Insulin resistance and Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Insulin resistance and Alzheimer's disease
Suzanne M de la Monte. BMB Rep. 2009.
Abstract
Emerging data demonstrate pivotal roles for brain insulin resistance and insulin deficiency as mediators of cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration, particularly Alzheimer's disease (AD). Insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) regulate neuronal survival, energy metabolism, and plasticity, which are required for learning and memory. Hence, endogenous brain-specific impairments in insulin and IGF signaling account for the majority of AD-associated abnormalities. However, a second major mechanism of cognitive impairment has been linked to obesity and Type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Human and experimental animal studies revealed that neurodegeneration associated with peripheral insulin resistance is likely effectuated via a liver-brain axis whereby toxic lipids, including ceramides, cross the blood brain barrier and cause brain insulin resistance, oxidative stress, neuro-inflammation, and cell death. In essence, there are dual mechanisms of brain insulin resistance leading to AD-type neurodegeneration: one mediated by endogenous, CNS factors; and the other, peripheral insulin resistance with excess cytotoxic ceramide production.
Figures
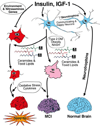
Fig. 1
Dual and overlapping pathways of insulin/IGF resistance mediated neurodegeneration. CNS neuronal survival, metabolic activity, and homeostasis are stimulated by insulin and IGF-1, which promote neurotrophin expression and plasticity for maintenance of normal brain structure, learning, and memory. Peripheral insulin resistance diseases such as T2DM and NASH, contribute to neurodegeneration through increased production of cytotoxic ceramides and other toxic lipids, which cause insulin resistance, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and limited neurodegeneration. Environmental exposures, including nitrosamines, plus genetic factors, cause insulin and IGF resistance, which leads to neurodegeneration. T2DM and other peripheral insulin resistance diseases exacerbate the neurodegeneration cascade due to increased production of toxic lipids and ceramides. Finally, oxidative stress and cytokine activation contribute to neurodegeneration and dementia, but alone are not sufficient to cause dementia.
Similar articles
- Contributions of brain insulin resistance and deficiency in amyloid-related neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease.
de la Monte SM. de la Monte SM. Drugs. 2012 Jan 1;72(1):49-66. doi: 10.2165/11597760-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22191795 Free PMC article. Review. - Brain metabolic dysfunction at the core of Alzheimer's disease.
de la Monte SM, Tong M. de la Monte SM, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 15;88(4):548-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24380887 Free PMC article. Review. - Metabolic derangements mediate cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: role of peripheral insulin-resistance diseases.
De La Monte SM. De La Monte SM. Panminerva Med. 2012 Sep;54(3):171-8. Panminerva Med. 2012. PMID: 22801434 Free PMC article. Review. - Triangulated mal-signaling in Alzheimer's disease: roles of neurotoxic ceramides, ER stress, and insulin resistance reviewed.
de la Monte SM. de la Monte SM. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30 Suppl 2(0 2):S231-49. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111727. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22337830 Free PMC article. Review. - Ceramide-mediated insulin resistance and impairment of cognitive-motor functions.
de la Monte SM, Tong M, Nguyen V, Setshedi M, Longato L, Wands JR. de la Monte SM, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(3):967-84. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-091726. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20693650 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Insulin resistance in the nervous system.
Kim B, Feldman EL. Kim B, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar;23(3):133-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.12.004. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22245457 Free PMC article. Review. - Association of Insulin Resistance With Cerebral Glucose Uptake in Late Middle-Aged Adults at Risk for Alzheimer Disease.
Willette AA, Bendlin BB, Starks EJ, Birdsill AC, Johnson SC, Christian BT, Okonkwo OC, La Rue A, Hermann BP, Koscik RL, Jonaitis EM, Sager MA, Asthana S. Willette AA, et al. JAMA Neurol. 2015 Sep;72(9):1013-20. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0613. JAMA Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26214150 Free PMC article. - A State-of-Art Review of the Vicious Circle of Sleep Disorders, Diabetes and Neurodegeneration Involving Metabolism and Microbiota Alterations.
Versace S, Pellitteri G, Sperotto R, Tartaglia S, Da Porto A, Catena C, Gigli GL, Cavarape A, Valente M. Versace S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 25;24(13):10615. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310615. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445790 Free PMC article. Review. - A Review of miRNAs as Biomarkers and Effect of Dietary Modulation in Obesity Associated Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Perdoncin M, Konrad A, Wyner JR, Lohana S, Pillai SS, Pereira DG, Lakhani HV, Sodhi K. Perdoncin M, et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 7;14:756499. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.756499. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34690698 Free PMC article. Review. - Altered expression of insulin-degrading enzyme and regulator of calcineurin in the rat intracerebral streptozotocin model and human apolipoprotein E-ε4-associated Alzheimer's disease.
Delikkaya B, Moriel N, Tong M, Gallucci G, de la Monte SM. Delikkaya B, et al. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2019 May 15;11:392-404. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.03.004. eCollection 2019 Dec. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31193223 Free PMC article.
References
- de la Monte SM, Wands JR. Review of insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression, signaling, and malfunction in the central nervous system: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2005;7:45–61. - PubMed
- Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease--is this type 3 diabetes? J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2005;7:63–80. - PubMed
- D'Ercole AJ, Ye P, Calikoglu AS, Gutierrez-Ospina G. The role of the insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996;13:227–255. - PubMed
- Wozniak M, Rydzewski B, Baker SP, Raizada MK. The cellular and physiological actions of insulin in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 1993;22:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AA-12908/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA011431/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA-11431/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012908/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AA011431/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA-16126/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011431/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AA016126/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical