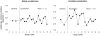Social stress desensitizes lymphocytes to regulation by endogenous glucocorticoids: insights from in vivo cell trafficking dynamics in rhesus macaques - PubMed (original) (raw)
Social stress desensitizes lymphocytes to regulation by endogenous glucocorticoids: insights from in vivo cell trafficking dynamics in rhesus macaques
Steve W Cole et al. Psychosom Med. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether chronic social stress can desensitize leukocytes to normal physiologic regulation by endogenous glucocorticoids.
Methods: We analyzed the longitudinal relationship between plasma cortisol levels and peripheral blood lymphocyte counts over 16 monthly assessments in 18 rhesus macaques randomized to recurrent social encounters with a stable set of conspecifics or continually varying social partners (unstable socialization).
Results: Animals socialized under stable conditions showed the expected inverse relationship between plasma cortisol concentrations and circulating lymphocyte frequencies. That relationship was significantly attenuated in animals subject to unstable social conditions. Differences in leukocyte redistributional sensitivity to endogenous glucocorticoids emerged within the first week of differential socialization, persisted throughout the 60-week study period, and were correlated with other measures of glucocorticoid desensitization (blunted hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis response to acute stress and redistributional response to dexamethasone challenge). Effects of unstable social conditions on leukocyte sensitivity to cortisol regulation were not related to physical aggression.
Conclusion: Chronic social stress can impair normal physiologic regulation of leukocyte function by the HPA axis in ways that may contribute to the increased physical health risks associated with social adversity.
Figures
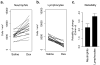
FIGURE 1
Effect of dexamethasone administration on (a.) circulating neutrophil numbers, and (b.) circulating lymphocyte numbers. (c.) Reliability of leukocyte subset responses to dexamethasone injection, expressed as change relative to baseline standard deviation (Cohen’s d).
FIGURE 2
Sensitivity of circulating lymphocyte frequencies to endogenous cortisol levels in Stable vs. Unstable social conditions. Magnitude of cortisol sensitivity is quantified by the Spearman rank correlation between plasma cortisol concentrations and circulating lymphocyte numbers at 2 and 4 months prior to study entry, and monthly afterward during 16 months of differential socialization.
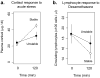
FIGURE 3
(a.) Effect of acute restraint stress on plasma cortisol levels in macaques subject to Stable (dashed line) vs. Unstable social conditions (solid line). (b.) Effect of pharmacologic dexamethasone challenge on circulating lymphocyte numbers in macaques subject to Stable (dashed line) vs. Unstable social conditions (solid line).
Similar articles
- Relationship between social rank and cortisol and testosterone concentrations in male cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).
Czoty PW, Gould RW, Nader MA. Czoty PW, et al. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Jan;21(1):68-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01800.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19094095 Free PMC article. - Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.
Salisbury L, Baraitser L. Salisbury L, et al. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.
Elwenspoek MM, Thom H, Sheppard AL, Keeney E, O'Donnell R, Jackson J, Roadevin C, Dawson S, Lane D, Stubbs J, Everitt H, Watson JC, Hay AD, Gillett P, Robins G, Jones HE, Mallett S, Whiting PF. Elwenspoek MM, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article. - Ceftazidime with avibactam for treating severe aerobic Gram-negative bacterial infections: technology evaluation to inform a novel subscription-style payment model.
Harnan S, Kearns B, Scope A, Schmitt L, Jankovic D, Hamilton J, Srivastava T, Hill H, Ku CC, Ren S, Rothery C, Bojke L, Sculpher M, Woods B. Harnan S, et al. Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(73):1-230. doi: 10.3310/YAPL9347. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487661 Free PMC article. - Pharmacological treatments in panic disorder in adults: a network meta-analysis.
Guaiana G, Meader N, Barbui C, Davies SJ, Furukawa TA, Imai H, Dias S, Caldwell DM, Koesters M, Tajika A, Bighelli I, Pompoli A, Cipriani A, Dawson S, Robertson L. Guaiana G, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):CD012729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012729.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38014714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Interactions of early adversity with stress-related gene polymorphisms impact regional brain structure in females.
Gupta A, Labus J, Kilpatrick LA, Bonyadi M, Ashe-McNalley C, Heendeniya N, Bradesi S, Chang L, Mayer EA. Gupta A, et al. Brain Struct Funct. 2016 Apr;221(3):1667-79. doi: 10.1007/s00429-015-0996-9. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Brain Struct Funct. 2016. PMID: 25630611 Free PMC article. - Salubrious effects of oxytocin on social stress-induced deficits.
Smith AS, Wang Z. Smith AS, et al. Horm Behav. 2012 Mar;61(3):320-30. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.11.010. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Horm Behav. 2012. PMID: 22178036 Free PMC article. Review. - Social regulation of the lymph node transcriptome in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).
Chun K, Capitanio JP, Lamkin DM, Sloan EK, Arevalo JM, Cole SW. Chun K, et al. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017 Feb;76:107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.10.029. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. PMID: 27902946 Free PMC article. - Exploratory Review of the Takotsubo Syndrome and the Possible Role of the Psychosocial Stress Response and Inflammaging.
Frank N, Herrmann MJ, Lauer M, Förster CY. Frank N, et al. Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 31;14(2):167. doi: 10.3390/biom14020167. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397404 Free PMC article. Review. - Laboratory rhesus macaque social housing and social changes: Implications for research.
Hannibal DL, Bliss-Moreau E, Vandeleest J, McCowan B, Capitanio J. Hannibal DL, et al. Am J Primatol. 2017 Jan;79(1):1-14. doi: 10.1002/ajp.22528. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Am J Primatol. 2017. PMID: 26848542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Caspi A, Harrington H, Moffitt TE, Milne BJ, Poulton R. Socially isolated children 20 years later: risk of cardiovascular disease. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160:805–11. - PubMed
- Cohen S, Doyle WJ, Skoner DP, Rabin BS, Gwaltney JM. Social ties and susceptibility to the common cold. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1997;227:1940–1944. - PubMed
- Cole SW, Kemeny ME, Fahey JL, Zack JA, Naliboff BD. Psychological risk factors for HIV pathogenesis: Mediation by the autonomic nervous system. Biological Psychiatry. 2003;54:1444–1456. - PubMed
- Eng PM, Rimm EB, Fitzmaurice G, Kawachi I. Social ties and change in social ties in relation to subsequent total and cause-specific mortality and coronary heart disease incidence in men. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155:700–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR000169/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116778-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MH49033/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH049033/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA024441/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA116778/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116778/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000169/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024441/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical