MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
. 2009 Oct 1;15(19):6192-200.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1467. Epub 2009 Sep 29.
Giang Huong Nguyen, Elise D Bowman, Yiqiang Zhao, Anuradha Budhu, Aaron J Schetter, Rosemary Braun, Mark Reimers, Kensuke Kumamoto, Duncan Hughes, Nasser K Altorki, Alan G Casson, Chang-Gong Liu, Xin Wei Wang, Nozomu Yanaihara, Nobutoshi Hagiwara, Andrew J Dannenberg, Masao Miyashita, Carlo M Croce, Curtis C Harris
Affiliations
- PMID: 19789312
- PMCID: PMC2933109
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1467
Multicenter Study
MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival
Ewy A Mathé et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2009.
Abstract
Purpose: The dismal outcome of esophageal cancer patients highlights the need for novel prognostic biomarkers, such as microRNAs (miRNA). Although recent studies have established the role of miRNAs in esophageal carcinoma, a comprehensive multicenter study investigating different histologic types, including squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and adenocarcinoma with or without Barrett's, is still lacking.
Experimental design: miRNA expression was measured in cancerous and adjacent noncancerous tissue pairs collected from 100 adenocarcinoma and 70 SCC patients enrolled at four clinical centers from the United States, Canada, and Japan. Microarray-based expression was measured in a subset of samples in two cohorts and was validated in all available samples.
Results: In adenocarcinoma patients, miR-21, miR-223, miR-192, and miR-194 expression was elevated, whereas miR-203 expression was reduced in cancerous compared with noncancerous tissue. In SCC patients, we found elevated miR-21 and reduced miR-375 expression levels in cancerous compared with noncancerous tissue. When comparing cancerous tissue expression between adenocarcinoma and SCC patients, miR-194 and miR-375 were elevated in adenocarcinoma patients. Significantly, elevated miR-21 expression in noncancerous tissue of SCC patients and reduced levels of miR-375 in cancerous tissue of adenocarcinoma patients with Barrett's were strongly associated with worse prognosis. Associations with prognosis were independent of tumor stage or nodal status, cohort type, and chemoradiation therapy.
Conclusions: Our multicenter-based results highlight miRNAs involved in major histologic types of esophageal carcinoma and uncover significant associations with prognosis. Elucidating miRNAs relevant to esophageal carcinogenesis is potentially clinically useful for developing prognostic biomarkers and identifying novel drug targets and therapies.
Figures
Figure 1
Study design flow chart. Differential expression analysis and associations with prognosis were performed in patients with ADC and SCC, separately. Microarray analysis was performed on a subset of samples as a hypothesis-generating tool to subsequently focus further validation on a subset of miRNAs that are potentially relevant to esophageal carcinogenesis. Validation using qRT-PCR was performed on all samples available.
Figure 2
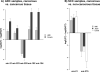
qRT-PCR validation of differentially expressed miRNAs. A) Altered expression between cancerous tissue (NCT) and non-cancerous tissue (NCT) in ADC patients is shown. Mir-21, mir-223, mir-192, and mir-194 are over-expressed in tumors while mir-203 is under-expressed in tumors. B) Differential expression between CT and NCT in SCC patients demonstrates that mir-21 is up-regulated and mir-375 is down-regulated in SCC tumors. All expression values are normalized to RNAU66, and differential expression is statistically significant (P<0.005).
Figure 3
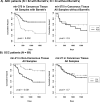
Kaplan-Meier Analysis depicting associations with qRT-PCR miRNA expression and survival. MiRNA expression values were dichotomized into low and high groups, using the within cohort median expression value as a cutoff. A) Associations observed in adenocarcinoma (ADC) patients with and without Barrett's. Reduced expression of mir-375 in cancerous tissue of ADC patients with Barrett's is associated with worse prognosis. This association is not observed in ADC patients without Barrett's. Survival profiles were compared using the log rank test. B) Associations observed in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) patients. Elevated expression of mir-21 in non-cancerous tissue is associated with worse prognosis. This association is not found when cancerous tissue expression is evaluated.
Similar articles
- MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer.
Feber A, Xi L, Luketich JD, Pennathur A, Landreneau RJ, Wu M, Swanson SJ, Godfrey TE, Litle VR. Feber A, et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008 Feb;135(2):255-60; discussion 260. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.08.055. Epub 2007 Dec 26. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. PMID: 18242245 Free PMC article. - Dynamic changes in microRNA expression profiles reflect progression of Barrett's esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Slaby O, Srovnal J, Radova L, Gregar J, Juracek J, Luzna P, Svoboda M, Hajduch M, Ehrmann J. Slaby O, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2015 May;36(5):521-7. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv023. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25784377 Clinical Trial. - MicroRNA profile in neosquamous esophageal mucosa following ablation of Barrett's esophagus.
Sreedharan L, Mayne GC, Watson DI, Bright T, Lord RV, Ansar A, Wang T, Kist J, Astill DS, Hussey DJ. Sreedharan L, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 14;23(30):5508-5518. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5508. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28852310 Free PMC article. - A review of the current understanding and clinical utility of miRNAs in esophageal cancer.
Sakai NS, Samia-Aly E, Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. Sakai NS, et al. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013 Dec;23(6 Pt B):512-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013. PMID: 24013023 Review. - MicroRNAs and esophageal cancer--implications for pathogenesis and therapy.
Mayne GC, Hussey DJ, Watson DI. Mayne GC, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(7):1211-26. doi: 10.2174/138161213804805702. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23092342 Review.
Cited by
- Genomics, microRNA, epigenetics, and proteomics for future diagnosis, treatment and monitoring response in upper GI cancers.
Brücher BL, Li Y, Schnabel P, Daumer M, Wallace TJ, Kube R, Zilberstein B, Steele S, Voskuil JL, Jamall IS. Brücher BL, et al. Clin Transl Med. 2016 Mar;5(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0093-6. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27053248 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human gastric cancer by targeting FBXW7/hCdc4.
Li J, Guo Y, Liang X, Sun M, Wang G, De W, Wu W. Li J, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 May;138(5):763-74. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1154-x. Epub 2012 Jan 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22270966 - GERD-Barrett-Adenocarcinoma: Do We Have Suitable Prognostic and Predictive Molecular Markers?
Illig R, Klieser E, Kiesslich T, Neureiter D. Illig R, et al. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:643084. doi: 10.1155/2013/643084. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013. PMID: 23573078 Free PMC article. - System Review about Function Role of ESCC Driver Gene KDM6A by Network Biology Approach.
Ran J, Li H, Li H. Ran J, et al. ScientificWorldJournal. 2016;2016:1970904. doi: 10.1155/2016/1970904. Epub 2016 May 17. ScientificWorldJournal. 2016. PMID: 27294188 Free PMC article. - Mir-375 enhances ruthenium-derived compound Rawq01 induced cell death in human ovarian cancer.
Shao X, Mei W, Weng W, Qin J, Zhou J, Liu J, Cheng J. Shao X, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 May 15;6(6):1095-102. Print 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23696927 Free PMC article.
References
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
- Sant M, Aareleid T, Berrino F, et al. EUROCARE-3: survival of cancer patients diagnosed 1990-94--results and commentary. Ann Oncol. 2003;14(Suppl 5):v61–118. - PubMed
- Surveillance and Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) 2007.
- Crew KD, Neugut AI. Epidemiology of upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:450–64. - PubMed
- Maley CC, Rustgi AK. Barrett's esophagus and its progression to adenocarcinoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2006;4:367–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials