Deacetylase inhibition increases regulatory T cell function and decreases incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Deacetylase inhibition increases regulatory T cell function and decreases incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis
Sandra J Saouaf et al. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009 Oct.
Abstract
Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) is an established mouse model of disease with hallmarks of clinical rheumatoid arthritis. Histone/protein deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are known to inhibit the pathogenesis of CIA and other models of autoimmune disease, although the mechanisms responsible are unclear. Regulatory T cell (Treg) function is defective in rheumatoid arthritis. FOXP3 proteins in Tregs are present in a dynamic protein complex containing histone acetyltransferase and HDAC enzymes, and FOXP3 itself is acetylated on lysine residues. We therefore investigated the effects of HDACi therapy on regulatory T cell function in the CIA model. Administration of an HDACi, valproic acid (VPA), significantly decreased disease incidence (p<0.005) and severity (p<0.03) in CIA. In addition, VPA treatment increased both the suppressive function of CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs (p<0.04) and the numbers of CD25(+)FOXP3(+) Tregs in vivo. Hence, clinically approved HDACi such as VPA may limit autoimmune disease in vivo through effects on the production and function of FOXP3(+) Treg cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
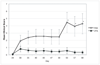
Mean clinical disease score of CIA-induced mice treated with PBS or VPA. CIA was induced in DBA/1 mice as described in materials and methods. VPA (400mg/kg) or PBS was administered daily starting on day 21 and clinical disease was scored every 2–3 days starting on day 21 of the study with a score of 0–16 possible for each mouse. Values shown are mean clinical score +/− SEM. Data from representative experiment are shown with PBS n=11 and VPA n=9. * p< 0.04 in two-tailed t-test.
Figure 2
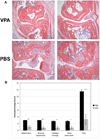
Histopathology of the proximal interphalangeal joints of CIA-induced mice. A. Photomicrographs are H&E-stained paraffin sections (original magnifications ×0) of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints of CIA-induced mice from day 60 of the study. Sections from VPA-treated mice show well-preserved PIP joints with negligible inflammation, synovial hypertrophy, cartilage damage or bone destruction (top). Sections from control PBS-treated mice show severe arthritis, marked erosion of articular surfaces, cartilage breakdown, synovial hypertrophy and inflammatory cell infiltration (bottom). B. Histopathologic score of PIP joint sections from CIA-induced mice using a standard 0–3 histologic scale (0/normal, 1/mild, 2/moderate, 3/severe) for each of 4 points: inflammation, synovial hypertrophy, cartilage damage and bone destruction. Data are shown as the mean histopathology score ± SEM. Statistical evaluation using a two-tailed t-test revealed **p<0.003, *p<0.015 as indicated.
Figure 3
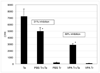
Regulatory T cells from VPA-treated CIA-induced mice have improved function. CD25+CD4+ Treg cells were purified on day 60 of the study from splenocytes of CIA-induced mice treated with VPA or PBS as described in material and methods and were co-cultured with CD25−CD4+ T effector cells from naïve mice at a 1:2 ratio of Treg : Teff on anti-CD3ε mAb coated plates (1µg/ml anti-CD3ε mAb) for 72 hrs. Teff and T reg cells were also cultured separately as shown. Proliferative response was measured by incorporation of tritiated thymidine during the last 12–18 hours of culture. Mean CPM are shown +/− SEM, *p<0.04 in two-tailed t-test. Percent inhibition is calculated as 100 – [(CPM PBS or CPM VPA/CPM control)*100], where control is culture containing T effector cells only.
Figure 4
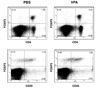
Flow cytometric analysis of splenocytes from CIA-induced mice treated with PBS or VPA. Representative dot plots of splenocytes isolated on day 60 of the study from PBS or VPA treated CIA-induced mice stained for cell surface CD4, CD25 and intracellular FOXP3 are shown.
Figure 5
Immunoperoxidase staining of PIP joints and adjacent synovial tissue of CIA-induced mice. (a, b) Decreased recruitment of host leukocytes, as reflected in staining for the leukocyte-common antigen, CD45, in joints harvested from CIA-induced mice on day 60 of the study receiving VPA therapy. (c, d) VPA induced a marked increase in nuclear staining for acetylated lysine within the joints and associated tissues. Arrows indicate examples of positively-stained nuclei. (e, f) Inflamed joints of PBS-treated mice lacked infiltration by FOXP3+ cells, whereas VPA therapy was associated with recruitment of FOXP3+ mononuclear cells to peri-articular tissues (arrows). (Hematoxylin-counterstained paraffin sections, ×250 original magnifications, representative of data from analysis of 4 paws/group).
Similar articles
- Therapeutic effect of a novel histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor, CKD-L, on collagen-induced arthritis in vivo and regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis in vitro.
Oh BR, Suh DH, Bae D, Ha N, Choi YI, Yoo HJ, Park JK, Lee EY, Lee EB, Song YW. Oh BR, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Jul 3;19(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1357-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28673326 Free PMC article. - IL-2-Anti-IL-2 Monoclonal Antibody Immune Complexes Inhibit Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Augmenting Regulatory T Cell Functions.
Yokoyama Y, Iwasaki T, Kitano S, Satake A, Nomura S, Furukawa T, Matsui K, Sano H. Yokoyama Y, et al. J Immunol. 2018 Oct 1;201(7):1899-1906. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701502. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30143591 - Efficient Therapeutic Function and Mechanisms of Human Polyclonal CD8+CD103+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice.
Sun J, Yang Y, Huo X, Zhu B, Li Z, Jiang X, Xie R, Gao L, Sun Y, Fan H, Zhu Y, Yang J. Sun J, et al. J Immunol Res. 2019 Feb 19;2019:8575407. doi: 10.1155/2019/8575407. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30915372 Free PMC article. - Histone deacetylase inhibitors and transplantation.
Tao R, de Zoeten EF, Ozkaynak E, Wang L, Li B, Greene MI, Wells AD, Hancock WW. Tao R, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Oct;19(5):589-95. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.015. Epub 2007 Aug 24. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17719760 Free PMC article. Review. - Histone/protein deacetylase inhibitor therapy for enhancement of Foxp3+ T-regulatory cell function posttransplantation.
Wang L, Beier UH, Akimova T, Dahiya S, Han R, Samanta A, Levine MH, Hancock WW. Wang L, et al. Am J Transplant. 2018 Jul;18(7):1596-1603. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14749. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Am J Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29603600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Histone deacetylases as targets for treatment of multiple diseases.
Tang J, Yan H, Zhuang S. Tang J, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Jun;124(11):651-62. doi: 10.1042/CS20120504. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23414309 Free PMC article. Review. - Molecular targets related to inflammation and insulin resistance and potential interventions.
Hirabara SM, Gorjão R, Vinolo MA, Rodrigues AC, Nachbar RT, Curi R. Hirabara SM, et al. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:379024. doi: 10.1155/2012/379024. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23049242 Free PMC article. Review. - Immunomodulatory effects of deacetylase inhibitors: therapeutic targeting of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells.
Wang L, de Zoeten EF, Greene MI, Hancock WW. Wang L, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Dec;8(12):969-81. doi: 10.1038/nrd3031. Epub 2009 Oct 26. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009. PMID: 19855427 Free PMC article. Review. - The emerging spectrum of early life exposure-related inflammation and epigenetic therapy.
Yang Q, Ali M, El Andaloussi A, Al-Hendy A. Yang Q, et al. Cancer Stud Mol Med. 2018 Nov;4(1):13-23. doi: 10.17140/CSMMOJ-4-125. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Cancer Stud Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30474062 Free PMC article. - Immune regulation by histone deacetylases: a focus on the alteration of FOXP3 activity.
Zhang H, Xiao Y, Zhu Z, Li B, Greene MI. Zhang H, et al. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;90(1):95-100. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.101. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22124370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Camelo S, Iglesias AH, Hwang D, Due B, Ryu H, Smith K, Gray SG, Imitola J, Duran G, Assaf B, Langley B, Khoury SJ, Stephanopoulos G, De Girolami U, Ratan RR, Ferrante RJ, Dangond F. Transcriptional therapy with the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2005;164:10–21. - PubMed
- Chung YL, Lee MY, Wang AJ, Yao LF. A therapeutic strategy uses histone deacetylase inhibitors to modulate the expression of genes involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Ther. 2003;8:707–717. - PubMed
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials