An EGFR and AKT Signaling Pathway was Identified with Mediation Model in Osteosarcomas Clinical Study - PubMed (original) (raw)
An EGFR and AKT Signaling Pathway was Identified with Mediation Model in Osteosarcomas Clinical Study
Huiyun Wu et al. Biomark Insights. 2007.
Abstract
Identification of correlation pattern and signal pathway among biomarkers in patients has become increasingly interesting for its potential values in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. EGFR and p-AKT signaling in osteosarcoma (OS) patients were analyzed for its relationship with cancer cell proliferation maker, Ki-67, using causal procedures and statistical tests. A total of 69 patients were collected who present to Vanderbilt University Medical Center with newly diagnosed, previously untreated osteosarcomas during the clinical study period 1994 through 2003. Tissue microarrays were constructed for EGFR, p-AKT and Ki-67. The mediation model was constructed with structural equation model (SEM) for the causal analysis of the three biomarkers in osteosarcoma patients. The results suggested a mediating effect of p-AKT for the causal relationship between EGFR and Ki-67. The study also found significant associations between EGFR and Ki-67 (p = 0.002), EGFR and p-AKT (p = 0.027), and p-AKT and Ki-67 controlling EGFR (p = 0.004). After the impact of EGFR on Ki-67 was accounted for by p-AKT, the relation between EGFR and Ki-67 was no longer significant (p = 0.381). The mediating effect was confirmed with Sobel test (p < 0.001) and Goodman (I) test (p < 0.001). The study indicated that a mediation model could be an approach to exploring the correlation pattern of EGFR and AKT signal pathway for cancer cell proliferation in OS patients in clinical study.
Keywords: AKT; EGFR; clinical study; mediation model; osteosarcomas.
Figures
Figure 1
Path for Model 1. A two-variable correlation model between an explanatory variable and an outcome variable. τ is the parameter of interest. ɛ is the error term.
Figure 2
Paths for Model 2 and Model 3. A three-variable mediation model. X, M, and Y are symbols of the three variables. α_,_ β and τ′ are the parameters of interest. ɛ is the error term.
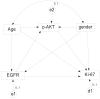
Figure 3
Structural equation modeling for mediation effect. Dependent variable Ki-67 is predicted with single-headed EGFR and p-AKT. Each single-headed arrow represents a regression weights. Age and gender are considered to be associated with all the three biomarkers and are also allowed to be correlated and represented with double-headed arrow. Circles of e1, e2 and d1 are error terms with mean at 0 and variance at 1.
Figure 4
Expression of EGFR and p-AKT. Left panel: membrane staining in tumor cells with EGFR; right panel: nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in tumor cells with p-AKT.
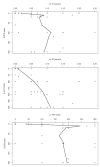
Figure 5
Scatter plots with lowess lines. Circles are data points and lines are the lowess smoothing lines.
Similar articles
- CSN5 controls the growth of osteosarcoma via modulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt axis.
Wan Z, Huang S, Mo F, Yao Y, Liu G, Han Z, Chen M, Zhiyun L. Wan Z, et al. Exp Cell Res. 2019 Nov 15;384(2):111646. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111646. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31560888 - Diffusion kurtosis imaging: correlation analysis of quantitative model parameters with molecular features in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.
Peng Q, Tang W, Huang Y, Wu N, Yang L, Li N. Peng Q, et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Oct 20;133(20):2403-2409. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001074. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 32960838 Free PMC article. - The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream signaling molecules in osteosarcoma.
Do SI, Jung WW, Kim HS, Park YK. Do SI, et al. Int J Oncol. 2009 Mar;34(3):797-803. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000205. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19212684 - Nimotuzuma restrains proliferation and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by regulation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT signal pathway.
Liu M, Zhang J, Dong H, Wang W. Liu M, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):20879-20887. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28693. Epub 2019 Apr 18. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31001861 Retracted. - The relationship between the expression of Ki-67 and the prognosis of osteosarcoma.
Zeng M, Zhou J, Wen L, Zhu Y, Luo Y, Wang W. Zeng M, et al. BMC Cancer. 2021 Mar 1;21(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07880-y. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33648449 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Molecular Mechanisms of Canine Osteosarcoma Metastasis.
Wilk SS, Zabielska-Koczywąs KA. Wilk SS, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 31;22(7):3639. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073639. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807419 Free PMC article. Review. - Effect and Mechanism of EGFL7 Downregulation in Human Osteosarcoma Cells on the Biological Function of Co-cultured HUVEC.
Li X, Liu LF, Liu YZ, Pan YT, Li G, Lu QY, Li ZC. Li X, et al. Balkan Med J. 2018 Mar 15;35(2):155-162. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0045. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Balkan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29363485 Free PMC article. - MAT2B promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteosarcoma by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
Yuan Y, Wang Y, Liu Z, Sun Y, Yao Y, Yu W, Shen Z. Yuan Y, et al. Int J Oncol. 2019 Jun;54(6):2019-2029. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4764. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30942439 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of EGFR-AKT axis results in the suppression of ovarian tumors in vitro and in preclinical mouse model.
Loganathan S, Kandala PK, Gupta P, Srivastava SK. Loganathan S, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043577. Epub 2012 Aug 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952709 Free PMC article. - PD-L1, STAT3, IL6, and EGFR Immunoexpressions in High-Grade Osteosarcoma.
Rahmadiani N, Norahmawati E, Endharti AT, Hambalie AO, Isma SPP. Rahmadiani N, et al. Adv Orthop. 2024 Feb 23;2024:9036225. doi: 10.1155/2024/9036225. eCollection 2024. Adv Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38434518 Free PMC article.
References
- Anninga JK, van de Vijver MJ, Cleton-Jansen AM, Kristel PM, Taminiau AH, Nooij M, Egeler RM, Hogendoorn PC. Overexpression of the HER-2 oncogene does not play a role in high-grade osteosarcomas. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:963–70. - PubMed
- Arteaga CL. Overview of epidermal growth factor receptor biology and its role as a therapeutic target in human neoplasia. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:3–9. - PubMed
- Beck SL. Symptom clusters: impediments and suggestions for solutions. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2004:137–8. - PubMed
- Beck SL, Dudley WN, Barsevick A. Pain, sleep disturbance, and fatigue in patients with cancer: using a mediation model to test a symptom cluster. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2005;32:542. - PubMed
- Curtis RK, Oresic M, Vidal-Puig A. Pathways to the analysis of microarray data. Trends Biotechnol. 2005;23:429–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous