Coiled-coil interactions are required for post-Golgi R-SNARE trafficking - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Coiled-coil interactions are required for post-Golgi R-SNARE trafficking
David E Gordon et al. EMBO Rep. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
The sorting of post-Golgi R-SNAREs (vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)1, 2, 3, 4, 7 and 8) is still poorly understood. To address this, we developed a system to investigate their localization, trafficking and cell-surface levels. Here, we show that the distribution and internalization of VAMPs 3 and 8 are determined solely through a new conserved mechanism that uses coiled-coil interactions, and that VAMP4 does not require these interactions for its trafficking. We propose that VAMPs 3 and 8 are trafficked while in a complex with Q-SNAREs. We also show that the dileucine motif of VAMP4 is required for both its internalization and retrieval to the trans-Golgi network. However, when the dileucine motif is mutated, the construct can still be internalized potentially through coiled-coil interactions with Q-SNAREs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
Schematic of VAMP-HA constructs. (A) VAMP-HA constructs were generated by two-step PCR (TM, transmembrane domain; HA-serine linker and HA tag). Numbers indicate amino acids positions. The VAMP4 dileucine motif (underlined) was mutated to AA (V4AA). (B) Alignment of the coiled-coil domains of VAMPs 3–8. Conserved hydrophobic residues are highlighted in grey; these residues were mutated to proline to generate the coiled-coil mutants (P). Residues marked with an asterisk were mutated to AA in VAMP3 (ADIA). HA, haemagglutinin; VAMP, vesicle-associated membrane protein.
Figure 2
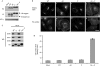
VAMP4 can be internalized through its dileucine motif or its coiled-coil domain. (A) Expression levels of VAMP4-HA constructs were determined by Western blotting. Extracts from HeLa cells stably transduced with empty vector (mock), wild-type (WT) and mutant constructs (AA, P and AA+P) were probed with HA, VAMP4 (V4) and γ antibodies (AP-1, γ was used as a loading control). (B) To determine the steady state localization of the VAMP4-HA constructs, immunofluorescence microscopy was performed on fixed cells stained with HA antibodies. For HA-uptake experiments, cells were incubated in the presence of HA antibodies for 4 h at 37°C before being fixed. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) To measure SNARE complex formation immunoprecipitations (anti-HA) were performed on detergent extracts generated from wild-type and mutant VAMP4-HA cells. Blots were probed with HA, syntaxin (STX) 6, 7 and 8 antibodies. (D) Cell surface levels of VAMP4-HA constructs were measured by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence for each cell population was calculated. The data shown are the average of three experiments, ±s.e. AA, dileucine mutant; HA, haemagglutinin; IP, immunoprecipitation; P, proline mutant coiled-coil; VAMP, vesicle-associated membrane protein; WB, Western blotting.
Figure 3
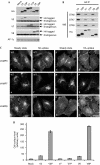
VAMPs 3 and 8 are trafficked through their coiled-coil domains. (A) Expression levels of VAMP-HA constructs were determined by Western blotting. Extracts generated from HeLa cells stably transduced with empty vector (mock), wild-type and proline mutant coiled-coil (P) constructs, were probed with HA, VAMPs 3, 7, 8 and γ antibodies (AP-1, γ was used as a loading control). (B) To measure SNARE complex formation immunoprecipitations (IPs; anti-HA) were performed on detergent extracts generated from wild-type or mutant VAMP-HA cells. Blots were probed with HA, syntaxin (STX) 6, 7 and 8 antibodies. (C) To determine the steady state localization of the VAMP-HA constructs, immunofluorescence microscopy was performed on fixed cells stained with HA antibodies. For HA-uptake experiments, cells were incubated in the presence of HA antibodies for 4 h at 37 °C before being fixed. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Cells surface levels of VAMP-HA constructs were measured by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence for each cell population was calculated. The data shown are the average of three experiments, ±s.e. HA, haemagglutinin; P, proline mutant coiled-coil; VAMP, vesicle-associated membrane protein; WB, Western blotting.
Figure 4
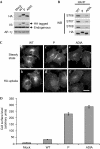
Mutation of VDIM to ADIA in the coiled-coil domain of VAMP3 causes defects in SNARE complex formation and trafficking. (A) Expression levels of VAMP3-HA constructs were determined by Western blotting. Extracts generated from HeLa cells stably transduced with empty vector (mock), wild-type (WT), coiled-coil mutant (P) and 26VDIM29 to 26ADIA29 mutant (ADIA) constructs were probed with HA, VAMP3 and γ antibodies (AP-1, γ was used as a loading control). (B) To measure SNARE complex formation immunoprecipitations (IP; anti-HA) were performed on detergent extracts generated from HeLa cells stably expressing wild-type and mutant VAMP3-HA constructs. Blots were probed with HA, syntaxin (STX) 6, 7 and 8 antibodies. (C) To determine the steady state localization of the VAMP3-HA constructs, immunofluorescence microscopy was performed on fixed cells stained with HA antibodies. For HA-uptake experiments, cells were incubated in the presence of HA antibodies for 4 h at 37 °C before being fixed. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Cells surface levels of VAMP3-HA constructs were measured by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence for each cell population was calculated. The data shown are the average of three experiments, ±s.e. HA, haemagglutinin; P, proline mutant coiled-coil; VAMP, vesicle-associated membrane protein; WB, Western blotting.
Similar articles
- The Q-soluble N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive Factor Attachment Protein Receptor (Q-SNARE) SNAP-47 Regulates Trafficking of Selected Vesicle-associated Membrane Proteins (VAMPs).
Kuster A, Nola S, Dingli F, Vacca B, Gauchy C, Beaujouan JC, Nunez M, Moncion T, Loew D, Formstecher E, Galli T, Proux-Gillardeaux V. Kuster A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 20;290(47):28056-28069. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.666362. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26359495 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive analysis of expression, subcellular localization, and cognate pairing of SNARE proteins in oligodendrocytes.
Feldmann A, Winterstein C, White R, Trotter J, Krämer-Albers EM. Feldmann A, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2009 Jun;87(8):1760-72. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22020. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19185015 - Fusogenic pairings of vesicle-associated membrane proteins (VAMPs) and plasma membrane t-SNAREs--VAMP5 as the exception.
Hasan N, Corbin D, Hu C. Hasan N, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Dec 6;5(12):e14238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014238. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21151919 Free PMC article. - Maintaining order: COG complex controls Golgi trafficking, processing, and sorting.
Blackburn JB, D'Souza Z, Lupashin VV. Blackburn JB, et al. FEBS Lett. 2019 Sep;593(17):2466-2487. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13570. Epub 2019 Aug 16. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31381138 Free PMC article. Review. - Retrograde vesicle transport in the Golgi.
Cottam NP, Ungar D. Cottam NP, et al. Protoplasma. 2012 Oct;249(4):943-55. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0361-7. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 22160157 Review.
Cited by
- The Rhodococcus equi virulence protein VapA disrupts endolysosome function and stimulates lysosome biogenesis.
Rofe AP, Davis LJ, Whittingham JL, Latimer-Bowman EC, Wilkinson AJ, Pryor PR. Rofe AP, et al. Microbiologyopen. 2017 Apr;6(2):e00416. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.416. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Microbiologyopen. 2017. PMID: 27762083 Free PMC article. - BLOC-1 and BLOC-3 regulate VAMP7 cycling to and from melanosomes via distinct tubular transport carriers.
Dennis MK, Delevoye C, Acosta-Ruiz A, Hurbain I, Romao M, Hesketh GG, Goff PS, Sviderskaya EV, Bennett DC, Luzio JP, Galli T, Owen DJ, Raposo G, Marks MS. Dennis MK, et al. J Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 1;214(3):293-308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201605090. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27482051 Free PMC article. - Epsin N-terminal homology domains bind on opposite sides of two SNAREs.
Wang J, Gossing M, Fang P, Zimmermann J, Li X, von Mollard GF, Niu L, Teng M. Wang J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 26;108(30):12277-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013101108. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21746902 Free PMC article. - Reversible assembly and disassembly of V-ATPase during the lysosome regeneration cycle.
Sava I, Davis LJ, Gray SR, Bright NA, Luzio JP. Sava I, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2024 May 1;35(5):ar63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-08-0322. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38446621 Free PMC article. - Tumor protein D54 defines a new class of intracellular transport vesicles.
Larocque G, La-Borde PJ, Clarke NI, Carter NJ, Royle SJ. Larocque G, et al. J Cell Biol. 2020 Jan 6;219(1):e201812044. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201812044. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31672706 Free PMC article.
References
- Grote E, Hao JC, Bennett MK, Kelly RB (1995) A targeting signal in VAMP regulating transport to synaptic vesicles. Cell 81: 581–589 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous