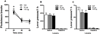Effects of mGluR1 antagonism in the dorsal hippocampus on drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effects of mGluR1 antagonism in the dorsal hippocampus on drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats
Xiaohu Xie et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Jan.
Abstract
Rationale: The functional integrity of the dorsal hippocampus (DH) is necessary for drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. However, the neuropharmacological mechanisms of this phenomenon are poorly understood.
Objectives: Given the known significance of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), including the mGluR1 subtype, in drug-induced behaviors, the present study was designed to evaluate the contribution of mGluR1s in the DH to drug context-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were trained to lever press for unsignaled cocaine infusions in a distinct environmental context (cocaine-paired context) followed by extinction training in a distinctly different environmental context (extinction context). Using a counterbalanced partial within-subjects testing design, rats were re-exposed to the cocaine-paired context or the extinction context while cocaine-seeking behavior (nonreinforced active lever pressing) was assessed. Prior to each test session, rats received bilateral microinfusions of the highly potent mGluR1-selective antagonist JNJ16259685 (0.6, 30, or 120 pg/0.5 microl per hemisphere) or vehicle into the DH or the overlying somatosensory cortex trunk region (SStr; anatomical control).
Results: Intra-DH, but not intra-SStr, JNJ16259685 infusions dose dependently attenuated drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking relative to vehicle treatment, without attenuating instrumental behavior in the extinction context, general motor activity, or food-reinforced instrumental behavior in control experiments.
Conclusions: Stimulation of mGluR1s in the DH is necessary for incentive motivational and/or memory processes that contribute to drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior. These findings indicate that the mGluR1 is an interesting target from an addiction treatment perspective.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
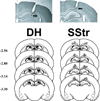
Fig. 1
Schematic and photographic representation of injection cannula placements within the dorsal hippocampus (DH) and trunk region of the somatosensory cortex (SStr). Arrows identify the most ventral point of the infusion cannula tracts on each photomicrograph of representative cresyl violet-stained brain sections. Filled circles, open triangles, and open circles represent the most ventral point of the cannula tracts for rats in the DH-cannulated cocaine-trained, DH-cannulated food-trained, and SStr-cannulated cocaine-trained groups, respectively, on schematics from the rat brain atlas of Paxinos and Watson (1997). Numbers indicate the distance from bregma in millimeters.
Fig. 2
Non-reinforced active and inactive lever responses (mean/1 h ± SEM) during testing in the extinction (EXT) and previously cocaine-paired contexts (COC). JNJ16259685 or vehicle was infused bilaterally into the DH (A, B: N = 10–14/group) or the SStr (C, D: N = 12) before testing. The Asterisks represent a significant difference relative to responding in the extinction context (Panel A: ANOVA context simple main effect, Tukey test, p < 0.05; Panels B, C, D: ANOVA context main effect, p < 0.05). The Dagger represents a significant difference relative to the vehicle treatment (ANOVA treatment simple main effect, Tukey test, p < 0.05).
Fig. 3
Locomotor activity (A; mean photobeam breaks/1 h ± SEM) in a novel context as well as
preprandial
food-reinforced instrumental behavior (B; mean lever presses/1 h ± SEM) and
postprandial
food-reinforced instrumental behavior (C; mean lever presses/1 h ± SEM) in contexts 1 or 2. JNJ16259685 or vehicle was administered bilaterally into the DH (Panel A: N = 10–14/group; Panel B: N = 10; Panel C: N = 8) before testing. Rats in the postprandial condition received 100 45-mg food pellets 1 h before each behavioral session. The Plus sign represents a significant difference relative to all other time points (ANOVA time simple main effect, Tukey test, p < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Subregion-specific role of glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens on drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats.
Xie X, Lasseter HC, Ramirez DR, Ponds KL, Wells AM, Fuchs RA. Xie X, et al. Addict Biol. 2012 Mar;17(2):287-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00325.x. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Addict Biol. 2012. PMID: 21521425 Free PMC article. - Nucleus accumbens shell and core involvement in drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats.
Fuchs RA, Ramirez DR, Bell GH. Fuchs RA, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Nov;200(4):545-56. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1234-4. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18597075 Free PMC article. - Role of a hippocampal SRC-family kinase-mediated glutamatergic mechanism in drug context-induced cocaine seeking.
Xie X, Arguello AA, Wells AM, Reittinger AM, Fuchs RA. Xie X, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Dec;38(13):2657-65. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.175. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23872878 Free PMC article. - Sub-region specific contribution of the ventral hippocampus to drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats.
Lasseter HC, Xie X, Ramirez DR, Fuchs RA. Lasseter HC, et al. Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 15;171(3):830-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.032. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20870011 Free PMC article. - Cocaine seeking and taking: role of hippocampal dopamine D1-like receptors.
Xie X, Wells AM, Fuchs RA. Xie X, et al. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Sep;17(9):1533-8. doi: 10.1017/S1461145714000340. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24655895 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 within nucleus accumbens shell modulates environment-elicited cocaine conditioning expression.
Martínez-Rivera A, Rodríguez-Borrero E, Matías-Alemán M, Montalvo-Acevedo A, Guerrero-Figuereo K, Febo-Rodríguez LJ, Morales-Rivera A, Maldonado-Vlaar CS. Martínez-Rivera A, et al. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 Sep;110:154-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013. PMID: 23850523 Free PMC article. - mGlu receptors and drug addiction.
Cleva RM, Olive MF. Cleva RM, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2012 May;1(3):281-295. doi: 10.1002/wmts.18. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2012. PMID: 22662312 Free PMC article. - Using metabotropic glutamate receptors to modulate cocaine's synaptic and behavioral effects: mGluR1 finds a niche.
Loweth JA, Tseng KY, Wolf ME. Loweth JA, et al. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;23(4):500-6. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23385114 Free PMC article. Review. - Antagonism of metabotropic glutamate 1 receptors attenuates behavioral effects of cocaine and methamphetamine in squirrel monkeys.
Achat-Mendes C, Platt DM, Spealman RD. Achat-Mendes C, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Oct;343(1):214-24. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.196295. Epub 2012 Jul 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22815535 Free PMC article. - Therapeutic potential of metabotropic glutamate receptor modulators.
Hovelsø N, Sotty F, Montezinho LP, Pinheiro PS, Herrik KF, Mørk A. Hovelsø N, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012 Mar;10(1):12-48. doi: 10.2174/157015912799362805. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22942876 Free PMC article.
References
- Amaral DG, Witter MP. Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G, editor. The rat nervous system. Los Angeles, CA: Academic; 1995. pp. 443–493.
- Bäckström P, Hyytiä P. Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007;192:571–580. - PubMed
- Bäckström P, Hyytiä P. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonism attenuates cue-induced cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:778–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources