Pathogenesis of tendinopathies: inflammation or degeneration? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Pathogenesis of tendinopathies: inflammation or degeneration?
Michele Abate et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009.
Abstract
The intrinsic pathogenetic mechanisms of tendinopathies are largely unknown and whether inflammation or degeneration has the prominent role is still a matter of debate. Assuming that there is a continuum from physiology to pathology, overuse may be considered as the initial disease factor; in this context, microruptures of tendon fibers occur and several molecules are expressed, some of which promote the healing process, while others, including inflammatory cytokines, act as disease mediators. Neural in-growth that accompanies the neovessels explains the occurrence of pain and triggers neurogenic-mediated inflammation. It is conceivable that inflammation and degeneration are not mutually exclusive, but work together in the pathogenesis of tendinopathies.
Figures
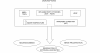
Figure 1
Mechanisms of damage. EGF, epidermal growth factor; HIF, hypoxia inducible factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
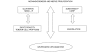
Figure 2
From neovascularization to neurogenic inflammation. CGRP, Calcitonin gene related peptide; NMDA-R, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor.
Figure 3
The iceberg theory.
Similar articles
- A systematic review of inflammatory cells and markers in human tendinopathy.
Jomaa G, Kwan CK, Fu SC, Ling SK, Chan KM, Yung PS, Rolf C. Jomaa G, et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Feb 6;21(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-3094-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32028937 Free PMC article. - Inflammation in tendinopathy.
D'Addona A, Maffulli N, Formisano S, Rosa D. D'Addona A, et al. Surgeon. 2017 Oct;15(5):297-302. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Surgeon. 2017. PMID: 28596062 Review. - Alarmins in tendinopathy: unravelling new mechanisms in a common disease.
Millar NL, Murrell GA, McInnes IB. Millar NL, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013 May;52(5):769-79. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes409. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013. PMID: 23362223 Review. - PRP Treatment Efficacy for Tendinopathy: A Review of Basic Science Studies.
Zhou Y, Wang JH. Zhou Y, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9103792. doi: 10.1155/2016/9103792. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27610386 Free PMC article. Review. - Cytokines and apoptosis in supraspinatus tendinopathy.
Millar NL, Wei AQ, Molloy TJ, Bonar F, Murrell GA. Millar NL, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009 Mar;91(3):417-24. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.91B3.21652. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. PMID: 19258623
Cited by
- Correlation between the Long Head of the Biceps Microscopic Degeneration and Extent of Apoptotic Process.
Jaworski Ł, Zabrzyński J, Millett PJ, Rupp MC, Familiari F, Huri G, Erdmann J, Błachowski M, Pękala P, Gagat M. Jaworski Ł, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 2;13(15):4520. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154520. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124786 Free PMC article. - Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of a New Mixture of Vitamin C, Collagen Peptides, Resveratrol, and Astaxanthin in Tenocytes: Molecular Basis for Future Applications in Tendinopathies.
Marzagalli M, Battaglia S, Raimondi M, Fontana F, Cozzi M, Ranieri FR, Sacchi R, Curti V, Limonta P. Marzagalli M, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Jul 30;2024:5273198. doi: 10.1155/2024/5273198. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 39108992 Free PMC article. - The Biological Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Rotator Cuff Tears: A Prospective Randomized In Vivo Study.
Pitsilos C, Karachrysafi S, Fragou A, Gigis I, Papadopoulos P, Chalidis B. Pitsilos C, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7957. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147957. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063199 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Diagnostic Value of Superb Microvascular Imaging of the Rotator Cuff Interval for the Early Diagnosis of Frozen Shoulder.
Xu W, Xu J, Zhou Y, Yang W, Huang H, Xue J, Zhang J. Xu W, et al. Int J Gen Med. 2024 Jul 10;17:3039-3046. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S465952. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39006912 Free PMC article. - The Efficacy of Intratissue Percutaneous Electrolysis (EPI®) and Nutritional Factors for the Treatment of Induced Tendinopathy in Wistar Rats: Hepatic Intermediary Metabolism Effects.
Ramos-Barbero M, Pérez-Jiménez A, Serrano-Carmona S, Mokhtari K, Lupiáñez JA, Rufino-Palomares EE. Ramos-Barbero M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 3;25(13):7315. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137315. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000426 Free PMC article.
References
- Bamji AN, Dieppe PA, Haslock DI, Shipley ME. What do rheumatologists do? A pilot audit study. Br J Rheumatol. 1990;29:295–298. - PubMed
- Alfredson H, Ljung BO, Thorsen K, Lorentzon R. In vivo investigation of ECRB tendons with microdialysis technique – no signs of inflammation but high amounts of glutamate in tennis elbow. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:475–479. - PubMed
- Alfredson H, Forsgren S, Thorsen K, Lorentzon R. In vivo microdialysis and immunohistochemical analyses of tendon tissue demonstrated high amounts of free glutamate and glutamate NMDAR1 receptors, but no signs of inflammation, in Jumper's knee. J Orthop Res. 2001;19:881–886. - PubMed
- Maffulli N, Khan KM, Puddu G. Overuse tendon conditions: time to change a confusing terminology. Arthroscopy. 1998;14:840–843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical