Bacillus subtilis homologs of MviN (MurJ), the putative Escherichia coli lipid II flippase, are not essential for growth - PubMed (original) (raw)
Bacillus subtilis homologs of MviN (MurJ), the putative Escherichia coli lipid II flippase, are not essential for growth
Allison Fay et al. J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct.
Abstract
Although peptidoglycan synthesis is one of the best-studied metabolic pathways in bacteria, the mechanism underlying the membrane translocation of lipid II, the undecaprenyl-disaccharide pentapeptide peptidoglycan precursor, remains mysterious. Recently, it was proposed that the essential Escherichia coli mviN gene encodes the lipid II flippase. Bacillus subtilis contains four proteins that are putatively homologous to MviN, including SpoVB, previously reported to be necessary for spore cortex peptidoglycan synthesis during sporulation. MviN complemented the sporulation defect of a DeltaspoVB mutation, and SpoVB and another of the B. subtilis homologs, YtgP, complemented the growth defect of an E. coli strain depleted for MviN. Thus, these B. subtilis proteins are likely to be MviN homologs. However, B. subtilis strains lacking these four proteins have no defects in growth, indicating that they likely do not serve as lipid II flippases in this organism.
Figures
FIG. 1.
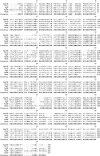
Alignment of B. subtilis MviN homologs. A ClustalW alignment of E. coli MviN and B. subtilis SpoVD, YtgP, YabM, and YkvU is shown. The alignment was generated after a BLASTp query of the B. subtilis genome with the E. coli MviN sequence followed by a second BLASTp query using YtgP, the highest-scoring sequence.
FIG. 2.
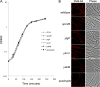
Growth of B. subtilis strains carrying mutations in putative MviN homologs. (A) Strains carrying the single mutation Δ_ytgP_::mls (JDB2327), Δ_ykvU_::mls (JDB2330), Δ_yabM_::cm (JDB2386), or _spoVB_Δ::tet (JDB1097) or all four mutations (JDB2361) were grown in LB at 37°C following dilution to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.04 from an overnight culture grown in LB. OD600 was measured at a series of time points for each of the strains. (B) B. subtilis strains carrying the mutations in single MviN homologs or mutations in all four homologs were grown in LB to an OD600 of 0.9. After collection, cells were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline with 1 mg/ml FM4-64 and imaged. Bar, 5 mm.
FIG. 3.
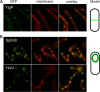
Localization of GFP fusions. (A) A strain expressing YtgP-GFP (JDB2356) was grown in CH growth medium, cells were collected at an OD600 of 0.7, and the membranes were stained with FM4-64. (B) Strains expressing SpoVB-GFP (JDB2329) and YkvU-GFP (JDB2358) were sporulated by resuspension in A+B medium, cells were collected at T3 of sporulation, and membranes were stained with FM4-64.
FIG. 4.
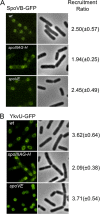
SpoVB-GFP and YkvU-GFP targeting requires additional sporulation-specific proteins. (A) SpoVB-GFP-expressing strains JDB2329 (wt), JDB2416 (spoIIIAG-H::kan), and JDB2418 (spoVE::tet) were sporulated by resuspension, and images were taken at 3 h. (B) YkvU-GFP-expressing strains JDB2358 (wt), JDB2377 (spoIIIAG-H::kan), and JDB2378 (spoVE::tet) were sporulated by resuspension, and images were taken at T3. Recruitment ratios are the ratios of the average maximum forespore fluorescence to the average maximum mother cell fluorescence.
FIG. 5.
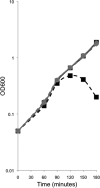
SpoVB-GFP and YtgP-GFP rescue the mviN depletion mutant. JDE1148 (pMMB207) (▪), JDE1140 (pAF374) (+), and JDE1147 (pAF375) (•) were depleted for mviN by growth in LB in the absence (dashed) or presence (solid) of the inducer arabinose. The presence of pMMB207 did not affect mviN depletion, as the strain required arabinose for growth and IPTG had no effect. Leaky expression of YtgP-GFP or SpoVB-GFP rescued the mviN mutation, as seen by growth without arabinose.
Similar articles
- Homologues of the Bacillus subtilis SpoVB protein are involved in cell wall metabolism.
Vasudevan P, McElligott J, Attkisson C, Betteken M, Popham DL. Vasudevan P, et al. J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):6012-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00604-09. Epub 2009 Jul 31. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19648239 Free PMC article. - MurJ and a novel lipid II flippase are required for cell wall biogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Meeske AJ, Sham LT, Kimsey H, Koo BM, Gross CA, Bernhardt TG, Rudner DZ. Meeske AJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 19;112(20):6437-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504967112. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25918422 Free PMC article. - A Burkholderia cenocepacia MurJ (MviN) homolog is essential for cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis and bacterial viability.
Mohamed YF, Valvano MA. Mohamed YF, et al. Glycobiology. 2014 Jun;24(6):564-76. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu025. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24688094 Free PMC article. - Class A PBPs: It is time to rethink traditional paradigms.
Straume D, Piechowiak KW, Kjos M, Håvarstein LS. Straume D, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2021 Jul;116(1):41-52. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14714. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33709487 Review. - Hit 'em where it hurts: The growing and structurally diverse family of peptides that target lipid-II.
Oppedijk SF, Martin NI, Breukink E. Oppedijk SF, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1858(5):947-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.024. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26523408 Review.
Cited by
- Recent Advances in Peptidoglycan Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
Galinier A, Delan-Forino C, Foulquier E, Lakhal H, Pompeo F. Galinier A, et al. Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 22;13(5):720. doi: 10.3390/biom13050720. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238589 Free PMC article. Review. - The Bacterial Cell Wall: From Lipid II Flipping to Polymerization.
Kumar S, Mollo A, Kahne D, Ruiz N. Kumar S, et al. Chem Rev. 2022 May 11;122(9):8884-8910. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00773. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35274942 Free PMC article. Review. - GtcA is required for LTA glycosylation in Listeria monocytogenes serovar 1/2a and Bacillus subtilis.
Rismondo J, Haddad TFM, Shen Y, Loessner MJ, Gründling A. Rismondo J, et al. Cell Surf. 2020 Feb 19;6:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2020.100038. eCollection 2020 Dec. Cell Surf. 2020. PMID: 32743150 Free PMC article. - The transpeptidase PbpA and noncanonical transglycosylase RodA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis play important roles in regulating bacterial cell lengths.
Arora D, Chawla Y, Malakar B, Singh A, Nandicoori VK. Arora D, et al. J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 27;293(17):6497-6516. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.811190. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29530985 Free PMC article.
References
- Aertsen, A., I. Van Opstal, S. C. Vanmuysen, E. Y. Wuytack, and C. W. Michiels. 2005. Screening for Bacillus subtilis mutants deficient in pressure induced spore germination: identification of ykvU as a novel germination gene. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 243:385-391. - PubMed
- Daniel, R. A., S. Drake, C. E. Buchanan, R. Scholle, and J. Errington. 1994. The Bacillus subtilis spoVD gene encodes a mother-cell-specific penicillin-binding protein required for spore morphogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 235:209-220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01GM081368-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM081368/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI07161-29/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM081368-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007161/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases