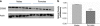Sex differences in social interaction in rats: role of the immediate-early gene zif268 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sex differences in social interaction in rats: role of the immediate-early gene zif268
Ashley Stack et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Jan.
Abstract
Given both the high prevalence of anxiety disorders in women and the fact that little is known about the mechanisms of gender differences in anxiety, our primary aim in this study was to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying sex differences in social anxiety-like behavior in rats. Through the use of zif268 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (zif ASO), we induced a temporary downregulation of zif268 expression in the medial prefrontal cortex of male and female rats and found that zif268 ASO male rats show more social anxiety-like behaviors when compared with control male rats in the social interaction test. In fact, zif268 ASO males displayed social anxiety-like behaviors, which were similar to control females, thus downregulation of zif268 expression in the mPFC of male rats eliminated sex differences previously found in the social anxiety-like behavior tests. Interestingly, zif268 ASO in female rats had no effect on their social interaction. Our novel findings have led us to ascertain that sexually dimorphic zif268 expression in the mPFC is a key molecular factor in mediating sex-specific anxiety-like behavior in the social interaction test.
Figures
Figure 1
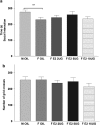
Sex differences in social interaction behaviors. (a) sham male rats treated with sesame oil (M OIL, _n_=12) spent more time interacting than did female rats treated with sesame oil (F OIL, _n_=12) did. Ovariectomized females treated with 17_β_-estradiol at 2 μg (F E2 2 UG, _n_=12), 5 μg (F E2 5 UG, _n_=12) or 10 μg (F E2 10 UG, _n_=12) interacted similarly as ovariectomized female rats treated with sesame oil. (b) All experimental groups showed the same locomotor activity during the first 10 min of exposure to the open field. *Significant difference when compared with M OIL. **p<0.01.
Figure 2
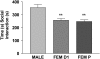
Estrous cycle in female rats does not alter their social interaction: intact male rats (MALE, _n_=16) show greater social interaction than female rats in diestrous 1 (FEM D1, _n_=16) or in proestrous (FEM P, _n_=14). *Significant difference when compared with MALE. **p<0.01.
Figure 3
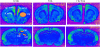
Sex differences in zif268 mRNA expression following social interaction test: Color-enhanced photomicrographs from x-ray films exposed for 5 days after in situ hybridization with antisense cRNA probe against zif268 mRNA. These representative images show that sham male rats treated with oil (M OIL) have greater zif268 expression than ovariectomized female rats treated with oil (F OIL) or with E2 5 UG (F E2 5 UG) in the cingulate cortex 1 (cg1 mPFC), prelimbic (PL mPFC), infralimbic (IL mPFC) and striatum (STR). M OIL, F OIL and F E2 5 UG show, however, similar mRNA expression in the hippocampal areas: CA1, CA3 and DG. The orange outlines show an example of where zif268 mRNA was sampled for quantification.
Figure 4
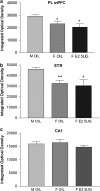
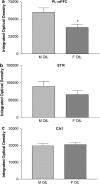
Sex differences in zif268 mRNA expression following social interaction test: sham male rats (M OIL, _n_=8) showed greater zif268 mRNA expression in the cg1, PL and IL medial prefrontal cortex (only PL mPFC is represented in (a)) and dorsal striatum (STR) (b) when compared with ovariectomized female rats treated with oil (F OIL, _n_=8) or treated with E2 5 UG (_n_=8). The three groups showed the same zif268 mRNA expression in hippocampal CA1 region, CA3, and DG (only CA1 is represented in (c)). *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Figure 5
Sex differences in zif268 mRNA expression in basal non-stress conditions: sham male rats injected with oil and killed 48 h later in stress-free conditions (M OIL, _n_=8) show greater zif268 mRNA expression in the dorsal and ventral mPFC ((a) show PL mPFC), but not in the STR (b) and hippocampus ((c) show CA1), when compared with OVX female rats injected with oil and killed 48 h later in the same stress-free conditions (F OIL, _n_=8). *p<0.05.
Figure 6
Sex differences in zif268 protein in mPFC in basal non-stress conditions: intact male rats (_n_=7) show greater zif268 protein expression than intact female rats (_n_=6) in mPFC. (a) Western blots from mPFC lysate show that male rats have more zif268 protein expression than female rats. (b) Western blot quantified data are shown as optical density of zif268 expression divided by optical density of actin for each rat. ***p<0.001.
Figure 7
zif268 ASO reduces zif268 protein expression in the mPFC: intact male rats treated with zif268 ASO (_n_=4) show lower zif268 protein expression than male rats treated with zif268 MSO (_n_=4). (a) Western blots from mPFC lysate show that rats treated with zif268 MSO have more zif268 protein expression than male rats treated with zif268 ASO. Zif268 MSO and zif268 ASO-treated rats have similar actin protein expression. (b) Western blot quantified data are shown as optical density of zif268 expression divided by optical density of actin for each rat. *p<0.05.
Figure 8
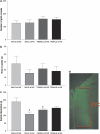
Downregulation of zif268 in male rats, but not in female rats, abolishes sex differences in social interaction: (a) intact male and female rats treated zif268 missense or antisense oligodeoxynucleotide exhibit similar locomotor activity during the open field test. (b) intact male and female rats treated zif268 missense or antisense oligodeoxynucleotide spend similar time in the center of the open field. (c) intact male rats treated with zif268 missense-oligodeoxynucleotide (MALE zif MS, _n_=8) show greater social interaction than female rats treated with the same construct (FEMALE zif MS, _n_=10). This sex difference in social interaction is abolished when male rats are treated with zif268 antisense (MALE zif AS, _n_=9). Female rats treated with zif268 MSO or zif268 AS (FEMALE zif AS, _n_=7) do not differ in their social interaction time. *Significant difference when compared with MALE zif MS. (d) extent of diffusion of biotinylated-zif268-MSO within the mPFC. The diffusion covered the cingulate cortex 1 and prelimbic mPFC. *p<0.05.
Similar articles
- Viral-mediated Zif268 expression in the prefrontal cortex protects against gonadectomy-induced working memory, long-term memory, and social interaction deficits in male rats.
Dossat AM, Jourdi H, Wright KN, Strong CE, Sarkar A, Kabbaj M. Dossat AM, et al. Neuroscience. 2017 Jan 6;340:243-257. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.10.062. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 27816701 Free PMC article. - Sex differences in anxiety-like behaviors in rats.
Scholl JL, Afzal A, Fox LC, Watt MJ, Forster GL. Scholl JL, et al. Physiol Behav. 2019 Nov 1;211:112670. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112670. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Physiol Behav. 2019. PMID: 31487491 - Isolation rearing attenuates social interaction-induced expression of immediate early gene protein products in the medial prefrontal cortex of male and female rats.
Wall VL, Fischer EK, Bland ST. Wall VL, et al. Physiol Behav. 2012 Oct 10;107(3):440-50. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Physiol Behav. 2012. PMID: 22982514 Free PMC article. - Brief social defeat stress: long lasting effects on cocaine taking during a binge and zif268 mRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
Covington HE 3rd, Kikusui T, Goodhue J, Nikulina EM, Hammer RP Jr, Miczek KA. Covington HE 3rd, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Feb;30(2):310-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300587. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15496936
Cited by
- The Lysine Demethylase KDM7A Regulates Immediate Early Genes in Neurons.
Wang Y, Hong Q, Xia Y, Zhang Z, Wen B. Wang Y, et al. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(28):e2301367. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301367. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37565374 Free PMC article. - Effects of sex and deletion of neuropeptide Y2 receptors from GABAergic neurons on affective and alcohol drinking behaviors in mice.
McCall NM, Sprow GM, Delpire E, Thiele TE, Kash TL, Pleil KE. McCall NM, et al. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013 Dec 25;7:100. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2013.00100. eCollection 2013. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24399943 Free PMC article. - Hedonic sensitivity to low-dose ketamine is modulated by gonadal hormones in a sex-dependent manner.
Saland SK, Schoepfer KJ, Kabbaj M. Saland SK, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 18;6:21322. doi: 10.1038/srep21322. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26888470 Free PMC article. - Sex differences in anxiety and emotional behavior.
Donner NC, Lowry CA. Donner NC, et al. Pflugers Arch. 2013 May;465(5):601-26. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1271-7. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23588380 Free PMC article. Review. - Single-Cell Transcriptional Profiling and Gene Regulatory Network Modeling in Tg2576 Mice Reveal Gender-Dependent Molecular Features Preceding Alzheimer-Like Pathologies.
Ali M, Huarte OU, Heurtaux T, Garcia P, Rodriguez BP, Grzyb K, Halder R, Skupin A, Buttini M, Glaab E. Ali M, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb;61(2):541-566. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02985-2. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 35980567 Free PMC article.
References
- Anderson SW, Bechara A, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio AR. Impairment of social and moral behavior related to early damage in human prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:1032–1037. - PubMed
- Barrash J, Tranel D, Anderson SW. Acquired personality disturbances associated with bilateral damage to the ventromedial prefrontal region. Dev Neuropsychol. 2000;18:355–381. - PubMed
- Best NR, Rees MP, Barlow DH, Cowen PJ. Effect of estradiol implant on noradrenergic function and mood in menopausal subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1992;17:87–93. - PubMed
- Bjorn I, Sundstrom-Poromaa I, Bixo M, Nyberg S, Backstrom G, Backstrom T. Increase of estrogen dose deteriorates mood during progestin phase in sequential hormonal therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2026–2030. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical