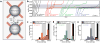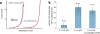Nucleosomal fluctuations govern the transcription dynamics of RNA polymerase II - PubMed (original) (raw)
Nucleosomal fluctuations govern the transcription dynamics of RNA polymerase II
Courtney Hodges et al. Science. 2009.
Abstract
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) must overcome the barriers imposed by nucleosomes during transcription elongation. We have developed an optical tweezers assay to follow individual Pol II complexes as they transcribe nucleosomal DNA. Our results indicate that the nucleosome behaves as a fluctuating barrier that locally increases pause density, slows pause recovery, and reduces the apparent pause-free velocity of Pol II. The polymerase, rather than actively separating DNA from histones, functions instead as a ratchet that rectifies nucleosomal fluctuations. We also obtained direct evidence that transcription through a nucleosome involves transfer of the core histones behind the transcribing polymerase via a transient DNA loop. The interplay between polymerase dynamics and nucleosome fluctuations provides a physical basis for the regulation of eukaryotic transcription.
Figures
Figure 1. Transcription through a nucleosome
(a) Geometry for the dual-trap optical tweezers experiments. (b) Representative trajectories of individual transcribing polymerases with or without the nucleosome at different ionic strengths. (c), (d), and (e) Probability of arrest or termination as a function of polymerase position on the DNA template at 300, 150, and 40 mM KCl respectively. Arrest is defined as a pause that lasts longer than 20 minutes or until the tether breaks. Data for transcription of bare DNA is in solid black, and nucleosome data is in semi-translucent colors. The shaded region represents the NPS.
Figure 2. Effect of the nucleosome on transcription dynamics
In each subplot, only traces that passed the NPS are considered. (a) Pause density with a nucleosome (dashed red line) and on bare DNA (solid black line). The pink shaded area represents the predicted pause density confidence interval at the nucleosome based on the model presented in the text. The gray shaded region is the confidence interval for pause density on bare DNA used in the model. Error bars are SEM. (b) Cumulative distributions of pause durations with (solid red line) and without (solid black line) a nucleosome present. Theoretical cumulative distributions for nucleosomal (pink dashed line) and non-nucleosomal (gray dashed line) pauses. (c) Pause-free velocities with (pink) and without (gray) a nucleosome with fits to normal distributions (solid lines). The predicted values based on the diffusive model with and without a nucleosome are shown as red and black circles, respectively.
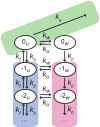
Figure 3. Kinetic model of transcription through a nucleosome
The green area corresponds to on-pathway elongation (ke). The pink and blue areas represent off-pathway paused states where Pol II is backtracked; negative numbers indicate how many bases Pol II has backtracked from the elongation competent state, denoted by 0. The label u refers to the nucleosome being locally unwrapped (blue area), while w denotes the states where the nucleosome is wrapped in front of Pol II (pink area).
Figure 4. Histone transfer during transcription
(a) Force-extension curves of transcribed DNA. Pulling curves are shown in black and relaxation curves in red. (b) Frequency of histone transfer as a function of applied force during transcription.
Comment in
- Biochemistry. Nudging through a nucleosome.
Otterstrom JJ, van Oijen AM. Otterstrom JJ, et al. Science. 2009 Jul 31;325(5940):547-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1177311. Science. 2009. PMID: 19644099 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Biochemistry. Nudging through a nucleosome.
Otterstrom JJ, van Oijen AM. Otterstrom JJ, et al. Science. 2009 Jul 31;325(5940):547-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1177311. Science. 2009. PMID: 19644099 No abstract available. - Nature of the nucleosomal barrier to RNA polymerase II.
Kireeva ML, Hancock B, Cremona GH, Walter W, Studitsky VM, Kashlev M. Kireeva ML, et al. Mol Cell. 2005 Apr 1;18(1):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.027. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15808512 - RNA polymerase I (Pol I) passage through nucleosomes depends on Pol I subunits binding its lobe structure.
Merkl PE, Pilsl M, Fremter T, Schwank K, Engel C, Längst G, Milkereit P, Griesenbeck J, Tschochner H. Merkl PE, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 10;295(15):4782-4795. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011827. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32060094 Free PMC article. - Mechanism of transcription through a nucleosome by RNA polymerase II.
Kulaeva OI, Hsieh FK, Chang HW, Luse DS, Studitsky VM. Kulaeva OI, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982194 Free PMC article. Review. - Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription.
Venkatesh S, Workman JL. Venkatesh S, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;16(3):178-89. doi: 10.1038/nrm3941. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25650798 Review.
Cited by
- Spt6 prevents transcription-coupled loss of posttranslationally modified histone H3.
Kato H, Okazaki K, Iida T, Nakayama J, Murakami Y, Urano T. Kato H, et al. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2186. doi: 10.1038/srep02186. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23851719 Free PMC article. - Interactions With Histone H3 & Tools to Study Them.
Scott WA, Campos EI. Scott WA, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 31;8:701. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00701. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850821 Free PMC article. Review. - A bumpy road for RNA polymerase II.
Giono LE, Kornblihtt AR. Giono LE, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 May;22(5):353-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3020. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25945884 No abstract available. - DNA looping mediates nucleosome transfer.
Brennan LD, Forties RA, Patel SS, Wang MD. Brennan LD, et al. Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 3;7:13337. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13337. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27808093 Free PMC article. - RNA polymerase complexes cooperate to relieve the nucleosomal barrier and evict histones.
Kulaeva OI, Hsieh FK, Studitsky VM. Kulaeva OI, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11325-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001148107. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534568 Free PMC article.
References
- Izban MG, Luse DS. Genes Dev. 1991;5:683. - PubMed
- Kireeva ML, et al. Mol Cell. 2002;9:541. - PubMed
- Walter W, Kireeva ML, Studitsky VM, Kashlev M. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:36148. - PubMed
- Kireeva ML, et al. Mol Cell. 2005;18:97. - PubMed
- Bondarenko VA, et al. Mol Cell. 2006;24:469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R37 GM032543/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM032543-27/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM32543/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases