HeLa cells.
Clever M, Funakoshi T, Mimura Y, Takagi M, Imamoto N. Clever M, et al. Nucleus. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):187-99. doi: 10.4161/nucl.19595. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Nucleus. 2012. PMID: 22555603 Free PMC article. - Nuclear pore biogenesis into an intact nuclear envelope.
Doucet CM, Hetzer MW. Doucet CM, et al. Chromosoma. 2010 Oct;119(5):469-77. doi: 10.1007/s00412-010-0289-2. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Chromosoma. 2010. PMID: 20721671 Review. - Pom33, a novel transmembrane nucleoporin required for proper nuclear pore complex distribution.
Chadrin A, Hess B, San Roman M, Gatti X, Lombard B, Loew D, Barral Y, Palancade B, Doye V. Chadrin A, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 May 31;189(5):795-811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200910043. Epub 2010 May 24. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20498018 Free PMC article.
References
- Tran EJ, Wente SR. Dynamic nuclear pore complexes: life on the edge. Cell. 2006;125:1041–1053. - PubMed
- Hetzer MW, Walther TC, Mattaj IW. Pushing the envelope: structure, function, and dynamics of the nuclear periphery. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:347–380. - PubMed
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, et al. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature. 2007;450:683–694. - PubMed
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007;450:695–701.Using diverse sources of proteomic and structural experimental data, for the first time the authors were able to calculate a structure for the whole yeast NPC where the position of each nucleoporin within the overall architecture of the NPC is resolved. Major structural features of the NPC and their nucleoporin composition are described, revealing a close evolutionary relationship between the structures of membrane coating complexes and the NPC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM062427-07/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM062427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220-05/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM071329/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071329/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases