Directed evolution: new parts and optimized function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Directed evolution: new parts and optimized function
Michael J Dougherty et al. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
Constructing novel biological systems that function in a robust and predictable manner requires better methods for discovering new functional molecules and for optimizing their assembly in novel biological contexts. By enabling functional diversification and optimization in the absence of detailed mechanistic understanding, directed evolution is a powerful complement to 'rational' engineering approaches. Aided by clever selection schemes, directed evolution has generated new parts for genetic circuits, cell-cell communication systems, and non-natural metabolic pathways in bacteria.
Figures
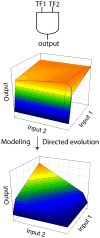
Figure 1
Synthetic gene circuits frequently do not function as designed due to mismatches in component properties. Mathematical modeling combined with directed evolution can rapidly tune circuit performance. For example, the sensitivities of two transcription factors to individual inputs can be tuned to generate a functional AND gate from a non-functional circuit.
Figure 2
Directed evolution can be used to generate novel metabolic routes to useful chemicals. A phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-independent route (shown in black) to the key intermediate, 3-deoxy-D-_arabino_-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP), was engineered by using directed evolution to enhance a weak DAHP-synthesizing activity present in 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogalactonate (KDPGal) aldolase [23•]. The original route using DAHP synthase is shown in gray.
Similar articles
- Directed Evolution: Methodologies and Applications.
Wang Y, Xue P, Cao M, Yu T, Lane ST, Zhao H. Wang Y, et al. Chem Rev. 2021 Oct 27;121(20):12384-12444. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00260. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 34297541 Review. - Directed evolution: the 'rational' basis for 'irrational' design.
Tobin MB, Gustafsson C, Huisman GW. Tobin MB, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2000 Aug;10(4):421-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00109-3. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 10981629 Review. - Learning Strategies in Protein Directed Evolution.
Cadet XF, Gelly JC, van Noord A, Cadet F, Acevedo-Rocha CG. Cadet XF, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2461:225-275. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2152-3_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35727454 Review. - Continuous directed evolution for strain and protein engineering.
d'Oelsnitz S, Ellington A. d'Oelsnitz S, et al. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2018 Oct;53:158-163. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.12.020. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29444489 Review. - Optimizing non-natural protein function with directed evolution.
Brustad EM, Arnold FH. Brustad EM, et al. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Apr;15(2):201-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.11.020. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21185770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Twins, quadruplexes, and more: functional aspects of native and engineered RNA self-assembly in vivo.
Lease RA, Arluison V, Lavelle C. Lease RA, et al. Front Life Sci. 2012 Mar;6(1-2):19-32. doi: 10.1080/21553769.2012.761163. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Front Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 23914307 Free PMC article. - Technologies of directed protein evolution in vivo.
Blagodatski A, Katanaev VL. Blagodatski A, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Apr;68(7):1207-14. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0610-5. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21190058 Free PMC article. Review. - The coming of age of de novo protein design.
Huang PS, Boyken SE, Baker D. Huang PS, et al. Nature. 2016 Sep 15;537(7620):320-7. doi: 10.1038/nature19946. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27629638 Review. - Funneled energy landscape unifies principles of protein binding and evolution.
Yan Z, Wang J. Yan Z, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 3;117(44):27218-27223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013822117. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33067388 Free PMC article. - A hierarchy of coupling free energies underlie the thermodynamic and functional architecture of protein structures.
Naganathan AN, Kannan A. Naganathan AN, et al. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021 Oct 8;3:257-267. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2021.09.003. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 34704074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Canton B, Labno A, Endy D. Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:787–793. - PubMed
- Jackel C, Kast P, Hilvert D. Protein design by directed evolution. Annu Rev Biophys. 2008;37:153–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM074712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM78975/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068664/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074712-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM078975/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources