Taste signaling elements expressed in gut enteroendocrine cells regulate nutrient-responsive secretion of gut hormones - PubMed (original) (raw)
Taste signaling elements expressed in gut enteroendocrine cells regulate nutrient-responsive secretion of gut hormones
Zaza Kokrashvili et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Sep.
Abstract
Many of the receptors and downstream signaling elements involved in taste detection and transduction are also expressed in enteroendocrine cells where they underlie the chemosensory functions of the gut. In one well-known example of gastrointestinal chemosensation (the "incretin effect"), it is known that glucose that is given orally, but not systemically, induces secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (the incretin hormones), which in turn regulate appetite, insulin secretion, and gut motility. Duodenal L cells express sweet taste receptors, the taste G protein gustducin, and several other taste transduction elements. Knockout mice that lack gustducin or the sweet taste receptor subunit T1r3 have deficiencies in secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and in the regulation of plasma concentrations of insulin and glucose in response to orally ingested carbohydrate-ie, their incretin effect is dysfunctional. Isolated small intestine and intestinal villi from gustducin null mice displayed markedly defective glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion in response to glucose, indicating that this is a local circuit of sugar detection by intestinal cells followed by hormone secretion from these same cells. Modulating hormone secretion from gut "taste cells" may provide novel treatments for obesity, diabetes, and malabsorption syndromes.
Figures
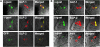
FIGURE 1
A: Indirect immunofluorescence staining of mouse duodenum showing co-expression of _α_-gustducin (_α_-gust) with glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), and GLP-2. Intrinsic fluorescence of green fluorescent protein (GFP) shows the expression of GFP and GLP-2 in the _α_-gustducin-expressing cells of _α_-gustducin–GFP transgenic mice. B: Indirect immunofluorescence of mouse jejunum showing the co-expression of _α_-gustin with GLP-1, GLP-2, and peptide YY (PYY). Bars, 15 _μ_m. Data are modified with permission from reference .
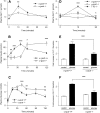
FIGURE 2
Secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) (A) and insulin (B) in response to glucose gavage (5 g/kg body weight) in _α_-gustducin knockout (α-gust−/−) mice and wild-type (α-gust+/+) mice. (C) Postfasting plasma glucose concentrations after feeding standard rodent diet in α-gust−/− mice and α-gust+/+ mice. (D) Secretion of GLP-1 in response to 10% glucose injected into surgically isolated duodenum in α-gust−/− mice, T1r3 knockout (T1r3−/−) mice, and α-gust+/+ mice. The duodenum was ligated away from the stomach and the rest of the intestines, and circulatory contact was maintained. (E) Secretion of GLP-1 ex vivo from minced proximal duodenum from α-gust−/− and α-gust+/+ mice in response to the addition of 10% glucose to the culture medium. (F) Secretion of GLP-1 ex vivo from isolated duodenal villi from α-gust−/− and α-gust+/+ mice in response to the addition of 10% glucose to the culture medium. For in vivo experiments, n = 5–12 animals/genotype; in vitro experiments were carried out in triplicate and replicated at least twice. All values are means ± SEMs. *,**,*** Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are modified with permission from Reference .
Similar articles
- Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1.
Jang HJ, Kokrashvili Z, Theodorakis MJ, Carlson OD, Kim BJ, Zhou J, Kim HH, Xu X, Chan SL, Juhaszova M, Bernier M, Mosinger B, Margolskee RF, Egan JM. Jang HJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 18;104(38):15069-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706890104. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17724330 Free PMC article. - T1r3 and alpha-gustducin in gut regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1.
Kokrashvili Z, Mosinger B, Margolskee RF. Kokrashvili Z, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:91-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04485.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686115 - Mechanisms underlying glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion.
Reimann F, Gribble FM. Reimann F, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):13-9. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12478. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186350 Free PMC article. Review. - Intestinal Gpr17 deficiency improves glucose metabolism by promoting GLP-1 secretion.
Yan S, Conley JM, Reilly AM, Stull ND, Abhyankar SD, Ericsson AC, Kono T, Molosh AI, Kubal CA, Evans-Molina C, Ren H. Yan S, et al. Cell Rep. 2022 Jan 4;38(1):110179. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110179. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 34986353 Free PMC article. - Dietary effects on incretin hormone secretion.
Wu T, Rayner CK, Jones K, Horowitz M. Wu T, et al. Vitam Horm. 2010;84:81-110. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381517-0.00003-5. Vitam Horm. 2010. PMID: 21094897 Review.
Cited by
- Chemosensors in the nose: guardians of the airways.
Tizzano M, Finger TE. Tizzano M, et al. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013 Jan;28(1):51-60. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00035.2012. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23280357 Free PMC article. Review. - Taste Receptors in Upper Airway Innate Immunity.
Carey RM, Lee RJ. Carey RM, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Aug 28;11(9):2017. doi: 10.3390/nu11092017. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31466230 Free PMC article. Review. - Stomach 'tastes' the food and adjusts its emptying: A neurophysiological hypothesis (Review).
Papacocea T, Papacocea R, Rădoi M, Pițuru S, Balan DG. Papacocea T, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2392-2395. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8874. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765721 Free PMC article. Review. - Chronic social defeat stress broadly inhibits gene expression in the peripheral taste system and alters taste responses in mice.
Tu K, Zhou M, Tan JJ, Markos L, Cloud C, Zhou M, Hayashi N, Rawson NE, Margolskee RF, Wang H. Tu K, et al. Physiol Behav. 2024 Mar 1;275:114446. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114446. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Physiol Behav. 2024. PMID: 38128683 - The cell biology of taste.
Chaudhari N, Roper SD. Chaudhari N, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 Aug 9;190(3):285-96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201003144. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20696704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Kinnamon SC, Margolskee RF. Taste transduction Basbaum A, Bushnell M, Smith S, et al., The senses: a comprehensive reference, Vol 4. Amsterdam, Netherlands; Boston, MA: Elsevier, 2008:219–36
- Max M, Shanker YG, Huang L, et al. Tas1r3, encoding a new candidate taste receptor, is allelic to the sweet responsiveness locus Sac. Nat Genet 2001;28:58–63 - PubMed
- Montmayeur JP, Liberles SD, Matsunami H, et al. A candidate taste receptor gene near a sweet taste locus. Nat Neurosci 2001;4:492–8 - PubMed
- Nelson G, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, et al. Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 2001;106:381–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical