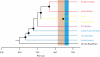Early origin of the bilaterian developmental toolkit - PubMed (original) (raw)
Early origin of the bilaterian developmental toolkit
Douglas H Erwin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009.
Abstract
Whole-genome sequences from the choanoflagellate Monosiga brevicollis, the placozoan Trichoplax adhaerens and the cnidarian Nematostella vectensis have confirmed results from comparative evolutionary developmental studies that much of the developmental toolkit once thought to be characteristic of bilaterians appeared much earlier in the evolution of animals. The diversity of transcription factors and signalling pathway genes in animals with a limited number of cell types and a restricted developmental repertoire is puzzling, particularly in light of claims that such highly conserved elements among bilaterians provide evidence of a morphologically complex protostome-deuterostome ancestor. Here, I explore the early origination of elements of what became the bilaterian toolkit, and suggest that placozoans and cnidarians represent a depauperate residue of a once more diverse assemblage of early animals, some of which may be represented in the Ediacaran fauna (c. 585-542 Myr ago).
Figures
Figure 1.
A phylogenetic tree for metazoans scaled against the molecular clock dates of Peterson et al. (2008). The ages of nodes are well calibrated by the molecular clock results of Peterson et al. and are shown as black boxes.
Figure 2.
Ediacaran fossils mentioned in the text. (a) Fracofusus from Mistaken Point, Newfoundland, 14 cm. (b) Rangea from southern Namibia; 5 cm. (c) Kimberella from White Sea, Russia; anterior to right, with the anterior elongation, 9 cm. (d) Yorgia from the White Sea, Russia; anterior (?) up, about 18 cm. (e) Ernietta from southern Namibia, approximately 15 cm. (f) Dickinsonia from Ediacaran Hills, south Australia, 6 cm.
Similar articles
- Early evolution of the LIM homeobox gene family.
Srivastava M, Larroux C, Lu DR, Mohanty K, Chapman J, Degnan BM, Rokhsar DS. Srivastava M, et al. BMC Biol. 2010 Jan 18;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-4. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 20082688 Free PMC article. - Evolution of the perlecan/HSPG2 gene and its activation in regenerating Nematostella vectensis.
Warren CR, Kassir E, Spurlin J, Martinez J, Putnam NH, Farach-Carson MC. Warren CR, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0124578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124578. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25876075 Free PMC article. - Origin of animal epithelia: insights from the sponge genome.
Fahey B, Degnan BM. Fahey B, et al. Evol Dev. 2010 Nov-Dec;12(6):601-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2010.00445.x. Evol Dev. 2010. PMID: 21040426 - The enigmatic Placozoa part 2: Exploring evolutionary controversies and promising questions on earth and in space.
Schierwater B, Osigus HJ, Bergmann T, Blackstone NW, Hadrys H, Hauslage J, Humbert PO, Kamm K, Kvansakul M, Wysocki K, DeSalle R. Schierwater B, et al. Bioessays. 2021 Oct;43(10):e2100083. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100083. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 34490659 Review. - The enigmatic Placozoa part 1: Exploring evolutionary controversies and poor ecological knowledge.
Schierwater B, Osigus HJ, Bergmann T, Blackstone NW, Hadrys H, Hauslage J, Humbert PO, Kamm K, Kvansakul M, Wysocki K, DeSalle R. Schierwater B, et al. Bioessays. 2021 Oct;43(10):e2100080. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100080. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 34472126 Review.
Cited by
- Stem cell differentiation trajectories in Hydra resolved at single-cell resolution.
Siebert S, Farrell JA, Cazet JF, Abeykoon Y, Primack AS, Schnitzler CE, Juliano CE. Siebert S, et al. Science. 2019 Jul 26;365(6451):eaav9314. doi: 10.1126/science.aav9314. Science. 2019. PMID: 31346039 Free PMC article. - Head transcriptome profiling of glossiphoniid leech (Helobdella austinensis) reveals clues about proboscis development.
Kwak HJ, Lee SG, Park SC, Kim JH, Weisblat DA, Park C, Cho SJ. Kwak HJ, et al. Open Biol. 2022 Mar;12(3):210298. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210298. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 35232253 Free PMC article. - Global marine redox changes drove the rise and fall of the Ediacara biota.
Zhang F, Xiao S, Romaniello SJ, Hardisty D, Li C, Melezhik V, Pokrovsky B, Cheng M, Shi W, Lenton TM, Anbar AD. Zhang F, et al. Geobiology. 2019 Nov;17(6):594-610. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12359. Epub 2019 Jul 28. Geobiology. 2019. PMID: 31353777 Free PMC article. - Transposon-derived transcription factors across metazoans.
Mukherjee K, Moroz LL. Mukherjee K, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 7;11:1113046. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1113046. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36960413 Free PMC article. - Metazoan opsin evolution reveals a simple route to animal vision.
Feuda R, Hamilton SC, McInerney JO, Pisani D. Feuda R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 13;109(46):18868-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204609109. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23112152 Free PMC article.
References
- Adamska M., Degnan S. M., Green K. M., Adamski M., Craigie A., Larroux C., Degnan B. M.2007Wnt and TGF-beta expression in the sponge Amphimedon queenslandica and the origin of metazoan embryonic patterning. PLoS ONE 2, e1031 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001031) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Arendt D., Nubler-Jung K.1994Inversion of dorso-ventral axis. Nature 371, 26 (doi:10.1038/371026a0) - DOI - PubMed
- Arendt D., Nubler-Jung K.1999Comparison of early nerve cord development in insects and vertebrates. Development 126, 2309–2325 - PubMed
- Arendt D., Technau U., Wittbrodt J.2001Evolution of the bilateria larval foregut. Nature 409, 81–85 (doi:10.1038/35051075) - DOI - PubMed
- Arendt D., Tessmar-Raible K., Snyman H., Dorresteijn A., Wittbrodt J.2004Ciliary photoreceptors with a vertebrate-type opsin in an invertebrate brain. Science 306, 869–871 (doi:10.1126/science.1099955) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources