Predicting flexible length linear B-cell epitopes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Predicting flexible length linear B-cell epitopes
Yasser El-Manzalawy et al. Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2008.
Abstract
Identifying B-cell epitopes play an important role in vaccine design, immunodiagnostic tests, and antibody production. Therefore, computational tools for reliably predicting B-cell epitopes are highly desirable. We explore two machine learning approaches for predicting flexible length linear B-cell epitopes. The first approach utilizes four sequence kernels for determining a similarity score between any arbitrary pair of variable length sequences. The second approach utilizes four different methods of mapping a variable length sequence into a fixed length feature vector. Based on our empirical comparisons, we propose FBCPred, a novel method for predicting flexible length linear B-cell epitopes using the subsequence kernel. Our results demonstrate that FBCPred significantly outperforms all other classifiers evaluated in this study. An implementation of FBCPred and the datasets used in this study are publicly available through our linear B-cell epitope prediction server, BCPREDS, at: http://ailab.cs.iastate.edu/bcpreds/.
Figures
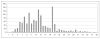
Fig. 1
Length distribution of unique linear B-cell epitopes in Bcipep database.
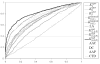
Fig. 2
ROC curves for different methods on original dataset of unique flexible length linear B-cell epitopes. The ROC curve of K(4,0.5)sub based classifier almost dominates all other ROC curves.
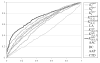
Fig. 3
ROC curves for different methods on homology-reduced dataset of flexible length linear B-cell epitopes. The ROC curve of K(4,0.5)sub based classifier almost dominates all other ROC curves.
Similar articles
- Predicting linear B-cell epitopes using string kernels.
El-Manzalawy Y, Dobbs D, Honavar V. El-Manzalawy Y, et al. J Mol Recognit. 2008 Jul-Aug;21(4):243-55. doi: 10.1002/jmr.893. J Mol Recognit. 2008. PMID: 18496882 Free PMC article. - Improved method for linear B-cell epitope prediction using antigen's primary sequence.
Singh H, Ansari HR, Raghava GP. Singh H, et al. PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e62216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062216. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667458 Free PMC article. - Introducing of an integrated artificial neural network and Chou's pseudo amino acid composition approach for computational epitope-mapping of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus antigens.
Nosrati M, Mohabatkar H, Behbahani M. Nosrati M, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:106020. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106020. Epub 2019 Nov 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31776090 - Machine learning-based methods for prediction of linear B-cell epitopes.
Wang HW, Pai TW. Wang HW, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1184:217-36. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1115-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25048127 Review. - Linear B-Cell Epitope Prediction for In Silico Vaccine Design: A Performance Review of Methods Available via Command-Line Interface.
Galanis KA, Nastou KC, Papandreou NC, Petichakis GN, Pigis DG, Iconomidou VA. Galanis KA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3210. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063210. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Proteomic analysis of Rickettsia akari proposes a 44 kDa-OMP as a potential biomarker for Rickettsialpox diagnosis.
Csicsay F, Flores-Ramirez G, Zuñiga-Navarrete F, Bartošová M, Fučíková A, Pajer P, Dresler J, Škultéty Ľ, Quevedo-Diaz M. Csicsay F, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jul 8;20(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01877-6. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32640994 Free PMC article. - Protection of mice against Staphylococcus aureus infection by a recombinant protein ClfA-IsdB-Hlg as a vaccine candidate.
Delfani S, Mohabati Mobarez A, Imani Fooladi AA, Amani J, Emaneini M. Delfani S, et al. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016 Feb;205(1):47-55. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0425-y. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26155981 - BIPS-A code base for designing and coding of a Phage ImmunoPrecipitation Oligo Library.
Leviatan S, Kalka IN, Vogl T, Klompas S, Weinberger A, Segal E. Leviatan S, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Nov 10;18(11):e1010663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010663. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36355866 Free PMC article. - BCEDB: a linear B-cell epitopes database for SARS-CoV-2.
Tai C, Li H, Zhang J. Tai C, et al. Database (Oxford). 2023 Sep 30;2023:baad065. doi: 10.1093/database/baad065. Database (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 37776561 Free PMC article. - Postgenomic Approaches and Bioinformatics Tools to Advance the Development of Vaccines against Bacteria of the Burkholderia cepacia Complex.
Sousa SA, Seixas AMM, Leitão JH. Sousa SA, et al. Vaccines (Basel). 2018 Jun 8;6(2):34. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6020034. Vaccines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29890657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Pier GB, Lyczak JB, Wetzler LM. Immunology, infection, and immunity. 1. ASM Press; PL Washington: 2004.
- Greenbaum JA, Andersen PH, Blythe M, Bui HH, Cachau RE, Crowe J, Davies M, Kolaskar AS, Lund O, Morrison S, et al. Towards a consensus on datasets and evaluation metrics for developing B-cell epitope prediction tools. J Mol Recognit. 2007;20:75–82. - PubMed
- Barlow DJ, Edwards MS, Thornton JM, et al. Continuous and discontinuous protein antigenic determinants. Nature. 1986;322:747–748. - PubMed
- Langeveld JP, martinez Torrecuadrada J, boshuizen RS, Meloen RH, Ignacio CJ. Characterisation of a protective linear B cell epitope against feline parvoviruses. Vaccine. 2001;19:2352–2360. - PubMed
- Walter G. Production and use of antibodies against synthetic peptides. J Immunol Methods. 1986;88:149–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources