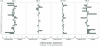Human prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are oligoclonal and PD-1+ - PubMed (original) (raw)
Human prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are oligoclonal and PD-1+
Karen S Sfanos et al. Prostate. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Prostate-infiltrating CD8(+) T lymphocytes (CD8(+) PIL) are prevalent in men with prostate cancer (PCa), however, it is unclear whether the presence of such cells reflects a non-specific immune infiltrate or an oligoclonal, antigen-driven adaptive immune response.
Methods: We investigated the complexity of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire in the prostate gland by examining the diversity of CD8(+) TCR beta chain variable region (Vbeta) gene sequences in both the peripheral blood and prostates of cancer patients. Vbeta repertoire analysis was performed by family-specific Vbeta spectratyping and flow cytometry, as well as direct sequence analysis (5' RACE and cloning). Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1 or PDCD1) expression on peripheral blood CD8(+) T cells and CD8(+) PIL was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: CD8(+) PIL isolated from cancer patients exhibited restricted TCR Vbeta gene usage, and identical clones were identified in multiple sites within the prostate. Furthermore, CD8(+) PIL express high levels of the inhibitory receptor PD-1, a cell surface protein associated with an "exhausted" CD8(+) T-cell phenotype.
Conclusions: CD8(+) PIL appear to have undergone clonal expansion in response to an as yet unidentified antigen; however, due to the high expression of PD-1, these cells are likely incapable of mounting an effective immune response. The results provide an important basis for further efforts aimed at the identification of specific antigens involved in prostatic inflammation, and suggest that PD-1 blockade may be useful in immunotherapy for PCa.
Figures
Figure 1
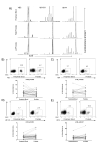
TCR Vβ skewing of select Vβ families in peripheral blood and prostate of PCa patients. A) Examples of skewing observed by TCR Vβ CDR3 spectratyping. Skewed CDR3 sizes in CD8+ PIL are observed in both the right and left lobes of the prostate, but not in the peripheral blood. B-E) Positively isolated CD8+ T cells were stained directly ex vivo and analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative FACS plots of CD3+CD8+Vβ2+, CD3+CD8+Vβ8+, CD3+CD8+Vβ13.6+, and CD3+CD8+Vβ14+ T cells in peripheral blood and prostate tissue of PCa patients are shown as well as a summary of the data. Several individual patients demonstrate a relative up-regulation of a particular Vβ family within the prostate gland. P values were calculated by paired Student’s t test, two sided.
Figure 2
Variation in clonality by patient and by Vβ family. Flow cytometry data (Fig. 1b-e) are shown as difference between % of prostate CD8+ T cells positive for given Vβ family - % of peripheral blood CD8+ T cells positive for given Vβ family. Positive values indicate higher expression on prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and negative values higher expression on peripheral blood CD8+ T cells. * = Significant difference as defined by % difference > +/−2 standard deviations (S.D.) of expression of Vβ family in peripheral blood of all patients. ND = Not Determined.
Figure 3
Clonality of prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T cells as evidenced by TCR Vβ CDR3 repertoire sequencing. A) RNA from positively isolated peripheral blood and prostate CD8+ T cells was subject to 5′ RACE analysis using a TCR Cβ constant region primer. PCR products were cloned and sequenced. Identical sequences found either five or more times in one anatomic site (blue) or ≥ 5 times in both right and left peripheral prostate (red) are shown. Identical sequences (< 5) were also identified in both right and left peripheral zone of the prostate of Patients 1,2,3,4 and 6. PB = peripheral blood, RP = right peripheral prostate, LP = left peripheral prostate. Number in parentheses is number of clones sequenced. B) Amino acid sequence of junctional regions observed from all sequences belonging to Vβ family 13.6 derived from Patient 1 and Vβ family 2.1 derived from Patient 3. * = Identical sequences observed in both right and left peripheral prostate. C) The same RNA samples used for Patient 1 5′ RACE and sequence analysis were reverse transcribed using an oligo d(T) primer. cDNA was then amplified using a Vβ13.6 family-specific forward primer and a 6-FAM labeled TCR Cβ constant region reverse primer. Spectratyping analysis of the PCR products reveals marked skewing towards one CDR3 region length for both right and left peripheral prostate, indicative of local clonal expansion. These results are in concordance with the nucleotide sequence analyses.
Figure 4
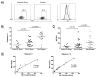
Prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T cells exhibit an exhausted phenotype. A) FACS analysis of prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Plots are gated on CD8+ T cells and gates set using appropriate isotype controls. Far right, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) comparison of peripheral blood CD8+PD-1+ T cells (black histogram) and prostate CD8+PD-1+ T cells (gray histogram). B) Summary of data above. % CD8+ T cells positive for PD-1 are shown. Bar = mean. C) Summary of data above. PD-1 MFI is shown. Bar = mean. P values were calculated for control peripheral blood (P. blood) versus PCa P. blood by unpaired Student’s t test, two sided and for PCa P. blood versus prostate by paired Student’s t test, two sided. D) Correlative analysis for PD-1 MFI for PCa P. blood versus prostate for low grade (Gleason 6) versus high grade (Gleason 7-9) disease.
Similar articles
- T cell receptor sequencing of activated CD8 T cells in the blood identifies tumor-infiltrating clones that expand after PD-1 therapy and radiation in a melanoma patient.
Wieland A, Kamphorst AO, Adsay NV, Masor JJ, Sarmiento J, Nasti TH, Darko S, Douek DC, Xue Y, Curran WJ, Lawson DH, Ahmed R. Wieland A, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018 Nov;67(11):1767-1776. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2228-7. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018. PMID: 30167863 Free PMC article. - Alterations in the T-cell receptor variable beta gene-restricted profile of CD8+ T lymphocytes in the peripheral circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Albers AE, Visus C, Tsukishiro T, Ferris RL, Gooding W, Whiteside TL, De Leo AB. Albers AE, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 15;12(8):2394-403. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1818. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16638844 - Clonality of CD4+ Blood T Cells Predicts Longer Survival With CTLA4 or PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibition in Advanced Melanoma.
Arakawa A, Vollmer S, Tietze J, Galinski A, Heppt MV, Bürdek M, Berking C, Prinz JC. Arakawa A, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 18;10:1336. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01336. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31275310 Free PMC article. - Recent Advances in Targeting CD8 T-Cell Immunity for More Effective Cancer Immunotherapy.
Durgeau A, Virk Y, Corgnac S, Mami-Chouaib F. Durgeau A, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 22;9:14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00014. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29403496 Free PMC article. Review. - Oligoclonal T cells in human cancer.
Halapi E. Halapi E. Med Oncol. 1998 Dec;15(4):203-11. doi: 10.1007/BF02787202. Med Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9951682 Review.
Cited by
- Immunotherapy Vaccines for Prostate Cancer Treatment.
He J, Wu J, Li Z, Zhao Z, Qiu L, Zhu X, Liu Z, Xia H, Hong P, Yang J, Ni L, Lu J. He J, et al. Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70294. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70294. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39463159 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting IRE1α reprograms the tumor microenvironment and enhances anti-tumor immunity in prostate cancer.
Unal B, Kuzu OF, Jin Y, Osorio D, Kildal W, Pradhan M, Kung SHY, Oo HZ, Daugaard M, Vendelbo M, Patterson JB, Thomsen MK, Kuijjer ML, Saatcioglu F. Unal B, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 15;15(1):8895. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53039-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39406723 Free PMC article. - Exploration of the causal relationship between inflammatory cytokines and prostate carcinoma: a comprehensive Mendelian randomization study.
Cai X, Wang D, Ding C, Li Y, Zheng J, Xue W. Cai X, et al. Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 29;14:1381803. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1381803. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39267848 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic profiling of prostate cancer reveals potential prognostic signatures.
Bernatz S, Reddin IG, Fenton TR, Vogl TJ, Wild PJ, Köllermann J, Mandel P, Wenzel M, Hoeh B, Mahmoudi S, Koch V, Grünewald LD, Hammerstingl R, Döring C, Harter PN, Weber KJ. Bernatz S, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Aug 24;150(8):396. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05921-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39180680 Free PMC article. - The cytokine Meteorin-like inhibits anti-tumor CD8+ T cell responses by disrupting mitochondrial function.
Jackson CM, Pant A, Dinalankara W, Choi J, Jain A, Nitta R, Yazigi E, Saleh L, Zhao L, Nirschl TR, Kochel CM, Hwa-Lin Bergsneider B, Routkevitch D, Patel K, Cho KB, Tzeng S, Neshat SY, Kim YH, Smith BJ, Ramello MC, Sotillo E, Wang X, Green JJ, Bettegowda C, Li G, Brem H, Mackall CL, Pardoll DM, Drake CG, Marchionni L, Lim M. Jackson CM, et al. Immunity. 2024 Aug 13;57(8):1864-1877.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.003. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39111315
References
- Karja V, Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Isotalo T, Talja M, Mokka R. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes: A prognostic factor of PSA-free survival in patients with local prostate carcinoma treated by radical prostatectomy. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(6C):4435–4438. - PubMed
- Striebich CC, Falta MT, Wang Y, Bill J, Kotzin BL. Selective accumulation of related CD4+ T cell clones in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1998;161(8):4428–4436. - PubMed
- Sfanos KS, Sauvageot J, Fedor HL, Dick JD, De Marzo AM, Isaacs WB. A molecular analysis of prokaryotic and viral DNA sequences in prostate tissue from patients with prostate cancer indicates the presence of multiple and diverse microorganisms. Prostate. 2008;68(3):306–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2T32DK007552/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA096948/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127153-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007552/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials