The opposing roles of Wnt-5a in cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The opposing roles of Wnt-5a in cancer
S L McDonald et al. Br J Cancer. 2009.
Abstract
Wnt-5a is one of the most highly investigated non-canonical Wnts and has been implicated in almost all aspects of non-canonical Wnt signalling. In terms of cancer development, Wnt-5a has, until recently, lived in the shadow of its better-characterised relatives. This was largely because of its apparent inability to transform cells or signal through the canonical beta-catenin pathway that is so important in cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. Recent work in a wide range of human tumours has pointed to a critical role for Wnt-5a in malignant progression, but there is conflicting evidence whether Wnt-5a has a tumour-promoting or -suppressing role. Emerging evidence suggests that the functions of Wnt-5a can be drastically altered depending on the availability of key receptors. Hence, the presence or absence of these receptors may go some way to explain the conflicting role of Wnt-5a in different cancers. This review summarises our current understanding of Wnt-5a and cancer.
Figures
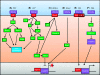
Figure 1
An overview of Wnt-5a signalling. (A) Wnt-5a can activate PCP through a process dependent on Roh A and possibly Roh B leading to the control of cellular movement. (B) Wnt-5a uses numerous signalling molecules leading to the release of Ca2+ resulting in various cellular effects including cell movement and inhibition of the canonical Wnt signalling pathway. (C) Wnt-5a can bind the ROR-2 receptor activating JNK and the cytoskeleton as well as inhibiting _β_-catenin/TCF dependent transcription. (D) Wnt-5a can inhibit _β_-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription through Shia-1. (E) In the presence of FZ4 and LRP-5, Wnt-5a can activate _β_-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription. (F) Wnt-5a can activate PKA, which in turn can inhibit GSK-β to promote _β_-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription. Figure adapted from Semenov et al (2007).
Similar articles
- Wnt5a and Wnt11 interact in a maternal Dkk1-regulated fashion to activate both canonical and non-canonical signaling in Xenopus axis formation.
Cha SW, Tadjuidje E, Tao Q, Wylie C, Heasman J. Cha SW, et al. Development. 2008 Nov;135(22):3719-29. doi: 10.1242/dev.029025. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Development. 2008. PMID: 18927149 - Wnt-5a-CKI{alpha} signaling promotes {beta}-catenin/E-cadherin complex formation and intercellular adhesion in human breast epithelial cells.
Medrek C, Landberg G, Andersson T, Leandersson K. Medrek C, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10968-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804923200. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19244247 Free PMC article. - Induction and transport of Wnt 5a during macrophage-induced malignant invasion is mediated by two types of extracellular vesicles.
Menck K, Klemm F, Gross JC, Pukrop T, Wenzel D, Binder C. Menck K, et al. Oncotarget. 2013 Nov;4(11):2057-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1336. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 24185202 Free PMC article. - Hear the Wnt Ror: how melanoma cells adjust to changes in Wnt.
O'Connell MP, Weeraratna AT. O'Connell MP, et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009 Dec;22(6):724-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2009.00627.x. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009. PMID: 19708915 Free PMC article. Review. - Wnt-5a gene expression in malignant human neuroblasts.
Blanc E, Goldschneider D, Douc-Rasy S, Bénard J, Raguénez G. Blanc E, et al. Cancer Lett. 2005 Oct 18;228(1-2):117-23. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.11.061. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 15925444 Review.
Cited by
- WNT5A in Cancer: A Pan-Cancer Analysis Revealing Its Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Potential.
Abdallah MM, Yahia M, Tagelsir Ahmed Y, Alfaki M. Abdallah MM, et al. Cureus. 2024 Jul 23;16(7):e65190. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65190. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39176352 Free PMC article. - Knockdown of LRP5 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Compensatory Activation of Akt Signaling.
Wang C, Li Y, Miao X, Wang Y, Yang G. Wang C, et al. J Cancer. 2024 Apr 15;15(10):3215-3226. doi: 10.7150/jca.93585. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38706907 Free PMC article. - Characterization and impact of non-canonical WNT signaling on outcomes of urothelial carcinoma.
Meagher M, Krause H, Elliott A, Farrell A, Antonarakis ES, Bastos B, Heath EI, Jamieson C, Stewart TF, Bagrodia A, Nabhan C, Oberley M, McKay RR, Salmasi A. Meagher M, et al. Cancer Med. 2024 Apr;13(7):e7148. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7148. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38558536 Free PMC article. - Differential expression of WNT5A long and short isoforms in non-muscle-invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma.
Strope AM, Phillips C, Khadgi S, Jenkinson SA, Coschigano KT, Malgor R. Strope AM, et al. Histol Histopathol. 2024 Jun;39(6):715-727. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-723. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38445662 - Altered binding affinity of SIX1-Q177R correlates with enhanced WNT5A and WNT pathway effector expression in Wilms tumor.
Stevenson MJ, Phanor SK, Patel U, Gisselbrecht SS, Bulyk ML, O'Brien LL. Stevenson MJ, et al. Dis Model Mech. 2023 Nov 1;16(11):dmm050208. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050208. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37815464 Free PMC article.
References
- Blanc E, Roux GL, Benard J, Raguenez G (2005) Low expression of Wnt-5a gene is associated with high-risk neuroblastoma. Oncogene 24: 1277–1283 - PubMed
- Chien AJ, Moore EC, Lonsdorf AS, Kulikauskas RM, Rothberg BG, Berger AJ, Major MB, Hwang ST, Rimm DL, Moon RT (2009) Activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma is associated with decreased proliferation in patient tumors and a murine melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 1193–1198 - PMC - PubMed
- Da Forno PD, Pringle JH, Hutchinson P, Osborn J, Huang Q, Potter L, Hancox RA, Fletcher A, Saldanha GS (2008) WNT5A expression increases during melanoma progression and correlates with outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14: 5825–5832 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources