Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol response in breast cancer cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol response in breast cancer cells
Poornima Bhat-Nakshatri et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
Estradiol (E2) regulates gene expression at the transcriptional level by functioning as a ligand for estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta). E2-inducible proteins c-Myc and E2Fs are required for optimal ERalpha activity and secondary estrogen responses, respectively. We show that E2 induces 21 microRNAs and represses seven microRNAs in MCF-7 breast cancer cells; these microRNAs have the potential to control 420 E2-regulated and 757 non-E2-regulated mRNAs at the post-transcriptional level. The serine/threonine kinase, AKT, alters E2-regulated expression of microRNAs. E2 induced the expression of eight Let-7 family members, miR-98 and miR-21 microRNAs; these microRNAs reduced the levels of c-Myc and E2F2 proteins. Dicer, a ribonuclease III enzyme required for microRNA processing, is also an E2-inducible gene. Several E2-regulated microRNA genes are associated with ERalpha-binding sites or located in the intragenic region of estrogen-regulated genes. We propose that the clinical course of ERalpha-positive breast cancers is dependent on the balance between E2-regulated tumor-suppressor microRNAs and oncogenic microRNAs. Additionally, our studies reveal a negative-regulatory loop controlling E2 response through microRNAs as well as differences in E2-induced transcriptome and proteome.
Figures
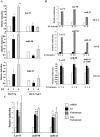
Figure 1.
(A) E2-inducible expression of Let-7f, miR98 and miR-21 in MCF-7p and MCF-7AKT cells. MCF-7p and MCF-7AKT cells were treated with E2 (10−8M) for indicated time and microRNA was subjected qRT–PCR. RNU66, small RNAs encoded in the intron of RPL5 gene (chr1:93 018 360–93 018 429) was used for normalization between samples. Mean plus standard error of the mean (SEM) are shown. *P < 0.03, ethanol versus 1-h E2-treated cells; **P < 0.001 ethanol versus 4 h E2-treated cells. (B) The effect of E2 on the expression of Let-7f, miR-98 and miR-21 in MCF-7 (top), T47-D (middle) and BT-474 (bottom) cells. (C) The effect of fulvestrant treatment on basal and E2-regulated expression of Let-7f, miR-98 and miR-21. Cells were pretreated with 100 nM fulvestrant for 24 h and then treated with E2 for 4 h. *P < 0.05, ethanol versus E2-treated; **P < 0.05, ethanol versus fulvestrant treated cells.
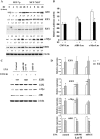
Figure 2.
Putative targets of E2-induced microRNAs. (A) MCF-7p and MCF-7AKT cells were treated with E2 for indicated time and western blotting was performed. (B) 3′-UTR of AIB1 or c-Myc reduces E2-inducible expression of a luciferase reporter under the control of CMV enhancer-promoter. MCF-7 cells were transfected with indicated reporters along with the internal control Renila-luciferase under TK promoter-enhancer and luciferase activity was measured in untreated and E2-treated cells. *P < 0.05, ethanol treated versus E2-treated cells. (C) LNA against Let-7f/miR-98 and miR-21 differentially affect basal and E2-inducible levels of c-Myc and E2F2 proteins in MCF-7p cells. Cells were treated with control or specific LNA and treated with E2 for 24 h. Western blot analysis was done with indicated antibodies. (D) Expression levels of E2F-1, E2F-2, c-Myc and AIB1 from three to five independent experiments, as measured by densitometric scanning (Mean plus SEM), are indicated. *P < 0.05, ethanol versus E2-treated cells; **P < 0.05, control LNA treated versus Let-7f/mir-98 or miR-21 LNA-treated cells. Note the effects of LNA against Let-7f/miR98 and miR-21 on E2F2 and c-Myc but not on E2F1 and AIB1 protein levels.
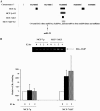
Figure 3.
The regulatory regions of miR-21 contain ERα-binding sites. (A) ERα DNA-binding patterns to the genomic region harboring miR-21 gene on chromosome 17. Black bars represent ERα-binding sites in two cell types observed under ethanol and E2-treated condition. (B) ChIP analysis of ERα binding to the genomic region (central bar) shown in A. ChIP DNA obtained with ERα antibody was subjected to semi-quantitative PCR (top) or Q-PCR (bottom) with specific primers and relative enrichment of ERα binding is shown after normalizing ERα binding in ethanol MCF-7p or MCF-7AKT cells to one unit. The level of ERα binding in E2-treated MCF-7AKT cells was significantly higher than in untreated cells.
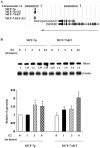
Figure 4.
Dicer is an E2-inducible gene. (A) ERα DNA-binding patterns to the genomic region harboring Dicer. Black bars represent ERα-binding sites in two cell types observed under ethanol-treated or E2-treated condition. (B) E2-inducible expression of Dicer in MCF-7p and MCF-7AKT cells was measured by northern blotting (top panel). The same blot was reprobed with 36B4 to ensure integrity of RNA. qRT–PCR confirming E2-inducible expression of Dicer is also shown (mean plus SEM, bottom panel). *P < 0.04 ethanol-treated versus E2-treated cells.
Figure 5.
A model depicting the possible effects of E2-regulated microRNAs on E2 response and differentiated phenotype of ERα-positive breast cancer cells.
Similar articles
- Estrogen regulates miRNA expression: implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2 in tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Jiang CF, Li DM, Shi ZM, Wang L, Liu MM, Ge X, Liu X, Qian YC, Wen YY, Zhen LL, Lin J, Liu LZ, Jiang BH. Jiang CF, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36940-36955. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9230. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27175587 Free PMC article. - The estrogen receptor-alpha-induced microRNA signature regulates itself and its transcriptional response.
Castellano L, Giamas G, Jacob J, Coombes RC, Lucchesi W, Thiruchelvam P, Barton G, Jiao LR, Wait R, Waxman J, Hannon GJ, Stebbing J. Castellano L, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 15;106(37):15732-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906947106. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706389 Free PMC article. - A MicroRNA196a2* and TP63 circuit regulated by estrogen receptor-α and ERK2 that controls breast cancer proliferation and invasiveness properties.
Kim K, Madak-Erdogan Z, Ventrella R, Katzenellenbogen BS. Kim K, et al. Horm Cancer. 2013 Apr;4(2):78-91. doi: 10.1007/s12672-012-0129-3. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Horm Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23250869 Free PMC article. - Genes regulated by estrogen in breast tumor cells in vitro are similarly regulated in vivo in tumor xenografts and human breast tumors.
Creighton CJ, Cordero KE, Larios JM, Miller RS, Johnson MD, Chinnaiyan AM, Lippman ME, Rae JM. Creighton CJ, et al. Genome Biol. 2006;7(4):R28. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-4-r28. Epub 2006 Apr 7. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16606439 Free PMC article. - MicroRNAs link estrogen receptor alpha status and Dicer levels in breast cancer.
Cochrane DR, Cittelly DM, Howe EN, Spoelstra NS, McKinsey EL, LaPara K, Elias A, Yee D, Richer JK. Cochrane DR, et al. Horm Cancer. 2010 Dec;1(6):306-19. doi: 10.1007/s12672-010-0043-5. Horm Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21761362 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Pilot Study of Serum MicroRNA-21 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Egyptian Breast Cancer Patients.
Toraih EA, Mohammed EA, Farrag S, Ramsis N, Hosny S. Toraih EA, et al. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015 Jun;19(3):179-90. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0143-6. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015. PMID: 26063582 - Estrogen receptor α signaling regulates breast tumor-initiating cells by down-regulating miR-140 which targets the transcription factor SOX2.
Zhang Y, Eades G, Yao Y, Li Q, Zhou Q. Zhang Y, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 30;287(49):41514-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.404871. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23060440 Free PMC article. - Glucocorticoids modulate microRNA expression and processing during lymphocyte apoptosis.
Smith LK, Shah RR, Cidlowski JA. Smith LK, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 19;285(47):36698-708. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.162123. Epub 2010 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20847043 Free PMC article. - Understanding the mechanisms of human tubal ectopic pregnancies: new evidence from knockout mouse models.
Shao R. Shao R. Hum Reprod. 2010 Mar;25(3):584-7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dep438. Epub 2009 Dec 19. Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20023297 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptomic and Functional Evidence That miRNA193a-3p Inhibits Lymphatic Endothelial Cell (LEC) and LEC + MCF-7 Spheroid Growth Directly and by Altering MCF-7 Secretome.
Azzarito G, Henry M, Rotshteyn T, Leeners B, Dubey RK. Azzarito G, et al. Cells. 2023 Jan 21;12(3):389. doi: 10.3390/cells12030389. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766731 Free PMC article.
References
- Jordan VC, O'Malley BW. Selective estrogen-receptor modulators and antihormonal resistance in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:5815–5824. - PubMed
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
- Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:9817–9824. - PubMed
- Gururaj AE, Rayala SK, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R. Novel mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy: genomic and nongenomic considerations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:1001s–1007s. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical