Risk factors associated with injury attributable to falling among elderly population with history of stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Risk factors associated with injury attributable to falling among elderly population with history of stroke
Afshin A Divani et al. Stroke. 2009 Oct.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Stroke survivors are at high risk for falling. Identifying physical, clinical, and social factors that predispose stroke patients to falls may reduce further disability and life-threatening complications, and improve overall quality of life.
Methods: We used 5 biennial waves (1998-2006) from the Health and Retirement Study to assess risk factors associated with falling accidents and fall-related injuries among stroke survivors. We abstracted demographic data, living status, self-evaluated general health, and comorbid conditions. We analyzed the rate ratio (RR) of falling and the OR of injury within 2 follow-up years using a multivariate random effects model.
Results: We identified 1174 stroke survivors (mean age+/-SD, 74.4+/-7.2 years; 53% female). The 2-year risks of falling, subsequent injury, and broken hip attributable to fall were 46%, 15%, and 2.1% among the subjects, respectively. Factors associated with an increased frequency of falling were living with spouse as compared to living alone (RR, 1.4), poor general health (RR, 1.1), time from first stroke (RR, 1.2), psychiatric problems (RR, 1.7), urinary incontinence (RR, 1.4), pain (RR, 1.4), motor impairment (RR, 1.2), and past frequency of > or = 3 falls (RR, 1.3). Risk factors associated with fall-related injury were female gender (OR, 1.5), poor general health (OR, 1.2), past injury from fall (OR, 3.2), past frequency of > or = 3 falls (OR, 3.1), psychiatric problems (OR, 1.4), urinary incontinence (OR, 1.4), impaired hearing (OR, 1.6), pain (OR, 1.8), motor impairment (OR, 1.3), and presence of multiple strokes (OR, 3.2).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the high prevalence of falls and fall-related injuries in stroke survivors, and identifies factors that increase the risk. Modifying these factors may prevent falls, which could lead to improved quality of life and less caregiver burden and cost in this population.
Figures
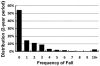
Figure
Distribution of the number of falls in a 2-year period among stroke survivors interviewed in HRS.
Similar articles
- [Falls in German hospitals and nursing homes 2006-2013. Frequencies, injuries, risk assessment, and preventive measures].
Lahmann NA, Heinze C, Rommel A. Lahmann NA, et al. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2014 Jun;57(6):650-9. doi: 10.1007/s00103-014-1966-8. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2014. PMID: 24863707 German. - Effect of obesity on falls, injury, and disability.
Himes CL, Reynolds SL. Himes CL, et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Jan;60(1):124-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03767.x. Epub 2011 Dec 8. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012. PMID: 22150343 - Sex-specific association between obesity and self-reported falls and injuries among community-dwelling Canadians aged 65 years and older.
Handrigan GA, Maltais N, Gagné M, Lamontagne P, Hamel D, Teasdale N, Hue O, Corbeil P, Brown JP, Jean S. Handrigan GA, et al. Osteoporos Int. 2017 Feb;28(2):483-494. doi: 10.1007/s00198-016-3745-x. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Osteoporos Int. 2017. PMID: 27562568 - Interventions to Prevent Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Guirguis-Blake JM, Michael YL, Perdue LA, Coppola EL, Beil TL, Thompson JH. Guirguis-Blake JM, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Apr. Report No.: 17-05232-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Apr. Report No.: 17-05232-EF-1. PMID: 30234932 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Interventions for preventing falls in older people in care facilities and hospitals.
Cameron ID, Gillespie LD, Robertson MC, Murray GR, Hill KD, Cumming RG, Kerse N. Cameron ID, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD005465. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005465.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235623 Updated. Review.
Cited by
- A Systematic Review of Fall Risk Factors in Stroke Survivors: Towards Improved Assessment Platforms and Protocols.
Abdollahi M, Whitton N, Zand R, Dombovy M, Parnianpour M, Khalaf K, Rashedi E. Abdollahi M, et al. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 8;10:910698. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.910698. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36003532 Free PMC article. - Global prevalence of falls in the older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.
Salari N, Darvishi N, Ahmadipanah M, Shohaimi S, Mohammadi M. Salari N, et al. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jun 28;17(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03222-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35765037 Free PMC article. Review. - Effect of a weekly functional independence measure scale on the recovery of patient with acute stroke: A retrospective study.
Kawamura K, Murayama K, Takamura J, Minegishi S. Kawamura K, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Mar 18;101(11):e28974. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028974. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35356904 Free PMC article. - Social Isolation Is Associated With Rapid Kidney Function Decline and the Development of Chronic Kidney Diseases in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: Findings From the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS).
Zhou W, Li Y, Ning Y, Gong S, Song N, Zhu B, Wang J, Zhao S, Shi Y, Ding X. Zhou W, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 2;8:782624. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.782624. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34926526 Free PMC article. - Active With Whom? Examining the Social Context of Physical Activity in Individuals After Stroke and Their Partners.
Pauly T, Ashe MC, Murphy R, Gerstorf D, Linden W, Madden KM, Hoppmann CA. Pauly T, et al. Front Public Health. 2021 Sep 29;9:754046. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.754046. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34660523 Free PMC article.
References
- Langhorne P, Stott DJ, Robertson L, MacDonald J, Jones L, McAlpine C, Dick F, Taylor GS, Murray G. Medical complications after stroke: A multicenter study. Stroke. 2000;31:1223–1229. - PubMed
- Nyberg L, Gustafson Y. Fall prediction index for patients in stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 1997;28:716–721. - PubMed
- Teasell R, McRae M, Foley N, Bhardwaj A. The incidence and consequences of falls in stroke patients during inpatient rehabilitation: Factors associated with high risk. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83:329–333. - PubMed
- Blake AJ, Morgan K, Bendall MJ, Dallosso H, Ebrahim SB, Arie TH, Fentem PH, Bassey EJ. Falls by elderly people at home: Prevalence and associated factors. Age Ageing. 1988;17:365–372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K02 NS047099/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS047099-06/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055808/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS055808-02/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous