A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Nov;41(11):1228-33.
doi: 10.1038/ng.468. Epub 2009 Oct 18.
Johanna K Sandling, Geoff Hom, Kimberly E Taylor, Sharon A Chung, Xin Sun, Ward Ortmann, Roman Kosoy, Ricardo C Ferreira, Gunnel Nordmark, Iva Gunnarsson, Elisabet Svenungsson, Leonid Padyukov, Gunnar Sturfelt, Andreas Jönsen, Anders A Bengtsson, Solbritt Rantapää-Dahlqvist, Emily C Baechler, Elizabeth E Brown, Graciela S Alarcón, Jeffrey C Edberg, Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman, Gerald McGwin Jr, John D Reveille, Luis M Vilá, Robert P Kimberly, Susan Manzi, Michelle A Petri, Annette Lee, Peter K Gregersen, Michael F Seldin, Lars Rönnblom, Lindsey A Criswell, Ann-Christine Syvänen, Timothy W Behrens, Robert R Graham
- PMID: 19838195
- PMCID: PMC2925843
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.468
A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus
Vesela Gateva et al. Nat Genet. 2009 Nov.
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies have recently identified at least 15 susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). To confirm additional risk loci, we selected SNPs from 2,466 regions that showed nominal evidence of association to SLE (P < 0.05) in a genome-wide study and genotyped them in an independent sample of 1,963 cases and 4,329 controls. This replication effort identified five new SLE susceptibility loci (P < 5 x 10(-8)): TNIP1 (odds ratio (OR) = 1.27), PRDM1 (OR = 1.20), JAZF1 (OR = 1.20), UHRF1BP1 (OR = 1.17) and IL10 (OR = 1.19). We identified 21 additional candidate loci with P< or = 1 x 10(-5). A candidate screen of alleles previously associated with other autoimmune diseases suggested five loci (P < 1 x 10(-3)) that may contribute to SLE: IFIH1, CFB, CLEC16A, IL12B and SH2B3. These results expand the number of confirmed and candidate SLE susceptibility loci and implicate several key immunologic pathways in SLE pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at http://www.nature.com/naturegenetics/.
Figures
Figure 1
Overview of experimental design. Variants were selected from loci with P < 0.05 in a genome-wide scan of 1,310 cases and 7,859 controls, previously reported SLE risk loci, confirmed loci from other autoimmune diseases and over 7,000 ancestry-informative markers, and these variants were incorporated into an Illumina custom SNP array. The array was genotyped in independent cases and controls from the United States and Sweden. 823 of the Swedish controls were genotyped using the Illumina 310K SNP array. Variants were analyzed as described in Online Methods.
Figure 2
Newly discovered genome-wide significant associations in SLE. (a–e) Association results from the GWA scan are plotted on the y axis versus genomic position on the indicated chromosome on the x axis within a 500-kb region surrounding the loci defined by (a) TNIP1, (b) PRDM1, (c) JAZF1, (d) UHRF1BP1 and (e) IL10. The meta-analysis P value for the most strongly associated marker is indicated by a red square. P values from the genome scan are shaded to indicate LD to the genome-wide associated variant: red, _r_2 > 0.8; yellow, _r_2 > 0.5; green, _r_2 > 0.2; gray, _r_2 < 0.2. Along the bottom are the recombination rates from the CEU HapMap (light blue line) and the known human genes (blue). A previously reported and independent SLE risk locus at the nearby ATG5 gene is indicated (b; rs2245214). (f) Histogram of P values of 1,256 independent SNPs (_r_2 < 0.1 to any other SNP in the array) in the 1,963 case and 4,329 control replication samples. Under a null distribution, the expected density of results is indicated by the dashed line. A significant enrichment of results with P < 0.05 was observed.
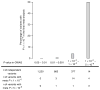
Figure 3
Percentage of newly discovered variants reaching candidate (P < 1 × 10−5) and confirmed (P < 5 × 10−8) status in the meta-analysis stratified by the P value in the original GWAS.
Similar articles
- A systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus pan-meta-GWAS reveals new shared susceptibility loci.
Martin JE, Assassi S, Diaz-Gallo LM, Broen JC, Simeon CP, Castellvi I, Vicente-Rabaneda E, Fonollosa V, Ortego-Centeno N, González-Gay MA, Espinosa G, Carreira P; Spanish Scleroderma Group; SLEGEN consortium; U.S. Scleroderma GWAS group; BIOLUPUS; Camps M, Sabio JM, D'alfonso S, Vonk MC, Voskuyl AE, Schuerwegh AJ, Kreuter A, Witte T, Riemekasten G, Hunzelmann N, Airo P, Beretta L, Scorza R, Lunardi C, Van Laar J, Chee MM, Worthington J, Herrick A, Denton C, Fonseca C, Tan FK, Arnett F, Zhou X, Reveille JD, Gorlova O, Koeleman BP, Radstake TR, Vyse T, Mayes MD, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Martin J. Martin JE, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):4021-9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt248. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23740937 Free PMC article. - The association of the UHRF1BP1 gene with systemic lupus erythematosus was replicated in a Han Chinese population from mainland China.
Wen L, Liu L, Shen X, Li H, Zhu Z, Huang H, Cai M, Qian D, Shen S, Qiu Y, Cui Y, Sheng Y. Wen L, et al. Ann Hum Genet. 2020 May;84(3):221-228. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12362. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Ann Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31691269 - Association of two independent functional risk haplotypes in TNIP1 with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Adrianto I, Wang S, Wiley GB, Lessard CJ, Kelly JA, Adler AJ, Glenn SB, Williams AH, Ziegler JT, Comeau ME, Marion MC, Wakeland BE, Liang C, Kaufman KM, Guthridge JM, Alarcón-Riquelme ME; BIOLUPUS and GENLES Networks; Alarcón GS, Anaya JM, Bae SC, Kim JH, Joo YB, Boackle SA, Brown EE, Petri MA, Ramsey-Goldman R, Reveille JD, Vilá LM, Criswell LA, Edberg JC, Freedman BI, Gilkeson GS, Jacob CO, James JA, Kamen DL, Kimberly RP, Martín J, Merrill JT, Niewold TB, Pons-Estel BA, Scofield RH, Stevens AM, Tsao BP, Vyse TJ, Langefeld CD, Harley JB, Wakeland EK, Moser KL, Montgomery CG, Gaffney PM. Adrianto I, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3695-705. doi: 10.1002/art.34642. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22833143 Free PMC article. - Transethnic meta-analysis identifies GSDMA and PRDM1 as susceptibility genes to systemic sclerosis.
Terao C, Kawaguchi T, Dieude P, Varga J, Kuwana M, Hudson M, Kawaguchi Y, Matucci-Cerinic M, Ohmura K, Riemekasten G, Kawasaki A, Airo P, Horita T, Oka A, Hachulla E, Yoshifuji H, Caramaschi P, Hunzelmann N, Baron M, Atsumi T, Hassoun P, Torii T, Takahashi M, Tabara Y, Shimizu M, Tochimoto A, Ayuzawa N, Yanagida H, Furukawa H, Tohma S, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Ishikawa O, Yamamoto T, Goto D, Asano Y, Jinnin M, Endo H, Takahashi H, Takehara K, Sato S, Ihn H, Raychaudhuri S, Liao K, Gregersen P, Tsuchiya N, Riccieri V, Melchers I, Valentini G, Cauvet A, Martinez M, Mimori T, Matsuda F, Allanore Y. Terao C, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):1150-1158. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210645. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28314753 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic susceptibility to SLE: recent progress from GWAS.
Cui Y, Sheng Y, Zhang X. Cui Y, et al. J Autoimmun. 2013 Mar;41:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.01.008. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23395425 Review.
Cited by
- Fibrinogen is not a prognostic factor for response to HELP-apheresis in sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL).
Berger T, Kaiser T, Scholz M, Bachmann A, Ceglarek U, Hesse G, Hagemeyer B, Stumvoll M, Thiery J, Dietz A. Berger T, et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Dec;272(12):3693-703. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3449-9. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25527412 - One novel susceptibility locus associate with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese Han population.
Yu ZY, Lu WS, Zuo XB, Hu J, Yao S, Li Y, Han JW, Sun LD, Cheng YL, Xu Q, Li J, Sheng YJ, Zhang XJ, Cui Y, Yang S. Yu ZY, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2013 Aug;33(8):2079-83. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2697-0. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23408151 - Cell-Free Genic Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiles of DNase Knockouts Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Relation with Common Fragile Sites.
Gerovska D, Fernández Moreno P, Zabala A, Araúzo-Bravo MJ. Gerovska D, et al. Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 28;12(1):80. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010080. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38255187 Free PMC article. - A systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus pan-meta-GWAS reveals new shared susceptibility loci.
Martin JE, Assassi S, Diaz-Gallo LM, Broen JC, Simeon CP, Castellvi I, Vicente-Rabaneda E, Fonollosa V, Ortego-Centeno N, González-Gay MA, Espinosa G, Carreira P; Spanish Scleroderma Group; SLEGEN consortium; U.S. Scleroderma GWAS group; BIOLUPUS; Camps M, Sabio JM, D'alfonso S, Vonk MC, Voskuyl AE, Schuerwegh AJ, Kreuter A, Witte T, Riemekasten G, Hunzelmann N, Airo P, Beretta L, Scorza R, Lunardi C, Van Laar J, Chee MM, Worthington J, Herrick A, Denton C, Fonseca C, Tan FK, Arnett F, Zhou X, Reveille JD, Gorlova O, Koeleman BP, Radstake TR, Vyse T, Mayes MD, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Martin J. Martin JE, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):4021-9. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt248. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23740937 Free PMC article. - IL-10RB rs2834167 (A/G) polymorphism is associated with the susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence from a study in Chinese Han population.
Peng H, Liu CY, Zhou M, Wen PF, Zhang M, Qiu LJ, Ni J, Liang Y, Pan HF, Ye DQ. Peng H, et al. Inflammation. 2013 Dec;36(6):1218-24. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9658-3. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 23749100
References
- Vyse TJ, Todd JA. Genetic analysis of autoimmune disease. Cell. 1996;85:311–318. - PubMed
- Graham RR, Hom G, Ortmann W, Behrens TW. Review of recent genome-wide association scans in lupus. J Intern Med. 2009;265:680–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044804-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 M01 RR-00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR02175/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR44804/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002175/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002175-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous