XBP1 governs late events in plasma cell differentiation and is not required for antigen-specific memory B cell development - PubMed (original) (raw)
XBP1 governs late events in plasma cell differentiation and is not required for antigen-specific memory B cell development
Derrick J Todd et al. J Exp Med. 2009.
Abstract
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a stress response pathway that is driven by the increased load of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum of highly secretory cells such as plasma cells (PCs). X box binding protein 1 (XBP1) is a transcription factor that mediates one branch of the UPR and is crucial for the development of antibody-secreting PCs. PCs represent only one class of terminally differentiated B cells, however, and little is known about the role for XBP1 in the other class: memory B cells. We have developed an XBP1(fl/fl) CD19(+/cre) conditional knockout (XBP1(CD19)) mouse to build upon our current understanding of the function of XBP1 in PC differentiation as well as to explore the role of XBP1 in memory cell development. Using this model, we show that XBP1(CD19) mice are protected from disease in an autoantibody-mediated mouse lupus model. We also identify a novel developmental stage at which B cells express the traditional PC marker CD138 (syndecan-1) but have yet to undergo XBP1-dependent functional and morphological differentiation into antibody-secreting cells. Finally, we show that memory B cells develop normally in XBP1(CD19) mice, demonstrating that XBP1-mediated functions occur independently of any memory cell lineage commitment.
Figures
Figure 1.
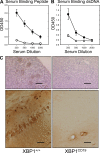
Female XBP1+/+ and XBP1CD19 mice were immunized i.p. with 100 µg MAP-DWEYS in CFA followed by booster immunizations with 100 µg MAP-DWEYS in IFA on days 14 and 28. (A and B) On day 35, serum was tested for anti-DWEYS (peptide; A) and anti-dsDNA (B) antibodies by ELISA of four serum dilutions. In both panels, each circle represents the mean ± SEM value for XBP1+/+ (closed circles) or XBP1CD19 (open circles) mice. (C) XBP1+/+ and XBP1CD19 mice from A and B were treated i.p. with 3 mg/kg LPS on days 52 and +54. Shown are representative images of IgG-specific IHC of kidney (top) and hippocampus (bottom) of mice 4–7 d after LPS treatment. XBP1+/+ mice demonstrated anti-IgG binding to neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. There was no anti-IgG binding in any of the XBP1CD19 animals. Bars: (kidney) 200 µm; (hippocampus) 100 µm. All panels represent results from a single experiment with five mice per group. A second independent experiment reproduced these findings (not depicted).
Figure 2.
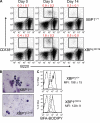
XBP1+/+ and XBP1CD19 mice were immunized i.p. with a single 100-µg dose of NP-KLH in alum. (A) Representative flow cytometry of cell surface CD138 (y axis) and B220 (x axis) expression in splenocytes isolated from XBP1+/+ and XBP1CD19 mice at days 0, 5, and 14 after immunization. Mean percentage ± SEM of B220int CD138+ cells is indicated. (B) B220int CD138+ cells were isolated by FACS from a subset of splenocytes at day 5 after immunization. Cytospin preparations of cells were stained with modified Wright-Giemsa stain. (C) Splenocytes were isolated from mice on day 5 after immunization and incubated with Brefeldin A BODIPY, which selectively stains ER and Golgi organelles. Shown are representative flow cytometry histograms for B220int CD138+ cells (solid line), B220+ CD138− cells (long dashed line), and unstained cells (short dashed line). Brefeldin A-BODIPY mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± SEM is indicated for B220int CD138+ cells (no difference in B220+ CD138− cells). All experiments were performed with individual mice in at least three independent experiments.
Figure 3.
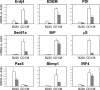
XBP1+/+ and XBP1CD19 mice were immunized i.p. with a single 100-µg dose of NP-KLH in alum. At day 5 after immunization, splenocytes were isolated and sorted by FACS for B220+ CD138− (B220) and B220int CD138+ (CD138) populations. Panels show relative expression of indicated mRNA versus actin as measured by RT-PCR of cDNA prepared from indicated cell populations. In all panels, each bar represents the mean ± SEM value of individual XBP1+/+ (open bar) and XBP1CD19 (solid bar) mice in three independent experiments.
Figure 4.
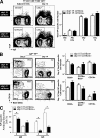
Memory B cells are present in normal numbers in XBP1CD19 mice. (A, left) Representative expression of IgD and NP on [PI, CD4, CD8, F4/80, GR1]neg splenocytes of day-14 mice immunized with Ribi (adjuvant) only (left) or NP-KLH in Ribi (right). Shown are XBP1fl/fl CD19+/+ (XBP1+/+) mice (top) and XBP1fl/fl CD19cre/+ (XBP1CD19) littermates (bottom). The inset represents the percentage of cells within profile (mean ± SEM; n = 3). (A, right) Total number of IgDlo NP-specific B cells from day 0 (naive BALB/c), adjuvant only (day 14 Ribi only), day 5, and day 14 NP-KLH in Ribi immunized XBP1+/+ mice (white columns) and XBP1CD19 (black columns) mice (mean ± SEM; n = 3). (B, left) Representative expression of B220 and CD138 at the surface of IgDlo NP-specific B cells at days 5 (left) and 14 (right) from XBP1+/+ mice (top) and XBP1CD19 littermates (bottom). The inset represents the percentage of cells within profile (mean ± SEM; n = 3). (B, right) Total number of NP-specific B cells compartment B220+, CD79b+ B220lo, or CD138+ at day 5 (top) or day 14 (bottom) immunized XBP1+/+ (white columns) and XBP1CD19 (black columns) mice (mean ± SEM; n = 3; unpaired Student's t test; P > 0.05 for all data points). (C) [PI, CD4, CD8, F4/80, GR1]neg IgDlo NP+ CD138+ splenocytes of day-5 and day-14 immunized mice were sorted directly ex vivo into NP-specific Ig (IgM or IgG) revealing ELISPOT assays. Positives were scored manually under a dissection microscope. Each assay was done in triplicate from three separate animals (mean ± SEM; n = 3; unpaired Student's t test; *, P ≤ 0.05).
Similar articles
- XBP1, downstream of Blimp-1, expands the secretory apparatus and other organelles, and increases protein synthesis in plasma cell differentiation.
Shaffer AL, Shapiro-Shelef M, Iwakoshi NN, Lee AH, Qian SB, Zhao H, Yu X, Yang L, Tan BK, Rosenwald A, Hurt EM, Petroulakis E, Sonenberg N, Yewdell JW, Calame K, Glimcher LH, Staudt LM. Shaffer AL, et al. Immunity. 2004 Jul;21(1):81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.010. Immunity. 2004. PMID: 15345222 - An in vitro model of differentiation of memory B cells into plasmablasts and plasma cells including detailed phenotypic and molecular characterization.
Jourdan M, Caraux A, De Vos J, Fiol G, Larroque M, Cognot C, Bret C, Duperray C, Hose D, Klein B. Jourdan M, et al. Blood. 2009 Dec 10;114(25):5173-81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235960. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19846886 Free PMC article. - IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response.
Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Kaufman RJ. Lee K, et al. Genes Dev. 2002 Feb 15;16(4):452-66. doi: 10.1101/gad.964702. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11850408 Free PMC article. - The emerging role of XBP1 in cancer.
Chen S, Chen J, Hua X, Sun Y, Cui R, Sha J, Zhu X. Chen S, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jul;127:110069. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110069. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32294597 Review. - The X-box binding protein-1 transcription factor is required for plasma cell differentiation and the unfolded protein response.
Iwakoshi NN, Lee AH, Glimcher LH. Iwakoshi NN, et al. Immunol Rev. 2003 Aug;194:29-38. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2003.00057.x. Immunol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12846805 Review.
Cited by
- Single-cell RNA sequencing of human femoral head _in vivo.
Qiu X, Liu Y, Shen H, Wang Z, Gong Y, Yang J, Li X, Zhang H, Chen Y, Zhou C, Lv W, Cheng L, Hu Y, Li B, Shen W, Zhu X, Tan LJ, Xiao HM, Deng HW. Qiu X, et al. Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 10;13(11):15595-15619. doi: 10.18632/aging.203124. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34111027 Free PMC article. - A CRISPR/Cas9-mediated screen identifies determinants of early plasma cell differentiation.
Xiong E, Popp O, Salomon C, Mertins P, Kocks C, Rajewsky K, Chu VT. Xiong E, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1083119. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1083119. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685499 Free PMC article. - Factors Affecting Early Antibody Secreting Cell Maturation Into Long-Lived Plasma Cells.
Nguyen DC, Joyner CJ, Sanz I, Lee FE. Nguyen DC, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 11;10:2138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02138. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572364 Free PMC article. Review. - Longitudinal Dynamics of Human B-Cell Response at the Single-Cell Level in Response to Tdap Vaccination.
Khatri I, Diks AM, van den Akker EB, Oosten LEM, Zwaginga JJ, Reinders MJT, van Dongen JJM, Berkowska MA. Khatri I, et al. Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;9(11):1352. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111352. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835283 Free PMC article. - IFITM3 affects the level of antibody response after influenza vaccination.
Lei N, Li Y, Sun Q, Lu J, Zhou J, Li Z, Liu L, Guo J, Qin K, Wang H, Zhao J, Li C, Sun L, Wang D, Zhao Z, Shu Y. Lei N, et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):976-987. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1756696. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32321380 Free PMC article.
References
- Angelin-Duclos C., Cattoretti G., Lin K.I., Calame K. 2000. Commitment of B lymphocytes to a plasma cell fate is associated with Blimp-1 expression in vivo.J. Immunol. 165:5462–5471 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI32412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007530/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI047231/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials