Experimental sleep fragmentation impairs spatial reference but not working memory in Fischer/Brown Norway rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Experimental sleep fragmentation impairs spatial reference but not working memory in Fischer/Brown Norway rats
Christopher P Ward et al. J Sleep Res. 2009 Jun.
Abstract
Sleep fragmentation is a common symptom in sleep disorders and other medical complaints resulting in excessive daytime sleepiness. The present study seeks to explore the effects of sleep fragmentation on learning and memory in a spatial reference memory task and a spatial working memory (WM) task. Fischer/Brown Norway rats lived in custom treadmills designed to induce locomotor activity every 2 min throughout a 24-h period. Separate rats were either on a treadmill schedule that allowed for consolidated sleep or experienced no locomotor activation. Rats were tested in one of two water maze-based tests of learning and memory immediately following 24 h of sleep interruption. Rats tested in a spatial reference memory task (eight massed acquisition trials) with a 24-h follow-up probe trial to assess memory retention showed no differences in acquisition performance but were impaired on the 24 h retention of the platform location. In contrast, the performance of rats tested in a spatial WM task (delayed matching to position task) was not impaired. Therefore, sleep fragmentation prior to testing impairs the ability to retain spatial reference memories but does not impair spatial reference memory acquisition or spatial WM in Fischer-Norway rats.
Figures
1
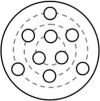
The Diagram represents the nine novel platform location used in the delayed matching to position task to asses spatial working memory (adapted from Steele and Morris 1999).
2
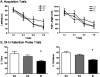
The recall of the platform location was impaired by 24 hours of SI. A: Mean (±SEM) latency (left) and path length (right) to reach the hidden platform over 8 consecutive acquisition trials. No significant differences in learning were observed among the 3 different groups of rats. B. Mean (+SEM) percent time (left) and distance (right) during probe trial that rats spent searching in the target quadrant that formerly contained the hidden platform. SI rats spent significantly less time in the target quadrant than did CC, but EC was not significantly different from CC. * p < 0.05
3
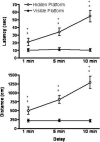
The delayed matching to position task tested spatial working memory in rats. Mean (±SEM) latency (top) and distance (bottom) for CC rats to find the visible platform in the first trial compared to finding the hidden platform in the second trial. Rats spent significantly longer periods of time finding the previously indicated platform location as delays increased from 1 to 5 to 10 minutes. * comparison between visible and hidden platform p < 0.05; + comparison between delays p < 0.05
4
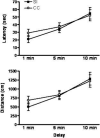
24 hours of SI prior to performance did not impact performance on the spatial working memory task. Mean (±SEM) latency (top) and distance (bottom) for rats to find the hidden platform for CC versus SI rats. No significant differences were observed between groups.
Similar articles
- The effects of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation and recovery on spatial reference memory of young rats.
Li S, Tian Y, Ding Y, Jin X, Yan C, Shen X. Li S, et al. Learn Behav. 2009 Aug;37(3):246-53. doi: 10.3758/LB.37.3.246. Learn Behav. 2009. PMID: 19542091 - Spatial learning and memory deficits following exposure to 24 h of sleep fragmentation or intermittent hypoxia in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea.
Ward CP, McCoy JG, McKenna JT, Connolly NP, McCarley RW, Strecker RE. Ward CP, et al. Brain Res. 2009 Oct 19;1294:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.064. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19643093 Free PMC article. - Testosterone modulates performance on a spatial working memory task in male rats.
Sandstrom NJ, Kim JH, Wasserman MA. Sandstrom NJ, et al. Horm Behav. 2006 Jun;50(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Nov 2. Horm Behav. 2006. PMID: 16263125 - Effects of mammillary body lesions on spatial reference and working memory tasks.
Santín LJ, Rubio S, Begega A, Arias JL. Santín LJ, et al. Behav Brain Res. 1999 Jul;102(1-2):137-50. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00011-x. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10403022 - Spatial Navigation (Water Maze) Tasks.
Terry AV Jr. Terry AV Jr. In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 13. In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 13. PMID: 21204326 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
- Differential effect of sleep deprivation on place cell representations, sleep architecture, and memory in young and old mice.
Yuan RK, Lopez MR, Ramos-Alvarez MM, Normandin ME, Thomas AS, Uygun DS, Cerda VR, Grenier AE, Wood MT, Gagliardi CM, Guajardo H, Muzzio IA. Yuan RK, et al. Cell Rep. 2021 Jun 15;35(11):109234. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109234. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34133936 Free PMC article. - Altered cognition and anxiety in adolescent offspring whose mothers underwent different-pattern maternal sleep deprivation, and cognition link to hippocampal expressions of Bdnf and Syt-1.
Wei RM, Zhang YM, Li Y, Wu QT, Wang YT, Li XY, Li XW, Chen GH. Wei RM, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Dec 8;16:1066725. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1066725. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36570704 Free PMC article. - Sleep deprivation impairs recall of social transmission of food preference in rats.
Wooden JI, Pido J, Mathews H, Kieltyka R, Montemayor BA, Ward CP. Wooden JI, et al. Nat Sci Sleep. 2014 Nov 4;6:129-35. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S68611. eCollection 2014. Nat Sci Sleep. 2014. PMID: 25395874 Free PMC article. - Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation Produces Long-Term Detrimental Effects in Spatial Memory and Modifies the Cellular Composition of the Subgranular Zone.
Soto-Rodriguez S, Lopez-Armas G, Luquin S, Ramos-Zuñiga R, Jauregui-Huerta F, Gonzalez-Perez O, Gonzalez-Castañeda RE. Soto-Rodriguez S, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 May 30;10:132. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00132. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27303266 Free PMC article. - Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Spatial Learning and Memory in Juvenile and Young Adult Rats.
Ward CP, Wooden JI, Kieltyka R. Ward CP, et al. Psychol Neurosci. 2017 Mar;10(1):109-116. doi: 10.1037/pne0000075. Psychol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28959381 Free PMC article.
References
- Bonnet MH. Performance and sleepiness following moderate sleep disruption and slow wave sleep deprivation. Physiol Behav. 1986;37:915–918. - PubMed
- Bonnet MH, Arand DL. Clinical effects of sleep fragmentation versus sleep deprivation. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003;7:297–310. - PubMed
- Curcio G, Ferrara M, De GL. Sleep loss, learning capacity and academic performance. Sleep Med. Rev. 2006;10:323–337. - PubMed
- Davis CJ, Harding JW, Wright JW. REM sleep deprivation-induced deficits in the latency-to-peak induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation within the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Brain Res. 2003;973:293–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical