p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer
Jorge Moscat et al. Cell. 2009.
Abstract
The signaling adaptor p62 is a multidomain protein implicated in the activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Recent findings link p62 activity to the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, and Mathew et al. (2009) now show that the modulation of p62 by autophagy is a key factor in tumorigenesis. These findings place p62 at critical decision points that control cell death and survival.
Figures
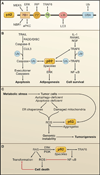
Figure 1. Cellular Functions of p62
(A) Structural domain organization of p62 and p62-interacting partners. p62 has a PB1 domain, a ZZ-type zinc finger domain, a TRAF6-binding (TB) domain, an LC3-interacting region (LIR), and a ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA). (B) p62 speckles promote the oligomerization of TRAF6 and caspase-8 leading to the enhancement of NF-κB activation and apoptosis, respectively. p62 speckles also sequester active ERK, restraining adipogenesis. (C) Autophagy deficiency in apoptosis-impaired tumor cells leads to increased p62 aggregation. This triggers a positive feedback loop for the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhanced genomic instability and tumorigenesis. (D) Ras-induced transformation promotes the accumulation of p62, which leads to an increase in NF-κB activity, thereby restraining ROS production and inhibiting tumor cell death. DISC, death-inducing signaling complex; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.
Similar articles
- Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62.
Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N, Chen G, Chen HY, Bray K, Reddy A, Bhanot G, Gelinas C, Dipaola RS, Karantza-Wadsworth V, White E. Mathew R, et al. Cell. 2009 Jun 12;137(6):1062-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.048. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19524509 Free PMC article. - p62 at the interface of autophagy, oxidative stress signaling, and cancer.
Nezis IP, Stenmark H. Nezis IP, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Sep 1;17(5):786-93. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4394. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22074114 Review. - Biology of p62/sequestosome-1 in Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD).
Wang L, Ebrahimi KB, Chyn M, Cano M, Handa JT. Wang L, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;854:17-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26427388 Review. - p62 participates in the inhibition of NF-κB signaling and apoptosis induced by sulfasalazine in human glioma U251 cells.
Su J, Liu F, Xia M, Xu Y, Li X, Kang J, Li Y, Sun L. Su J, et al. Oncol Rep. 2015 Jul;34(1):235-43. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3944. Epub 2015 May 4. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25937318 - p62/SQSTM1/A170: physiology and pathology.
Komatsu M, Kageyama S, Ichimura Y. Komatsu M, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2012 Dec;66(6):457-62. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22841931 Review.
Cited by
- Autophagy protein p62/SQSTM1 is involved in HAMLET-induced cell death by modulating apotosis in U87MG cells.
Zhang YB, Gong JL, Xing TY, Zheng SP, Ding W. Zhang YB, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2013 Mar 21;4(3):e550. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.77. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23519119 Free PMC article. - Dehydrodiisoeugenol inhibits colorectal cancer growth by endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagic pathways.
Li C, Zhang K, Pan G, Ji H, Li C, Wang X, Hu X, Liu R, Deng L, Wang Y, Yang L, Cui H. Li C, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 10;40(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01915-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33838688 Free PMC article. - Palmitic Acid Promotes Virus Replication in Fish Cell by Modulating Autophagy Flux and TBK1-IRF3/7 Pathway.
Yu Y, Li C, Liu J, Zhu F, Wei S, Huang Y, Huang X, Qin Q. Yu Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 5;11:1764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01764. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849631 Free PMC article. - Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy and Its Regulation by Cannabinoids in Cancer.
Lee XC, Werner E, Falasca M. Lee XC, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 10;13(6):1211. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061211. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802014 Free PMC article. Review. - 13-Acetoxysarcocrassolide Exhibits Cytotoxic Activity Against Oral Cancer Cells Through the Interruption of the Keap1/Nrf2/p62/SQSTM1 Pathway: The Need to Move Beyond Classical Concepts.
Liu YC, Peng BR, Hsu KC, El-Shazly M, Shih SP, Lin TE, Kuo FW, Chou YC, Lin HY, Lu MC. Liu YC, et al. Mar Drugs. 2020 Jul 23;18(8):382. doi: 10.3390/md18080382. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32718084 Free PMC article.
References
- Duran A, Serrano M, Leitges M, Flores JM, Picard S, Brown JP, Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT. Dev. Cell. 2004;6:303–309. - PubMed
- Duran A, Linares JF, Galvez AS, Wikenheiser K, Flores JM, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:343–354. - PubMed
- Geetha T, Jiang J, Wooten MW. Mol. Cell. 2005;20:301–312. - PubMed
- Jin Z, Li Y, Pitti R, Lawrence D, Pham V, Lill J, Ashkenazi A. Cell. 2009;137:721–735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources