Targeted metabolomic evaluation of arginine methylation and cardiovascular risks: potential mechanisms beyond nitric oxide synthase inhibition - PubMed (original) (raw)
Targeted metabolomic evaluation of arginine methylation and cardiovascular risks: potential mechanisms beyond nitric oxide synthase inhibition
Zeneng Wang et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Sep.
Abstract
Background: We examine the relationship of related posttranslational modification products of arginine methylation and coronary artery disease (CAD) phenotypes.
Methods and results: Plasma was isolated from 1011 consecutive consenting subjects undergoing elective diagnostic cardiac catheterization, and future major adverse cardiac events (MACE, including myocardial infarction, stroke, and death) at 3 years were investigated. Plasma levels of asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA, endogenous nitric oxide synthase [NOS] inhibitor), symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA, which lacks NOS inhibitory activity), N-mono-methylarginine (MMA, a potent NOS inhibitor), methyl-lysine (Methyl-Lys, an unrelated methylated amino acid), arginine, and its major catabolites (citrulline and ornithine) were quantified simultaneously by stable isotope dilution HPLC with online electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and adjusted for traditional risk factors, C-reactive protein, and estimated creatinine clearance. High SDMA levels (adjusted odds ratio [OR] 1.6, 95%CI, 1.1 to 2.6, P<0.001), low MMA (adjusted OR 0.5, 95%CI 0.4 to 0.8, P=0.007), but not ADMA (adjusted OR 1.3, 95%CI 0.88 to 2.0, P=0.177) were associated with increased prevalence of significantly obstructive CAD. Elevated levels of SDMA (adjusted Hazard Ratio [HR] 2.4, 95%CI 1.2 to 4.6, P=0.009), ADMA (adjusted HR 2.2, 95%CI 1.2 to 4.0, P=0.015), as well as an integrated index of arginine methylation [ArgMI=(ADMA+SDMA)/MMA] (adjusted HR 2.4, 95%CI 1.3 to 4.5, P=0.006) were significant independent predictors of incident MACE. ArgMI was predictive of incident MACE even following adjustments for global arginine bioavailability, particularly within secondary prevention patients.
Conclusions: ADMA, SDMA, and the integrated quantification of arginine methylation (in the form of a methylation index) provided independent risk prediction for both significantly obstructive CAD and incident MACE in stable patients undergoing cardiac evaluation. These results suggest that factors beyond direct NOS inhibition contribute to the clinical associations between methylarginines and CAD outcomes.
Figures
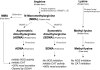
Figure 1
Schematic illustration of pathways for production of methyl derivatives of amino acids.
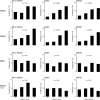
Figure 2
Distribution of MI/stroke, all-cause mortality, and the composite MACE according to methylated amino acid metabolites quartiles (ADMA, SDMA, MMA, and methyl-lysine)
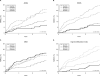
Figure 3
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for patients with major adverse cardiac events at 3-year follow up according to the quartiles of arginine metabolites quartiles (ADMA, SDMA, MMA and arginine methylation index).
Similar articles
- Diminished global arginine bioavailability and increased arginine catabolism as metabolic profile of increased cardiovascular risk.
Tang WH, Wang Z, Cho L, Brennan DM, Hazen SL. Tang WH, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Jun 2;53(22):2061-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.036. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19477356 Free PMC article. - Elevated levels of plasma symmetric dimethylarginine and increased arginase activity as potential indicators of cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatoid arthritis.
Chandrasekharan UM, Wang Z, Wu Y, Wilson Tang WH, Hazen SL, Wang S, Elaine Husni M. Chandrasekharan UM, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Jun 8;20(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1616-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29884228 Free PMC article. - Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) outperforms asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and other methylarginines as predictor of renal and cardiovascular outcome in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease.
Emrich IE, Zawada AM, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Fliser D, Wagenpfeil S, Heine GH, Bode-Böger SM. Emrich IE, et al. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018 Mar;107(3):201-213. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1172-4. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29101459 - From arginine methylation to ADMA: a novel mechanism with therapeutic potential in chronic lung diseases.
Zakrzewicz D, Eickelberg O. Zakrzewicz D, et al. BMC Pulm Med. 2009 Jan 29;9:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-9-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2009. PMID: 19178698 Free PMC article. Review. - [Biological and pathophysiological roles of endogenous methylarginines as inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase].
Masuda H, Azuma H. Masuda H, et al. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002 Jan;119(1):29-35. doi: 10.1254/fpj.119.29. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 11862754 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Arsenic Exposure-Related Hypertension in Bangladesh and Reduced Circulating Nitric Oxide Bioavailability.
Khatun M, Haque N, Siddique AE, Wahed AS, Islam MS, Khan S, Jubayar AM, Sadi J, Kabir E, Shila TT, Islam Z, Sarker MK, Banna HU, Hossain S, Sumi D, Saud ZA, Barchowsky A, Himeno S, Hossain K. Khatun M, et al. Environ Health Perspect. 2024 Apr;132(4):47003. doi: 10.1289/EHP13018. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Environ Health Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38573329 Free PMC article. - L-arginine and Its Derivatives Correlate with Exercise Capacity in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure.
Drohomirecka A, Waś J, Wiligórska N, Rywik TM, Komuda K, Sokołowska D, Lutyńska A, Zieliński T. Drohomirecka A, et al. Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 23;13(3):423. doi: 10.3390/biom13030423. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979359 Free PMC article. - The role of asymmetric dimethylarginine in endothelial dysfunction and abnormal nitric oxide metabolism in systemic sclerosis: results from a pilot study.
Pagkopoulou E, Soulaidopoulos S, Katsiki N, Malliari A, Loutradis C, Karagiannis A, Doumas M, Garyfallos A, Kitas G, Dimitroulas T. Pagkopoulou E, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;42(4):1077-1085. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06472-w. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36534350 - The Role of L-Arginine-NO System in Female Reproduction: A Narrative Review.
Bodis J, Farkas B, Nagy B, Kovacs K, Sulyok E. Bodis J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 28;23(23):14908. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314908. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499238 Free PMC article. Review. - Systematic Characterization of Lysine Post-translational Modification Sites Using MUscADEL.
Chen Z, Liu X, Li F, Li C, Marquez-Lago T, Leier A, Webb GI, Xu D, Akutsu T, Song J. Chen Z, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2499:205-219. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2317-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35696083
References
- Boger RH, Bode-Boger SM, Szuba A, Tsao PS, Chan JR, Tangphao O, Blaschke TF, Cooke JP. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): a novel risk factor for endothelial dysfunction: its role in hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 1998;98:1842–1847. - PubMed
- Miyazaki H, Matsuoka H, Cooke JP, Usui M, Ueda S, Okuda S, Imaizumi T. Endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor: a novel marker of atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1999;99:1141–1146. - PubMed
- Zoccali C, Bode-Boger S, Mallamaci F, Benedetto F, Tripepi G, Malatino L, Cataliotti A, Bellanuova I, Fermo I, Frolich J, Boger R. Plasma concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease: a prospective study. Lancet. 2001;358:2113–2117. - PubMed
- Meinitzer A, Seelhorst U, Wellnitz B, Halwachs-Baumann G, Boehm BO, Winkelmann BR, Marz W. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine independently predicts total and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with angiographic coronary artery disease (the Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health study) Clin Chem. 2007;53:273–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL087018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL077107-050004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL087018-020001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076491-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076491-055328/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous