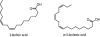Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their effects on cardiovascular disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2003 Winter;8(4):164-72.
Affiliations
- PMID: 19649216
- PMCID: PMC2719153
Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their effects on cardiovascular disease
Bradley P Ander et al. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2003 Winter.
Abstract
Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) affect a wide variety of physiological processes. Much attention has been given to the n-3 PUFAs and their role in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, stemming from evidence obtained through a number of epidemiological studies and clinical trials. Investigators are now focused on elucidating the pathways and mechanisms for the biological action of n-3 PUFAs. Dietary intervention is recognized as a key measure in patient therapy and in the maintenance of human health in general. This review provides a summary of several important clinical trials, and while the exact modes of action of n-3 PUFA are not known, current viewpoints regarding the mechanisms of these fatty acids on atherosclerosis, circulating lipid profile, cell membranes, cell proliferation, platelet aggregation and cardiac arrhythmias are discussed.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Diet; Polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Figures
Figure 1)
The structure of two essential fatty acids – linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid
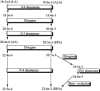
Figure 2)
The metabolic pathways of n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Metabolism of the two fatty acid families requires competition for the same elongation and desaturation enzymes. Note that the desaturation steps tend to be slow and rate-limiting compared with the more rapid elongation steps. Eicosanoids, such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes, can be derived from arachidonic acid (AA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and can mediate different physiological actions. ALA Alpha-linolenic acid; DHA Docosahexaenoic acid; LA Linoleic acid
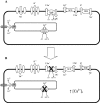
Figure 3)
The major ion channels and transporters in a myocardial cell. The Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) and sarcoplasmic endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) are normally responsible for Ca2+ extrusion following each contraction (A), but during ischemia (B), lack of O2 limits ATP production and, thus, the function of the Na+/K+ ATPase (NAK) and SERCA. Uptake of Ca2+ by SERCA is inhibited and the NCX functions in reverse to compensate and removes Na+, but brings Ca2+ into the cell, resulting in Ca2+ overload and subsequent contracture and/or potentially lethal arrhythmias. [Ca2+]i intracellular Ca2+ concentration; NAK Na+, K+ ATPase; RyR ryanodine receptor
Similar articles
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids and signalling via phospholipase C-beta and A2 in myocardium.
de Jonge HW, Dekkers DH, Lamers JM. de Jonge HW, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 1996 Apr 12-26;157(1-2):199-210. doi: 10.1007/BF00227899. Mol Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8739247 Review. - The effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiac rhythm: a critical reassessment.
Billman GE. Billman GE. Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;140(1):53-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23735203 Review. - The Physiological Effect of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (n-3 PUFAs) Intake and Exercise on Hemorheology, Microvascular Function, and Physical Performance in Health and Cardiovascular Diseases; Is There an Interaction of Exercise and Dietary n-3 PUFA Intake?
Stupin M, Kibel A, Stupin A, Selthofer-Relatić K, Matić A, Mihalj M, Mihaljević Z, Jukić I, Drenjančević I. Stupin M, et al. Front Physiol. 2019 Aug 30;10:1129. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01129. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31543828 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of dietary fats for preventing cardiovascular disease. A review.
Szostak-Wegierek D, Kłosiewicz-Latoszek L, Szostak WB, Cybulska B. Szostak-Wegierek D, et al. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2013;64(4):263-9. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2013. PMID: 24693710 Review. - The relation of lipid peroxidation processes with atherogenesis: a new theory on atherogenesis.
Spiteller G. Spiteller G. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005 Nov;49(11):999-1013. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500055. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005. PMID: 16270286 Review.
Cited by
- Direct evidence of bradycardic effect of omega-3 fatty acids acting on nucleus ambiguus.
Barr JL, Lindenau KL, Brailoiu E, Brailoiu GC. Barr JL, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2020 Sep 14;735:135196. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135196. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32585256 Free PMC article. - Nutraceuticals' Novel Formulations: The Good, the Bad, the Unknown and Patents Involved.
Helal NA, Eassa HA, Amer AM, Eltokhy MA, Edafiogho I, Nounou MI. Helal NA, et al. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019;13(2):105-156. doi: 10.2174/1872211313666190503112040. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019. PMID: 31577201 Free PMC article. Review. - Omega 3 and atrial fibrillation: Where are we?
Martino A, Pezzi L, Magnano R, Salustri E, Penco M, Calo' L. Martino A, et al. World J Cardiol. 2016 Feb 26;8(2):114-9. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i2.114. World J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26981208 Free PMC article. - High diet quality indices associated with lower risk of lipid profile abnormalities in Taiwanese kidney transplant recipients.
Lin IH, Van Duong T, Nien SW, Tseng IH, Wu YM, Chiang YJ, Wang HH, Chiang CY, Wang MH, Chiu CH, Lin YT, Wong TC. Lin IH, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 11;13(1):19662. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46736-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37952063 Free PMC article. - Genetic architecture of human plasma lipidome and its link to cardiovascular disease.
Tabassum R, Rämö JT, Ripatti P, Koskela JT, Kurki M, Karjalainen J, Palta P, Hassan S, Nunez-Fontarnau J, Kiiskinen TTJ, Söderlund S, Matikainen N, Gerl MJ, Surma MA, Klose C, Stitziel NO, Laivuori H, Havulinna AS, Service SK, Salomaa V, Pirinen M; FinnGen Project; Jauhiainen M, Daly MJ, Freimer NB, Palotie A, Taskinen MR, Simons K, Ripatti S. Tabassum R, et al. Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 24;10(1):4329. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11954-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31551469 Free PMC article.
References
- Salem N., Jr Introduction to polyunsaturated fatty acids. Backgrounder. 1999;3:1–8.
- Lanzmann-Petithory D. Alpha-linolenic acid and cardiovascular diseases. J Nutr Health Aging. 2001;5:179–83. - PubMed
- Dolecek TA, Granditis G. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and mortality in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT) World Rev Nutr Diet. 1991;66:205–16. - PubMed
- Singh RB, Niaz MA, Sharma JP, Kumar R, Rastogi V, Moshiri M. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fish oil and mustard oil in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction: The Indian experiment of infarct survival – 4. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 1997;11:485–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources