Reduced occipital and prefrontal brain volumes in dysbindin-associated schizophrenia - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.140.
Thomas Frodl, Derek Morris, Ilaria Spoletini, Dara M Cannon, Andrea Cherubini, Carlo Caltagirone, Paola Bossù, Colm McDonald, Michael Gill, Aiden P Corvin, Gianfranco Spalletta
Affiliations
- PMID: 19794403
- PMCID: PMC3055383
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.140
Reduced occipital and prefrontal brain volumes in dysbindin-associated schizophrenia
Gary Donohoe et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
A three-marker C-A-T dysbindin haplotype identified by Williams et al (PMID: 15066891) is associated with increased risk for schizophrenia, decreased mRNA expression, poorer cognitive performance, and early sensory processing deficits. We investigated whether this same dysbindin risk haplotype was also associated with structural variation in the gray matter volume (GMV). Using voxel-based morphometry, whole-volume analysis revealed significantly reduced GMVs in both the right dorsolateral prefrontal and left occipital cortex, corresponding to the behavioral findings of impaired spatial working memory and EEG findings of impaired visual processing already reported. These data provide important evidence of the influence of dysbindin risk variants on brain structure, and suggest a possible mechanism by which disease risk is being increased.
Figures
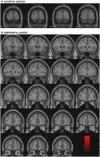
Figure 1
Differences between patient carriers and non-carriers of the dysbindin-risk haplotype. Risk carriers show significantly smaller gray matter volumes in (a) left occipital cortex and (b) right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (FWE corrected).
Similar articles
- Impact of schizophrenia-risk gene dysbindin 1 on brain activation in bilateral middle frontal gyrus during a working memory task in healthy individuals.
Markov V, Krug A, Krach S, Jansen A, Eggermann T, Zerres K, Stöcker T, Shah NJ, Nöthen MM, Treutlein J, Rietschel M, Kircher T. Markov V, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010 Feb;31(2):266-75. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20862. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010. PMID: 19650139 Free PMC article. - Early visual processing deficits in dysbindin-associated schizophrenia.
Donohoe G, Morris DW, De Sanctis P, Magno E, Montesi JL, Garavan HP, Robertson IH, Javitt DC, Gill M, Corvin AP, Foxe JJ. Donohoe G, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Mar 1;63(5):484-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.07.022. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17945199 - The DTNBP1 (dysbindin-1) gene variant rs2619522 is associated with variation of hippocampal and prefrontal grey matter volumes in humans.
Trost S, Platz B, Usher J, Scherk H, Wobrock T, Ekawardhani S, Meyer J, Reith W, Falkai P, Gruber O. Trost S, et al. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013 Feb;263(1):53-63. doi: 10.1007/s00406-012-0320-0. Epub 2012 May 13. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22580710 Free PMC article. - [Advances in the studies of the dysbindin gene in schizophrenia].
Zhao GF, Deng H, Yang YC, Chen Y. Zhao GF, et al. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Apr;26(2):175-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2009.02.012. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19350510 Review. Chinese. - Cognitive heterogeneity in schizophrenia.
Joyce EM, Roiser JP. Joyce EM, et al. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2007 May;20(3):268-72. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0b013e3280ba4975. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17415081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Increased dysbindin-1B isoform expression in schizophrenia and its propensity in aggresome formation.
Xu Y, Sun Y, Ye H, Zhu L, Liu J, Wu X, Wang L, He T, Shen Y, Wu JY, Xu Q. Xu Y, et al. Cell Discov. 2015 Nov 10;1:15032. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.32. eCollection 2015. Cell Discov. 2015. PMID: 27462430 Free PMC article. - Imaging genetics and psychiatric disorders.
Hashimoto R, Ohi K, Yamamori H, Yasuda Y, Fujimoto M, Umeda-Yano S, Watanabe Y, Fukunaga M, Takeda M. Hashimoto R, et al. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(2):168-75. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150303104159. Curr Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25732148 Free PMC article. Review. - Developmental Genes and Regulatory Proteins, Domains of Cognitive Impairment in Schizophrenia Spectrum Psychosis and Implications for Antipsychotic Drug Discovery: The Example of Dysbindin-1 Isoforms and Beyond.
Waddington JL, Zhen X, O'Tuathaigh CMP. Waddington JL, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 29;10:1638. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01638. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32063853 Free PMC article. Review. - Cell biology of the BLOC-1 complex subunit dysbindin, a schizophrenia susceptibility gene.
Mullin AP, Gokhale A, Larimore J, Faundez V. Mullin AP, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Aug;44(1):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8183-3. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21520000 Free PMC article. Review. - Analysis of schizophrenia-related genes and electrophysiological measures reveals ZNF804A association with amplitude of P300b elicited by novel sounds.
Del Re EC, Bergen SE, Mesholam-Gately RI, Niznikiewicz MA, Goldstein JM, Woo TU, Shenton ME, Seidman LJ, McCarley RW, Petryshen TL. Del Re EC, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Jan 14;4(1):e346. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.117. Transl Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24424392 Free PMC article.
References
- Allen brain atlas 2009. Allen Institute for Brain Science. . http://www.brain-map.org Accessed on 15 June 2009.
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage. 2005;26:839–851. - PubMed
- Bach Cuadra M, Cammoun L, Butz T, Cuisenaire O, Thiran JP. Comparison and validation of tissue modelization and statistical classification methods in T1-weighted MR brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005;24:1548–1565. - PubMed
- Bray NJ, Preece A, Williams NM, Moskvina V, Buckland PR, Owen MJ, et al. Haplotypes at the dystrobrevin binding protein 1 (DTNBP1) gene locus mediate risk for schizophrenia through reduced DTNBP1 expression. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:1947–1954. - PubMed
- Burdick KE, Lencz T, Funke B, Finn CT, Szeszko PR, Kane JM, et al. Genetic variation in DTNBP1 influences general cognitive ability. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1563–1568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous