Diffusion tensor imaging in cocaine dependence: regional effects of cocaine on corpus callosum and effect of cocaine administration route - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Diffusion tensor imaging in cocaine dependence: regional effects of cocaine on corpus callosum and effect of cocaine administration route
Liangsuo Ma et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009.
Abstract
Recent studies demonstrated that diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can provide information regarding white matter integrity of the corpus callosum (CC). In this study, DTI parameters were compared between cocaine dependent subjects (CDs) and non-drug using controls (NCs) in midsagittal CC. DTI images were acquired from 19 CDs and 18 age-matched NCs. The midsagittal CC was segmented into: genu, rostral body, anterior midbody, posterior midbody, isthmus, and splenium. Linear mixed models analyses showed that, relative to NCs, CDs had lower fractional anisotropy (FA), higher radial diffusivity (lambda(perpendicular)), and higher mean diffusivity (D(av)) in the isthmus; higher lambda(perpendicular) and D(av) in the rostral body; and lower FA in the splenium. After including mass of lifetime alcohol use in the mixed model analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) as a covariate, significant between group differences in lambda(perpendicular) in the rostral body and isthmus remained. These results suggest that alterations in lambda(perpendicular) in the rostral body and isthmus were mainly due to cocaine use, consistent with previous studies showing that cocaine may alter myelin integrity. Between group differences in FA in the isthmus and splenium, and D(av) in the rostral body and isthmus became non-significant after inclusion of alcohol use as a covariate. This is suggestive of alcohol influencing these values, or may be related to the decreased degrees of freedom for these effects. Consistent with clinical data of greater severity of drug use in smoked versus intranasal cocaine, subjects who smoked cocaine showed lower FA and higher lambda(perpendicular) compared to intranasal CDs.
Figures
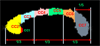
Fig. 1
Illustration of the DTI-based parcellation of the 7 subregions of the human corpus callosum. The magnified seven subregions of the midsagittal CC were based on the semi-automated DTI implementation of the Witelson (1989) geometric CC subdivisions. CC1 = rostrum; CC2 = genu; CC3 = rostral body; CC4 = anterior midbody; CC5 = posterior midbody; CC6 = isthmus; CC7 = splenium.
Similar articles
- Diffusion tensor imaging eigenvalues: preliminary evidence for altered myelin in cocaine dependence.
Moeller FG, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Kramer LA, Valdes I, Lai LY, Swann AC, Narayana PA. Moeller FG, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2007 Apr 15;154(3):253-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.11.004. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Psychiatry Res. 2007. PMID: 17321725 - Reduced anterior corpus callosum white matter integrity is related to increased impulsivity and reduced discriminability in cocaine-dependent subjects: diffusion tensor imaging.
Moeller FG, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Kramer LA, Dougherty DM, Santos RM, Valdes I, Swann AC, Barratt ES, Narayana PA. Moeller FG, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Mar;30(3):610-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300617. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15637640 - Altered white matter in cocaine-dependent subjects with traumatic brain injury: A diffusion tensor imaging study.
Ma L, Steinberg JL, Keyser-Marcus L, Ramesh D, Narayana PA, Merchant RE, Moeller FG, Cifu DX. Ma L, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Jun 1;151:128-34. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 25841982 Free PMC article. - Diffusion tensor imaging of cocaine-treated rodents.
Narayana PA, Ahobila-Vajjula P, Ramu J, Herrera J, Steinberg JL, Moeller FG. Narayana PA, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2009 Mar 31;171(3):242-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.04.004. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Psychiatry Res. 2009. PMID: 19217266 Free PMC article. - Longitudinal study of callosal microstructure in the normal adult aging brain using quantitative DTI fiber tracking.
Sullivan EV, Rohlfing T, Pfefferbaum A. Sullivan EV, et al. Dev Neuropsychol. 2010;35(3):233-56. doi: 10.1080/87565641003689556. Dev Neuropsychol. 2010. PMID: 20446131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Enhanced dopamine D1 and BDNF signaling in the adult dorsal striatum but not nucleus accumbens of prenatal cocaine treated mice.
Tropea TF, Kabir ZD, Kaur G, Rajadhyaksha AM, Kosofsky BE. Tropea TF, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2011 Dec 7;2:67. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00067. eCollection 2011. Front Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22162970 Free PMC article. - Diffusion tensor imaging and decision making in cocaine dependence.
Lane SD, Steinberg JL, Ma L, Hasan KM, Kramer LA, Zuniga EA, Narayana PA, Moeller FG. Lane SD, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Jul 16;5(7):e11591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011591. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20661285 Free PMC article. - Regionally-specific alterations in myelin proteins in nonhuman primate white matter following prolonged cocaine self-administration.
Smith HR, Beveridge TJ, Nader MA, Porrino LJ. Smith HR, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014 Apr 1;137:143-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.01.015. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014. PMID: 24529965 Free PMC article. - Chronic cocaine administration causes extensive white matter damage in brain: diffusion tensor imaging and immunohistochemistry studies.
Narayana PA, Herrera JJ, Bockhorst KH, Esparza-Coss E, Xia Y, Steinberg JL, Moeller FG. Narayana PA, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2014 Mar 30;221(3):220-30. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Psychiatry Res. 2014. PMID: 24507117 Free PMC article. - PPAR-gamma agonist pioglitazone modifies craving intensity and brain white matter integrity in patients with primary cocaine use disorder: a double-blind randomized controlled pilot trial.
Schmitz JM, Green CE, Hasan KM, Vincent J, Suchting R, Weaver MF, Moeller FG, Narayana PA, Cunningham KA, Dineley KT, Lane SD. Schmitz JM, et al. Addiction. 2017 Oct;112(10):1861-1868. doi: 10.1111/add.13868. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Addiction. 2017. PMID: 28498501 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Fisher RS, Zaidel E. Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res. 1992;598:143–153. - PubMed
- Anderson CM, Maas LC, Frederick B, Bendor JT, Spencer TJ, Livni E, Lukas SE, Fischman AJ, Madras BK, Renshaw PF, Kaufman MJ. Cerebellar vermis involvement in cocaine-related behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:1318–1326. - PubMed
- Arnone D, Barrick TR, Chengappa S, Mackay CE, Clark CA, Abou-Saleh MT. Corpus callosum damage in heavy marijuana use: preliminary evidence from diffusion tensor tractography and tract-based spatial statistics. Neuroimage. 2008;41:1067–1074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K02 DA000403/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-120006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-11A10006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-14/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-149001/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-159001/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052505-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-150006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-01A2/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-05/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-07/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-15/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-04/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-140006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-02/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-130006/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA00403/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009262-13/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-08/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA000403-06A2/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical