TIMP3 is reduced in atherosclerotic plaques from subjects with type 2 diabetes and increased by SirT1 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Oct;58(10):2396-401.
doi: 10.2337/db09-0280. Epub 2009 Jul 6.
Rossella Menghini, Eugenio Martelli, Viviana Casagrande, Arianna Marino, Stefano Rizza, Ottavia Porzio, Alessandro Mauriello, Anna Solini, Arnaldo Ippoliti, Renato Lauro, Franco Folli, Massimo Federici
Affiliations
- PMID: 19581416
- PMCID: PMC2750223
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0280
TIMP3 is reduced in atherosclerotic plaques from subjects with type 2 diabetes and increased by SirT1
Marina Cardellini et al. Diabetes. 2009 Oct.
Abstract
Objective: Atherosclerosis is accelerated in subjects with type 2 diabetes by unknown mechanisms. We identified tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3), the endogenous inhibitor of A disintegrin and metalloprotease domain 17 (ADAM17) and other matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), as a gene modifier for insulin resistance and vascular inflammation in mice. We tested its association with atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes and identified Sirtuin 1 (SirT1) as a major regulator of TIMP3 expression.
Research design and methods: We investigated ADAM10, ADAM17, MMP9, TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 expression levels in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques (n = 60) from subjects with and without diabetes. Human vascular smooth muscle cells exposed to several metabolic stimuli were used to identify regulators of TIMP3 expression. SirT1 small interference RNA, cDNA, and TIMP3 promoter gene reporter were used to study SirT1-dependent regulation of TIMP3.
Results: Here, we show that in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques, TIMP3 was significantly reduced in subjects with type 2 diabetes, leading to ADAM17 and MMP9 overactivity. Reduced expression of TIMP3 was associated in vivo with SirT1 levels. In smooth muscle cells, inhibition of SirT1 activity and levels reduced TIMP3 expression, whereas SirT1 overexpression increased TIMP3 promoter activity.
Conclusions: In atherosclerotic plaques from subjects with type 2 diabetes, the deregulation of ADAM17 and MMP9 activities is related to inadequate expression of TIMP3 via SirT1. Studies in vascular cells confirmed the role of SirT1 in tuning TIMP3 expression.
Figures
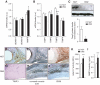
FIG. 1.
TIMP3 is reduced in atherosclerotic plaques of subjects with type 2 diabetes (DM2). ADAM10, ADAM17, and MMP9 (A) as well as TIMPs (B) expression in NGT (n = 37) and type 2 diabetes (n = 23) subjects; ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. C: Western blot using extracellular matrix extracts from representative NGT (n = 2) and type 2 diabetic (n = 4) subjects. *P < 0.05 NGT vs. type 2 diabetes by Student's t test. D–J: Immunohistochemistry confirmed that TIMP3 is reduced in type 2 diabetic (n = 8) versus NGT (n = 8) subjects; one representative image is shown for TIMP3, anti–α smooth muscle actin, and CD68 for NGT (D–F; 4× magnification) and type 2 diabetic (G–J; 4× magnification) subjects. K and I: ADAM17 activity measured by a fluorimetric assay (K) and MMP9 activity measured by a fluorimetric assay (I) are increased in type 2 diabetic (n = 23) compared with NGT (n = 37) subjects; ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test for both. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)
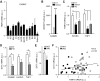
FIG. 2.
Effects of diabetes on TIMP3 expression in vascular cells. A: TIMP3 expression in CASMC treated with various metabolic stimuli: high glucose (HG) 20 mmol/l; mannitol (Man) 20 mmol/l; insulin (Ins) 10−7 M; LDL 100 μg/ml; oxidized LDL (oxLDL) 100 μg/ml; glycated LDL (glyLDL) 100 μg/ml; LXR agonists (T0901317 [T090] 5 μmol/l; GW3965 [GW] 3 μmol/l; R-hydroxycholesterol [RH] 10 μmol/l; 22-S-hydroxycholesterol [SH] 10 μmol/l); SirT1 inhibitor (Sirtinol) 50 μmol/l. n = 4 for all experiments; *P < 0.05 by Student's t test versus control (CT). B: Sirtinol increased ADAM17 activity in CASMC. n = 4 for all experiments; ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test. C: TIMP3 expression in HUVEC and THP1 treated with Sirtinol and high glucose (20 mmol/l). n = 4 for all experiments; *P < 0.05 by Student's t test versus control. D: SirT1 expression is reduced in CASMC, HUVEC, and THP1 treated with high glucose (20 mmol/l) compared with control. n = 4 for all experiments; *P < 0.05 by Student's t test. E: SirT1 levels are decreased in type 2 diabetic compared with NGT subjects. *P < 0.05 by Student's t test. F: SirT1 correlates with TIMP3 in atherosclerotic plaques from NGT (n = 37) and type 2 diabetic (DM2) (n = 23) subjects.
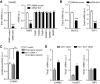
FIG. 3.
Regulation of TIMP3 expression in CASMC. A: SirT1 knockdown decreased TIMP3 expression but not TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP4, ADAM10, ADAM17, or MMP9 in CASMC. n = 4 for all experiments; ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test versus control. B: SirT1 knockdown decreased TIMP3 expression in HUVEC and THP1. n = 4 for all experiments; ***P < 0.001 by Student's t test. C: SirT1 cDNA overexpression increased Timp3 promoter activity. n = 4 for all experiments; **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. D: SirT1 overexpression increased and prevented loss of TIMP3 expression caused by high glucose (HG; 20 mmol/l) in CASMC, HUVEC, and THP1. n = 4 for all experiments; *P < 0.05 by Student's t test.
Similar articles
- SIRT1 mediates the inflammatory response of macrophages and regulates the TIMP3/ADAM17 pathway in atherosclerosis.
Jia D, Ping W, Wang M, Wang D, Zhang L, Cao Y. Jia D, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2024 Oct 1;442(2):114253. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114253. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39271099 - Advanced glycation endproducts induce fibrogenic activity in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating TNF-α-converting enzyme activity in mice.
Jiang JX, Chen X, Fukada H, Serizawa N, Devaraj S, Török NJ. Jiang JX, et al. Hepatology. 2013 Oct;58(4):1339-48. doi: 10.1002/hep.26491. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23703665 Free PMC article. - Impaired regulation of the TNF-alpha converting enzyme/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 proteolytic system in skeletal muscle of obese type 2 diabetic patients: a new mechanism of insulin resistance in humans.
Monroy A, Kamath S, Chavez AO, Centonze VE, Veerasamy M, Barrentine A, Wewer JJ, Coletta DK, Jenkinson C, Jhingan RM, Smokler D, Reyna S, Musi N, Khokka R, Federici M, Tripathy D, DeFronzo RA, Folli F. Monroy A, et al. Diabetologia. 2009 Oct;52(10):2169-81. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1451-3. Epub 2009 Jul 25. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19633828 Free PMC article. - Pathology of Human Coronary and Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis and Vascular Calcification in Diabetes Mellitus.
Yahagi K, Kolodgie FD, Lutter C, Mori H, Romero ME, Finn AV, Virmani R. Yahagi K, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Feb;37(2):191-204. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.306256. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27908890 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of ADAM17 in metabolic inflammation.
Menghini R, Fiorentino L, Casagrande V, Lauro R, Federici M. Menghini R, et al. Atherosclerosis. 2013 May;228(1):12-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.01.024. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Atherosclerosis. 2013. PMID: 23384719 Review.
Cited by
- Epigenetic protein families: a new frontier for drug discovery.
Arrowsmith CH, Bountra C, Fish PV, Lee K, Schapira M. Arrowsmith CH, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Apr 13;11(5):384-400. doi: 10.1038/nrd3674. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22498752 Review. - The Sirtuin System: The Holy Grail of Resveratrol?
Mohar DS, Malik S. Mohar DS, et al. J Clin Exp Cardiolog. 2012 Nov;3(11):216. doi: 10.4172/2155-9880.1000216. J Clin Exp Cardiolog. 2012. PMID: 23560248 Free PMC article. - PPARγ population shift produces disease-related changes in molecular networks associated with metabolic syndrome.
Jurkowski W, Roomp K, Crespo I, Schneider JG, Del Sol A. Jurkowski W, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2011 Aug 11;2(8):e192. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.74. Cell Death Dis. 2011. PMID: 21833030 Free PMC article. - Role of protein carbonylation in diabetes.
Hecker M, Wagner AH. Hecker M, et al. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 Jan;41(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0104-9. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018. PMID: 29110177 Review. - SIRT1: new avenues of discovery for disorders of oxidative stress.
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Wang S, Maiese K. Chong ZZ, et al. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 Feb;16(2):167-78. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.648926. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012. PMID: 22233091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P: Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 2002;287:2570–2581 - PubMed
- Kanter JE, Johansson F, LeBoeuf RC, Bornfeldt KE: Do glucose and lipids exert independent effects on atherosclerotic lesion initiation or progression to advanced plaques? Circ Res 2007;100:769–781 - PubMed
- Uemura S, Matsushita H, Li W, Glassford AJ, Asagami T, Lee KH, Harrison DG, Tsao PS: Diabetes mellitus enhances vascular matrix metalloproteinase activity: role of oxidative stress. Circ Res 2001;88:1291–1298 - PubMed
- Federici M, Menghini R, Mauriello A, Hribal ML, Ferrelli F, Lauro D, Sbraccia P, Spagnoli LG, Sesti G, Lauro R: Insulin-dependent activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is impaired by O-linked glycosylation modification of signaling proteins in human coronary endothelial cells. Circulation 2002;106:466–472 - PubMed
- Chung AW, Hsiang YN, Matzke LA, McManus BM, van Breemen C, Okon EB: Reduced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor paralleled with the increased angiostatin expression resulting from the upregulated activities of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human type 2 diabetic arterial vasculature. Circ Res 2006;99:140–148 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous