Nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and response in a phase II trial of bortezomib and docetaxel in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2010 Apr;21(4):864-870.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp390. Epub 2009 Oct 22.
J Aulino 2, N J Muldowney 3, H Hatakeyama 4, J Baumann 4, B Burkey 5, J Netterville 5, R Sinard 5, W G Yarbrough 6, A J Cmelak 7, R J Slebos 8, Y Shyr 9, J Parker 10, J Gilbert 4, B A Murphy 4
Affiliations
- PMID: 19850643
- PMCID: PMC2844946
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdp390
Clinical Trial
Nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and response in a phase II trial of bortezomib and docetaxel in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
C H Chung et al. Ann Oncol. 2010 Apr.
Abstract
Background: Our previous study has shown that nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB)-signaling pathway was associated with a higher rate of recurrence in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The combination of bortezomib, an NF-kappaB inhibitor by inhibition of proteasomes, plus docetaxel was assessed for efficacy and toxicity.
Materials and methods: Patients with recurrent and/or metastatic HNSCC were enrolled on a phase II bortezomib/docetaxel trial (bortezomib 1.6 mg/m(2) and docetaxel 40 mg/m(2) on days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle). Response was assessed using RECIST. Tissue specimens were evaluated for the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) and expression of NF-kappaB-associated genes.
Results: Twenty-one of 25 enrolled patients were assessable for response; one partial response (PR, 5%), 10 stable disease (SD, 48%) and 10 progressive disease (PD, 48%). Patients with PR/SD had significantly longer survival compared with patients with PD and the regimen was well tolerated. Only one of 20 tumors was positive for HPV. Patients with PD had higher expression of NF-kappaB and epidermal growth factor receptor-associated genes in their tumors by gene expression analysis.
Conclusion: Further understanding of treatment resistance and interactions between bortezomib and docetaxel may provide novel approaches in managing HNSCC.
Figures
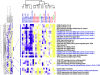
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier plots comparing patients with partial response (PR) and stable diseases (SD) versus progressive disease (PD). (A) Overall survival; median survival time 9.4 versus 4.3 months; log-rank test P = 0.028. (B) Progression-free survival; median survival time 3.0 versus 1.5 months; log-rank test P <0.0001. Red line: PR/SD; black line: PD.
Figure 2.
Hierarchical clustering of 25 samples using the 111-gene nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signature known to be modulated by NF-κB as previously published [10, 26]. Red: PR, partial response and SD, stable disease; blue: PD, progressive disease; green: normal mucosa adjacent to the tumors; purple squares: higher gene expression; yellow squares: lower gene expression.
Figure 3.
Hierarchical clustering of 25 samples using the 239 genes that were differentially expressed between tumors with partial response (PR)/stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PD). Red: PR/SD; blue: PD; green: normal mucosa adjacent to the tumors; purple squares: higher gene expression; yellow squares: lower gene expression.
Similar articles
- Phase II 2-arm trial of the proteasome inhibitor, PS-341 (bortezomib) in combination with irinotecan or PS-341 alone followed by the addition of irinotecan at time of progression in patients with locally recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (E1304): a trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group.
Gilbert J, Lee JW, Argiris A, Haigentz M Jr, Feldman LE, Jang M, Arun P, Van Waes C, Forastiere AA. Gilbert J, et al. Head Neck. 2013 Jul;35(7):942-8. doi: 10.1002/hed.23046. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Head Neck. 2013. PMID: 22791234 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB and target genes during combined therapy with proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and reirradiation in patients with recurrent head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Van Waes C, Chang AA, Lebowitz PF, Druzgal CH, Chen Z, Elsayed YA, Sunwoo JB, Rudy SF, Morris JC, Mitchell JB, Camphausen K, Gius D, Adams J, Sausville EA, Conley BA. Van Waes C, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Dec 1;63(5):1400-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.05.007. Epub 2005 Jul 11. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. PMID: 16005577 - Early tumor progression associated with enhanced EGFR signaling with bortezomib, cetuximab, and radiotherapy for head and neck cancer.
Argiris A, Duffy AG, Kummar S, Simone NL, Arai Y, Kim SW, Rudy SF, Kannabiran VR, Yang X, Jang M, Chen Z, Suksta N, Cooley-Zgela T, Ramanand SG, Ahsan A, Nyati MK, Wright JJ, Van Waes C. Argiris A, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;17(17):5755-64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0861. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21750205 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Triweekly reduced-dose docetaxel combined with cisplatin in recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a multicenter phase II study.
Chang PM, Tzeng CH, Chen MH, Tsao CJ, Su WC, Hwang WS, Chang YF, Chang SY, Yang MH. Chang PM, et al. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;68(6):1477-84. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1645-5. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21484308 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- Chemotherapy and signaling: How can targeted therapies supercharge cytotoxic agents?
Bagnyukova TV, Serebriiskii IG, Zhou Y, Hopper-Borge EA, Golemis EA, Astsaturov I. Bagnyukova TV, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Nov 1;10(9):839-53. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.9.13738. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20935499 Free PMC article. Review. - Can medical herbs stimulate regeneration or neuroprotection and treat neuropathic pain in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy?
Schröder S, Beckmann K, Franconi G, Meyer-Hamme G, Friedemann T, Greten HJ, Rostock M, Efferth T. Schröder S, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:423713. doi: 10.1155/2013/423713. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23983777 Free PMC article. - Preserving biological heterogeneity with a permuted surrogate variable analysis for genomics batch correction.
Parker HS, Leek JT, Favorov AV, Considine M, Xia X, Chavan S, Chung CH, Fertig EJ. Parker HS, et al. Bioinformatics. 2014 Oct;30(19):2757-63. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu375. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24907368 Free PMC article. - Autophagic action of new targeting agents in head and neck oncology.
Rikiishi H. Rikiishi H. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Sep;13(11):978-91. doi: 10.4161/cbt.21079. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22825332 Free PMC article. Review. - Application of molecular targeted therapies in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Kozakiewicz P, Grzybowska-Szatkowska L. Kozakiewicz P, et al. Oncol Lett. 2018 May;15(5):7497-7505. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8300. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29725456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Fakhry C, Westra WH, Li S, et al. Improved survival of patients with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a prospective clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:261–269. - PubMed
- Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, et al. Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for organ preservation in advanced laryngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2091–2098. - PubMed
- Urba SG, Forastiere AA. Systemic therapy of head and neck cancer: most effective agents, areas of promise. Oncology (Huntingt) 1989;3:79–88. discussion 88. - PubMed
- Kies MS, Levitan N, Hong WK. Chemotherapy of head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1985;18:533–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials