Upregulation of monocyte/macrophage HGFIN (Gpnmb/Osteoactivin) expression in end-stage renal disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Upregulation of monocyte/macrophage HGFIN (Gpnmb/Osteoactivin) expression in end-stage renal disease
Madeleine V Pahl et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hematopoietic growth factor-inducible neurokinin 1 (HGFIN), also known as Gpnmb and osteoactivin, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed in numerous cells, including osteoclasts, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It serves as an osteoblast differentiation factor, participates in bone mineralization, and functions as a negative regulator of inflammation in macrophages. Although measurable at low levels in monocytes, monocyte-to-macrophage transformation causes substantial increase in HGFIN expression. HGFIN is involved in systemic inflammation, bone demineralization, and soft tissue vascular calcification.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We explored HGFIN expression in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages in 21 stable hemodialysis patients and 22 control subjects.
Results: Dialysis patients exhibited marked upregulation of colony-stimulating factor and IL-6 and significant downregulation of IL-10 in intact monocytes and transformed macrophages. HGFIN expression in intact monocytes was negligible in control subjects but conspicuously elevated (8.6-fold) in dialysis patients. As expected, in vitro monocyte-to-macrophage transformation resulted in marked upregulation of HGFIN in cells obtained from both groups but much more so in dialysis patients (17.5-fold higher). Upregulation of HGFIN and inflammatory cytokines in the uremic monocyte-derived macrophages occurred when grown in the presence of either normal or uremic serum, suggesting the enduring effect of the in vivo uremic milieu on monocyte/macrophage phenotype and function.
Conclusions: Uremic macrophages exhibit increased HGFIN gene and protein expression and heightened expression of proinflammatory and a suppressed expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Further studies are needed to determine the role of heightened monocyte/macrophage HGFIN expression in the pathogenesis of ESRD-induced inflammation and vascular and soft tissue calcification.
Figures
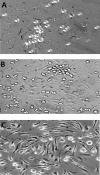
Figure 1.
Microscopic examination of normal monocytes after overnight culture (A) and after 7 d of culture using normal serum (B) and uremic serum (C).
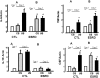
Figure 2.
mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF), anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10), and CSF (a marker/mediator of macrophage transformation) in monocytes from normal control subjects (CTL; A) and patients with ESRD (B) after overnight culture (day 1) and after macrophage transformation (day 7) grown in either control (CS) or uremic serum (US). mRNA levels are presented as a ratio of corresponding values found in the control cells at both day 1 and day 7. *P < 0.05.
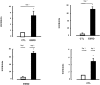
Figure 3.
Comparison of HGFIN mRNA expression in monocytes obtained from control subjects (CTL) and patients with ESRD after overnight culture (day 1; A) and macrophage-transformation (day 7; B). Comparison of HGFIN mRNA levels in ESRD (C) and CTL cells (D) at day 1 and at day 7 after monocyte-macrophage transformation. *P < 0.05.
Figure 4.
mRNA expression of HGFIN in monocyte-derived macrophages from normal control subjects (CTL) and patients with ESRD grown in either control (CS) or uremic serum (US). mRNA levels are presented as a ratio of the corresponding values found in the control cells at both day 1 and day 7. *P < 0.05.
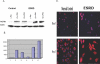
Figure 5.
HGFIN protein expression in control and ESRD cells. After overnight incubation (day 1) and macrophage transformation (day 7), cells were grown in normal serum (CS) and uremic serum (US). (A) Representative Western Blot. (B) Group data. (C) Immunocytochemical images of HGFIN protein expression in control and ESRD cells after overnight incubation (day 1) and macrophage transformation (day 7).
Similar articles
- Hematopoietic growth factor inducible neurokinin-1 (Gpnmb/Osteoactivin) is a biomarker of progressive renal injury across species.
Patel-Chamberlin M, Wang Y, Satirapoj B, Phillips LM, Nast CC, Dai T, Watkins RA, Wu X, Natarajan R, Leng A, Ulanday K, Hirschberg RR, Lapage J, Nam EJ, Haq T, Adler SG. Patel-Chamberlin M, et al. Kidney Int. 2011 May;79(10):1138-48. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.28. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21389974 - An mRNA atlas of G protein-coupled receptor expression during primary human monocyte/macrophage differentiation and lipopolysaccharide-mediated activation identifies targetable candidate regulators of inflammation.
Hohenhaus DM, Schaale K, Le Cao KA, Seow V, Iyer A, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ. Hohenhaus DM, et al. Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23948647 - Role of human HGFIN/nmb in breast cancer.
Metz RL, Patel PS, Hameed M, Bryan M, Rameshwar P. Metz RL, et al. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(5):R58. doi: 10.1186/bcr1764. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17845721 Free PMC article. - Monocytes and dendritic cells in a hypoxic environment: Spotlights on chemotaxis and migration.
Bosco MC, Puppo M, Blengio F, Fraone T, Cappello P, Giovarelli M, Varesio L. Bosco MC, et al. Immunobiology. 2008;213(9-10):733-49. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2008.07.031. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Immunobiology. 2008. PMID: 18926289 Review. - New Insights into the Roles of Monocytes/Macrophages in Cardiovascular Calcification Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease.
Hénaut L, Candellier A, Boudot C, Grissi M, Mentaverri R, Choukroun G, Brazier M, Kamel S, Massy ZA. Hénaut L, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 12;11(9):529. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090529. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) expression in the microglia by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via upregulation of glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma B (GPNMB) expression.
Shi F, Duan S, Cui J, Yan X, Li H, Wang Y, Chen F, Zhang L, Liu J, Xie X. Shi F, et al. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54(2):234-42. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0280-0. Epub 2014 Mar 30. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24682924 - Cross-species transcriptional network analysis defines shared inflammatory responses in murine and human lupus nephritis.
Berthier CC, Bethunaickan R, Gonzalez-Rivera T, Nair V, Ramanujam M, Zhang W, Bottinger EP, Segerer S, Lindenmeyer M, Cohen CD, Davidson A, Kretzler M. Berthier CC, et al. J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):988-1001. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103031. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22723521 Free PMC article. - Scoring of senescence signalling in multiple human tumour gene expression datasets, identification of a correlation between senescence score and drug toxicity in the NCI60 panel and a pro-inflammatory signature correlating with survival advantage in peritoneal mesothelioma.
Lafferty-Whyte K, Bilsland A, Cairney CJ, Hanley L, Jamieson NB, Zaffaroni N, Oien KA, Burns S, Roffey J, Boyd SM, Keith WN. Lafferty-Whyte K, et al. BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 1;11:532. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-532. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20920304 Free PMC article. - Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Protein B: An Emerging Biomarker for Lysosomal Dysfunction in Macrophages.
van der Lienden MJC, Gaspar P, Boot R, Aerts JMFG, van Eijk M. van der Lienden MJC, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 24;20(1):66. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010066. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30586924 Free PMC article. Review. - Atherosclerosis in chronic kidney disease: the role of macrophages.
Kon V, Linton MF, Fazio S. Kon V, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Jan;7(1):45-54. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2010.157. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21102540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Safadi F, Xu J, Smock S, Rico M, Owen T, Popoff S: Cloning and characterization of osteoactivin, a novel cDNA expressed in osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem 84: 12–26, 2001 - PubMed
- Haralanova-Ilieva B, Ramadori G, Armbrust T: Expression of osteoactivin in rat and human liver and isolated rat liver cells. J Hepatol 42: 565–572, 2005 - PubMed
- Shikano S, Bonkobara M, Zukas PK, Ariizumi K: Molecular cloning of dendritic cell-associated transmembrane protein, DC-HIL, that promotes RGD-dependent adhesion of endothelial cells through recognition of heparin sulfate. J Biol Chem 271: 8125–8134, 2001 - PubMed
- Bandari PS, Qian J, Yehia G, Joshi D, Maloof PB, Potian J, Oh H, Gascon P, Harrison J, Rameshwar P: Hematopoietic growth factor inducible neurokinin-1 (HGFIN) gene: A transmembrane protein that is similar to neurokinin-1 interacts with substance. Regul Pept 111: 169–178, 2003 - PubMed
- Bachner D, Schroder D, Gross G: mRNA expression of the murine glycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb (Gpnmb) gene is linked to the developing retinal pigment epithelium and iris. Brain Res Gene Expr Patterns 1: 159–165, 2002 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials