Beyond toxicity: aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated functions in the immune system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Beyond toxicity: aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated functions in the immune system
Brigitta Stockinger. J Biol. 2009.
Abstract
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a ligand-activated transcriptional regulator that binds dioxin and other exogenous contaminants and is responsible for their toxic effects, including immunosuppression. New evidence suggests, however, that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor has a physiological role in the immune system, and the immunosuppressive effects of dioxin may reflect a more subtle disruption of the regulatory interactions between immune cells.
Figures
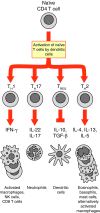
Figure 1
Functional subsets of CD4 T cells. Naïve CD4 T cells – that is, T cells that have not yet been activated by antigen – circulate in the blood and lymph until they are activated, usually by dendritic cells, which are specialized for that function. They then proliferate and differentiate into different functional subsets, distinguished by the different cytokines they produce (indicated under each CD4 T cell type): the cytokines act on other immune cells, activating them in turn. The four known subsets of CD4 T cells are TH1 cells, which induce infl ammatory responses that protect the tissues; TH2 cells, which are largely responsible for protecting the epithelial surfaces of the gut, lung and genitourinary system; TH17 cells, which produce early infl ammatory responses; and TREG cells, which inhibit the responses of the other cell types and are thought to provide protection from autoimmune disease. IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin, NK, natural killer; TGF, transforming growth factor. Modifi ed from Figure 5–22 in DeFranco AL, Locksley RM, Robertson M: Immunity: The Immune Response in Infectious and Infl ammatory Disease. London: New Science Press; 2007.
Similar articles
- Dioxin and immune regulation: emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the generation of regulatory T cells.
Marshall NB, Kerkvliet NI. Marshall NB, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:25-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05125.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20146706 Free PMC article. Review. - The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is functionally upregulated early in the course of human T-cell activation.
Prigent L, Robineau M, Jouneau S, Morzadec C, Louarn L, Vernhet L, Fardel O, Sparfel L. Prigent L, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2014 May;44(5):1330-40. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343920. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24549985 - Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by cAMP vs. dioxin: divergent signaling pathways.
Oesch-Bartlomowicz B, Huelster A, Wiss O, Antoniou-Lipfert P, Dietrich C, Arand M, Weiss C, Bockamp E, Oesch F. Oesch-Bartlomowicz B, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 28;102(26):9218-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503488102. Epub 2005 Jun 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15972329 Free PMC article. - Expression of constitutively-active aryl hydrocarbon receptor in T-cells enhances the down-regulation of CD62L, but does not alter expression of CD25 or suppress the allogeneic CTL response.
Funatake CJ, Ao K, Suzuki T, Murai H, Yamamoto M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kerkvliet NI, Nohara K. Funatake CJ, et al. J Immunotoxicol. 2009 Sep;6(3):194-203. doi: 10.1080/15476910903124454. J Immunotoxicol. 2009. PMID: 19635034 - Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis.
Furue M, Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Tsuji G. Furue M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 31;20(21):5424. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215424. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31683543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genetic susceptibility to nosocomial pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome and poor outcome in patients at risk of critical illness.
Salnikova LE, Smelaya TV, Vesnina IN, Golubev AM, Moroz VV. Salnikova LE, et al. Inflammation. 2014 Apr;37(2):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9740-x. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24127120 - Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Perturbations in Gene Expression during Early Stages of CD4(+) T-cell Differentiation.
Rohlman D, Pham D, Yu Z, Steppan LB, Kerkvliet NI. Rohlman D, et al. Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 6;3:223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00223. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22888330 Free PMC article. - The anti-inflammatory drug leflunomide is an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
O'Donnell EF, Saili KS, Koch DC, Kopparapu PR, Farrer D, Bisson WH, Mathew LK, Sengupta S, Kerkvliet NI, Tanguay RL, Kolluri SK. O'Donnell EF, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 1;5(10):e13128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013128. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20957046 Free PMC article. - Targeted deletion of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in dendritic cells prevents thymic atrophy in response to dioxin.
Beamer CA, Kreitinger JM, Cole SL, Shepherd DM. Beamer CA, et al. Arch Toxicol. 2019 Feb;93(2):355-368. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2366-x. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30499018 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic potential of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in autoimmunity.
Wang XS, Cao F, Zhang Y, Pan HF. Wang XS, et al. Inflammopharmacology. 2020 Feb;28(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00651-z. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Inflammopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31617124 Review.
References
- Fernandez-Salguero PM, Ward JM, Sundberg JP, Gonzalez FJ. Lesions of aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice. Vet Pathol. 1997;34:605–614. - PubMed
- Mimura J, Yamashita K, Nakamura K, Morita M, Takagi TN, Nakao K, Ema M, Sogawa K, Yasuda M, Katsuki M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Loss of teratogenic response to 2,3,7,8-tetra-chlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in mice lacking the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Genes Cells. 1997;2:645–654. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1997.1490345.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources