Activation and coagulation biomarkers are independent predictors of the development of opportunistic disease in patients with HIV infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2009 Sep 15;200(6):973-83.
doi: 10.1086/605447.
Collaborators, Affiliations
- PMID: 19678756
- PMCID: PMC2892757
- DOI: 10.1086/605447
Randomized Controlled Trial
Activation and coagulation biomarkers are independent predictors of the development of opportunistic disease in patients with HIV infection
Alison J Rodger et al. J Infect Dis. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Activation and coagulation biomarkers were measured within the Strategies for Management of Antiretroviral Therapy (SMART) trial. Their associations with opportunistic disease (OD) in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive patients were examined.
Methods: Inflammatory (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hsCRP], interleukin-6 [IL-6], amyloid-A, and amyloid-P) and coagulation (D-dimer and prothrombin-fragment 1+2) markers were determined. Conditional logistic regression analyses were used to assess associations between these biomarkers and risk of OD.
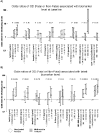
Results: The 91 patients who developed an OD were matched to 182 control subjects. Patients with an hsCRP level > or =5 microg/mL at baseline had a 3.5 higher odds of OD (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.5-8.1) than did those with an hsCRP level <1 microg/mL (P=.003, by test for trend) and patients with an IL-6 level > or =3 pg/mL at baseline had a 2.4 higher odds of OD (95% CI, 1.0-5.4) than did those with an IL-6 level <1.5 pg/mL (P=.02, by test for trend). No other baseline biomarkers predicted development of an OD. Latest follow-up hsCRP level for those with an hsCRP level > or =5 microg/mL (compared with a level <1 microg/mL; odds ratio [OR], 7.6; 95% CI, 2.0-28.5; [P=.002, by test for trend), latest amyloid-A level for those with an amyloid-A level > or =6 mg/L (compared with a level <2 mg/L; OR, 3.8; 95% CI, 1.1-13.4; P=.03, by test for trend), and latest IL-6 level for those with an IL-6 level > or =3 pg/mL (compared with a level <1.5 pg/mL; OR 2.4; 95% CI, 0.7-8.8; P=.04, by test for trend) were also associated with development of an OD.
Conclusions: Higher IL-6 and hsCRP levels independently predicted development of OD. These biomarkers could provide additional prognostic information for predicting the risk of OD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00027352.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No member of the Writing Group for this report has any financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work or constitute a conflict of interest, although most members of the group have, at some stage in the past, received funding from a variety of pharmaceutical companies for research, travel grants, speaking engagements or consultancy fees.
Figures
Figure 1
- P-values are derived from a test for trend in the multivariable analysis (i.e. they evaluate the impact of moving from the reference group to the intermediate group to the group containing the highest level of each biomarker)
- Multivariable models are adjusted for: in A) baseline CD4+ counts and HIV-RNA levels, age and prior AIDS; in B) latest and baseline CD4+ counts and HIV-RNA levels, age and prior AIDS
- Multivariable analyses for CD4+ and HIV-RNA are only adjusted for age and prior AIDS
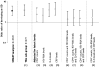
Figure 2
Odds ratios for opportunistic disease – comparisons between the DC arm and the VS arm
Similar articles
- Inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers and mortality in patients with HIV infection.
Kuller LH, Tracy R, Belloso W, De Wit S, Drummond F, Lane HC, Ledergerber B, Lundgren J, Neuhaus J, Nixon D, Paton NI, Neaton JD; INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Kuller LH, et al. PLoS Med. 2008 Oct 21;5(10):e203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050203. PLoS Med. 2008. PMID: 18942885 Free PMC article. - Pre-ART levels of inflammation and coagulation markers are strong predictors of death in a South African cohort with advanced HIV disease.
Ledwaba L, Tavel JA, Khabo P, Maja P, Qin J, Sangweni P, Liu X, Follmann D, Metcalf JA, Orsega S, Baseler B, Neaton JD, Lane HC; Project Phidisa Biomarkers Team. Ledwaba L, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e24243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024243. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22448211 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Biomarkers and electrocardiographic evidence of myocardial ischemia in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection.
Gupta M, Miller CJ, Baker JV, Lazar J, Bogner JR, Calmy A, Soliman EZ, Neaton JD; INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Gupta M, et al. Am J Cardiol. 2013 Mar 1;111(5):760-4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.11.032. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Am J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23276469 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Monocyte-activation phenotypes are associated with biomarkers of inflammation and coagulation in chronic HIV infection.
Wilson EM, Singh A, Hullsiek KH, Gibson D, Henry WK, Lichtenstein K, Önen NF, Kojic E, Patel P, Brooks JT, Sereti I, Baker JV; Study to Understand the Natural History of HIV/AIDS in the Era of Effective Therapy (SUN Study) Investigators. Wilson EM, et al. J Infect Dis. 2014 Nov 1;210(9):1396-406. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu275. Epub 2014 May 9. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24813472 Free PMC article. - Severity of cardiovascular disease outcomes among patients with HIV is related to markers of inflammation and coagulation.
Nordell AD, McKenna M, Borges ÁH, Duprez D, Neuhaus J, Neaton JD; INSIGHT SMART, ESPRIT Study Groups; SILCAAT Scientific Committee. Nordell AD, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 May 28;3(3):e000844. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.000844. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24870935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Distinct intestinal microbial signatures linked to accelerated systemic and intestinal biological aging.
Singh S, Giron LB, Shaikh MW, Shankaran S, Engen PA, Bogin ZR, Bambi SA, Goldman AR, Azevedo JLLC, Orgaz L, de Pedro N, González P, Giera M, Verhoeven A, Sánchez-López E, Pandrea I, Kannan T, Tanes CE, Bittinger K, Landay AL, Corley MJ, Keshavarzian A, Abdel-Mohsen M. Singh S, et al. Microbiome. 2024 Feb 22;12(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01758-4. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38383483 Free PMC article. - Pretreatment levels of soluble cellular receptors and interleukin-6 are associated with HIV disease progression in subjects treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy.
Kalayjian RC, Machekano RN, Rizk N, Robbins GK, Gandhi RT, Rodriguez BA, Pollard RB, Lederman MM, Landay A. Kalayjian RC, et al. J Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 15;201(12):1796-805. doi: 10.1086/652750. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20446847 Free PMC article. - HIV-Related Immune Activation and Inflammation: Current Understanding and Strategies.
Lv T, Cao W, Li T. Lv T, et al. J Immunol Res. 2021 Sep 29;2021:7316456. doi: 10.1155/2021/7316456. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34631899 Free PMC article. Review. - Decreased chronic morbidity but elevated HIV associated cytokine levels in HIV-infected older adults receiving HIV treatment: benefit of enhanced access to care?
Mutevedzi PC, Rodger AJ, Kowal P, Nyirenda M, Newell ML. Mutevedzi PC, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e77379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077379. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24143226 Free PMC article. - Markers of endothelial dysfunction, coagulation and tissue fibrosis independently predict venous thromboembolism in HIV.
Musselwhite LW, Sheikh V, Norton TD, Rupert A, Porter BO, Penzak SR, Skinner J, Mican JM, Hadigan C, Sereti I. Musselwhite LW, et al. AIDS. 2011 Mar 27;25(6):787-95. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283453fcb. AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21412059 Free PMC article.
References
- The Strategies for Management of Antiretroviral Therapy (SMART) Study Group. CD4+ count guided interruptions of antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2283–96. - PubMed
- Hata H, Xiao H, Petrucci MT, Woodliff J, Chang R, Epstein J. IL-6 gene expression in multiple myeloma: A characteristic of immature tumour cells. Blood. 1993;81:3357–64. - PubMed
- Hodge DR, Peng B, Cherry J, et al. Interleukin 6 supports the maintenance of p53 tumour suppressor gene promotor methylation. Cancer Res. 2005;65(11):4673–82. - PubMed
- Volpato S, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, et al. Cardiovascular disease, interleukin-6, and risk of mortality in older women: the women's health and aging study. Circulation. 2001;103(7):947–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI 042170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 46362/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046362/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U122886352/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AI042170-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials