Expression of delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) and markers of hypoxia in colon cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Nov 17;101(10):1749-57.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605368. Epub 2009 Oct 20.
H Turley, H C Moeller, G Steers, C Han, J-L Li, R Leek, E Y Tan, B Singh, N J Mortensen, I Noguera-Troise, F Pezzella, K C Gatter, G Thurston, S B Fox, A L Harris
Affiliations
- PMID: 19844231
- PMCID: PMC2778546
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605368
Expression of delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) and markers of hypoxia in colon cancer
A M Jubb et al. Br J Cancer. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) is a Notch ligand that is upregulated by hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and is reported to have a role in tumor angiogenesis. Evidence from xenograft studies suggests that inhibiting Dll4-Notch signalling may overcome resistance to anti-VEGF therapy. The aim of this study was to characterise the expression of Dll4 in colon cancer and to assess whether it is associated with markers of hypoxia and prognosis.
Method: In all, 177 colon cancers were represented in tissue microarrays. Immunohistochemistry was performed using validated antibodies against Dll4, VEGF, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, prolyl hydroxylase (PHD)1, PHD2, PHD3 and carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9).
Results: The expression of Dll4 was observed preferentially in the endothelium of 71% (125 out of 175) of colon cancers, but not in the endothelium adjacent to normal mucosa (none out of 107, P<0.0001). The expression of VEGF was significantly associated with HIF-2alpha (P<0.0001) and Dll4 (P=0.010). Only HIF-2alpha had a significant multivariate prognostic effect (hazard ratio 1.61, 95% confidence interval 1.01-2.57). Delta-like ligand 4 was also expressed by neoplastic cells, particularly neoplastic goblet cells.
Conclusion: Endothelial expression of Dll4 is not a prognostic factor, but is significantly associated with VEGF. Assessing endothelial Dll4 expression may be critical in predicting response to anti-VEGF therapies.
Figures
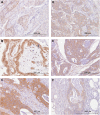
Figure 1
Representative examples of immunohistochemistry in colon cancer showing nuclear HIF-1_α_ (A) and HIF-2_α_ (B) expression, and cytoplasmic VEGF (C), PHD1 (D), PHD2 (E) and PHD3 (F) expression.
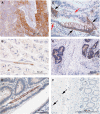
Figure 2
Representative examples of immunohistochemistry in colon cancer showing membranous CA9 adjacent necrosis (A) and endothelial Dll4 (B) expression. Immunohistochemistry for Dll4 shows membranous and cytoplasmic endothelial expression in a colon adenoma (C) and epithelial expression associated with goblet cell differentiation in a neoplastic crypt ((D) black arrows indicate Dll4-positive goblet cells, and red arrows indicate Dll4-negative non-goblet cells). Dll4 is also weakly expressed by neoplastic cells without goblet cell differentiation in a colon adenocarcinoma (E). Endothelial cells lining vessels (arrows) adjacent to normal colonic crypts did not express Dll4 by immunohistochemistry (F).
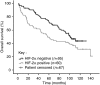
Figure 3
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for colon cancer patients subgrouped according to HIF-2_α_ expression. The patients with cancers who are positive for HIF-2_α_ have a significantly shorter median survival (57 months, 95% confidence interval 36–79 months) than patients with cancers who are negative for HIF-2_α_ (101 months, 95% confidence interval 81–121 months), _P_=0.027.
Similar articles
- Coexpression of hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha, carbonic anhydrase IX, and vascular endothelial growth factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and relationship to survival.
Hui EP, Chan AT, Pezzella F, Turley H, To KF, Poon TC, Zee B, Mo F, Teo PM, Huang DP, Gatter KC, Johnson PJ, Harris AL. Hui EP, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Aug;8(8):2595-604. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12171890 - Correlation of Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) with VEGF and HIF-1α expression in human glioma.
Li Z, Wang J, Gong L, Wen Z, Xu C, Huang X. Li Z, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(1):215-8. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011. PMID: 21517260 - Expression of vascular notch ligand delta-like 4 and inflammatory markers in breast cancer.
Jubb AM, Soilleux EJ, Turley H, Steers G, Parker A, Low I, Blades J, Li JL, Allen P, Leek R, Noguera-Troise I, Gatter KC, Thurston G, Harris AL. Jubb AM, et al. Am J Pathol. 2010 Apr;176(4):2019-28. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090908. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20167860 Free PMC article. - The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) as a target in angiogenesis-based cancer therapy?
Brzozowa M, Wojnicz R, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G, Helewski K. Brzozowa M, et al. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013;17(3):234-7. doi: 10.5114/wo.2013.35588. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013. PMID: 24596507 Free PMC article. Review. - The Prognostic Role and Significance of Dll4 and Toll-like Receptors in Cancer Development.
Fasoulakis Z, Koutras A, Ntounis T, Pergialiotis V, Chionis A, Katrachouras A, Palios VC, Symeonidis P, Valsamaki A, Syllaios A, Diakosavvas M, Angelou K, Samara AA, Pagkalos A, Theodora M, Schizas D, Kontomanolis EN. Fasoulakis Z, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;14(7):1649. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071649. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Prediction of DLL4 as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Gastric Cancer Using Anti-DLL4 Nanobody.
Afzalipour R, Abbasi-Dokht T, Sheikh M, Mohammadlou M, Nili F, Baharlou R. Afzalipour R, et al. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024 Sep;55(3):1380-1387. doi: 10.1007/s12029-024-01093-9. Epub 2024 Jul 24. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39046662 - Prognostic Index for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Based on Immune-Related Genes Expression.
Cao Y, Zhu H, Shen H, Liu D, Li Z, Shang H, Du H, Wang Y, Ye J. Cao Y, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 19;2022:4779811. doi: 10.1155/2022/4779811. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36193311 Free PMC article. - Prognostic value of HIF-1α in digestive system malignancies: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Arjmand MH, Moradi A, Rahimi HR, Es-Haghi A, Akbari A, Hadipanah MR, Afshar J, Mehrad-Majd H. Arjmand MH, et al. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022 Spring;15(2):108-119. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2022. PMID: 35845307 Free PMC article. - Phase I Open-Label Study Evaluating the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Preliminary Efficacy of Dilpacimab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors.
Gordon MS, Nemunaitis J, Barve M, Wainberg ZA, Hamilton EP, Ramanathan RK, Sledge GW Jr, Yue H, Morgan-Lappe SE, Blaney M, Kasichayanula S, Motwani M, Wang L, Naumovski L, Strickler JH. Gordon MS, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Oct;20(10):1988-1995. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0985. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34315767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Eosinophil and lymphocyte counts predict bevacizumab response and survival in recurrent glioblastoma.
Vaios EJ, Winter SF, Muzikansky A, Nahed BV, Dietrich J. Vaios EJ, et al. Neurooncol Adv. 2020 Mar 11;2(1):vdaa031. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaa031. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2020. PMID: 32642690 Free PMC article.
References
- Anderson AR, Weaver AM, Cummings PT, Quaranta V (2006) Tumor morphology and phenotypic evolution driven by selective pressure from the microenvironment. Cell 127: 905–915 - PubMed
- Appelhoff RJ, Tian YM, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM (2004) Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 279: 38458–38465 - PubMed
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B 57: 289–300
- Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J, Hanahan D (1999) Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice. Science 284: 808–812 - PubMed
- Boddy JL, Fox SB, Han C, Campo L, Turley H, Kanga S, Malone PR, Harris AL (2005) The androgen receptor is significantly associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia sensing via hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1a, HIF-2a, and the prolyl hydroxylases in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11: 7658–7663 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources