Chemotaxis in neutrophil-like HL-60 cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Chemotaxis in neutrophil-like HL-60 cells
Arthur Millius et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2009.
Abstract
Asymmetric localization of intracellular proteins and signals directs movement during axon guidance, endothelial cell invasion, and immune cell migration. In these processes, cell movement is guided by external chemical cues in a process known as chemotaxis. In particular, leukocyte migration in the innate immune system has been studied in the human neutrophil-like cell line (HL-60). Here, we describe the maintenance and transfection of HL-60 cells and explain how to analyze their behavior with two standard chemotactic assays. Finally, we demonstrate how to fix and stain the actin cytoskeleton of polarized cells for fluorescent microscopy imaging.
Figures
Fig. 1
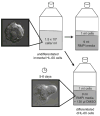
Passaging and differentiating HL-60 cells. When cells reach a density between 1 and 2 million cells/ml, split to 0.15 million cells/ml in a total volume of 10 ml prewarmed culture medium. Differentiate cells in culture medium plus 1.3% DMSO; cells take ~5 days to become migratory.
Fig. 2
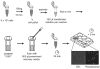
Transient transfection of HL-60 cells with amaxa nucleofection. Spin ~5 million cells at 100 × g. Aspirate supernatant and resuspend pellet in 100 μl transfection solution per reaction and nucleofect with amaxa program “Y-001.” Flush with prewarmed recovery medium and incubate in an Eppendorf tube for 30 min. Transfer to a 6-well dish with 1.5 ml of recovery medium; expression occurs after 2 h. Shown is an example of HL-60 cells 5 h after transfection with GFP visualized with DIC and fluorescence microscopy.
Fig. 3
Preparing a coverslip for live cell microscopy. (a) Dissolve 1 mg of bovine fibronectin in sterile water. After 1 h, add 4 ml of PBS and store 200 μg/ml fibronectin solution at 4°C. (b) Remove gaskets from plastic permanox 8-well chamber. Cut epoxy mold squares and stick to No. 1.5 gold seal cover glass. Add 125 μl of fibronectin, let sit for 1 h, rinse once with RPMI culture medium, and store in RPMI medium until ready to image.
Fig. 4
An example of an HL-60 cell crawling toward a micropipette visualized with DIC and TIRF microscopy. Asterisk indicates micropipette tip.
Fig. 5
The components of the EZ-TAXIS system are shown in (a) with the individual components in their order of assembly from top to bottom shown in (b). (c) An example of HL-60 cells migrating toward chemoattractant in the EZ-TAXIS assay visualized with brightfield microscopy.
Fig. 6
Staining the actin cytoskeleton. Add 2× fixation buffer to plated cells and fix for 20 min at 4°C. Remove fixation buffer and replace with stain buffer for 20 min; protect from light. Shown is an example of an HL-60 cell stained with rhodamine phalloidin visualized with structured illumination microscopy.
Similar articles
- Manipulation of neutrophil-like HL-60 cells for the study of directed cell migration.
Millius A, Weiner OD. Millius A, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;591:147-58. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-404-3_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19957129 Free PMC article. - Differentiated HL-60 cells are a valid model system for the analysis of human neutrophil migration and chemotaxis.
Hauert AB, Martinelli S, Marone C, Niggli V. Hauert AB, et al. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;34(7):838-54. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00010-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11950599 - Asymmetric localization of calpain 2 during neutrophil chemotaxis.
Nuzzi PA, Senetar MA, Huttenlocher A. Nuzzi PA, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Mar;18(3):795-805. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-09-0876. Epub 2006 Dec 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17192410 Free PMC article. - Directed migration of mesenchymal cells: where signaling and the cytoskeleton meet.
Bear JE, Haugh JM. Bear JE, et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;30:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24999834 Free PMC article. Review. - Signal transduction in neutrophil chemotaxis.
Katanaev VL. Katanaev VL. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2001 Apr;66(4):351-68. doi: 10.1023/a:1010293809553. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2001. PMID: 11403641 Review.
Cited by
- Oxidatively modified phosphatidylserines on the surface of apoptotic cells are essential phagocytic 'eat-me' signals: cleavage and inhibition of phagocytosis by Lp-PLA2.
Tyurin VA, Balasubramanian K, Winnica D, Tyurina YY, Vikulina AS, He RR, Kapralov AA, Macphee CH, Kagan VE. Tyurin VA, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2014 May;21(5):825-35. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.1. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24464221 Free PMC article. - GPCR-mediated PLCβγ/PKCβ/PKD signaling pathway regulates the cofilin phosphatase slingshot 2 in neutrophil chemotaxis.
Xu X, Gera N, Li H, Yun M, Zhang L, Wang Y, Wang QJ, Jin T. Xu X, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Mar 1;26(5):874-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-05-0982. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25568344 Free PMC article. - ELMO1 Directly Interacts with Gβγ Subunit to Transduce GPCR Signaling to Rac1 Activation in Chemotaxis.
Wang Y, Xu X, Pan M, Jin T. Wang Y, et al. J Cancer. 2016 May 12;7(8):973-83. doi: 10.7150/jca.15118. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27313788 Free PMC article. - Intestinal mucin activates human dendritic cells and IL-8 production in a glycan-specific manner.
Melo-Gonzalez F, Fenton TM, Forss C, Smedley C, Goenka A, MacDonald AS, Thornton DJ, Travis MA. Melo-Gonzalez F, et al. J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 1;293(22):8543-8553. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.789305. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29581231 Free PMC article. - Microfluidic device capable of medium recirculation for non-adherent cell culture.
Dixon AR, Rajan S, Kuo CH, Bersano T, Wold R, Futai N, Takayama S, Mehta G. Dixon AR, et al. Biomicrofluidics. 2014 Feb 25;8(1):016503. doi: 10.1063/1.4865855. eCollection 2014 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2014. PMID: 24753733 Free PMC article.
References
- Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, et al. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science. 2003;302:1704–1709. - PubMed
- Collins SJ, Gallo RC, Gallagher RE. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977;270:347–349. - PubMed
- Rao KM, Currie MS, Ruff JC, Cohen HJ. Lack of correlation between induction of chemotactic peptide receptors and stimulus-induced actin polymerization in HL-60 cells treated with dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate or retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 1988;48:6721–6726. - PubMed
- Carter BZ, Milella M, Tsao T, McQueen T, Schober WD, Hu W, et al. Regulation and targeting of antiapoptotic XIAP in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2003;17:2081–2089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources